- Continue Shopping
- Your Cart is Empty
As the seasons pass...
Every Corydoras breeder knows something that we all should know:
Environmental manipulations create unique opportunities to facilitate behavioral changes in our fishes.

It's hardly an earth-shattering idea in the aquarium hobby, but I think that the concept of "seasonal" environmental manipulation deserves some additional consideration.
It's been known for decades that environmental changes to the aquatic environment caused by weather (particularly "wet" or "dry" seasons/events) can stimulate fishes into spawning.

As a fish geek keen on not only replicating the look of our fishes' wild habitats, but as much of the "function" as possible, I can't help myself but to ponder the possibilities for greater success by manipulating the aquarium environment to simulate what happens in the wild.
Probably the group of aquarists who has had the most experience and success at incorporating such environmental manipulations into their breeding procedures is Corydoras catfish enthusiasts!

Many hobbyists who have bred Corydoras utilize the old trick of a 20%-30% water exchange with water that is up to 10° F cooler (6.5° C) than the aquarium water is normally maintained at. It seems almost like one of those, "Are you &^%$#@ crazy- a sudden lowering of temperature?"
However, it works, and you almost never hear of any fishes being lost as a result of such manipulations.

I often wondered what the rationale behind such a change was. My understanding is that it essentially is meant to mimic a rainstorm, in which an influx of cooler water is a feature. Makes sense. Weather conditions are such an important part of the life cycle of our fishes.
Still others attempt to simulate a "dry spell" by allowing the water quality to "degrade" somewhat (what exactly that means is open to interpretation!), while simultaneously increasing the aquarium temperature a degree or two. This is followed by a water exchange with softer water (ie; pure RO/DI), and resetting the tank temp to the tank's normal range of parameters.
The "variation" I have heard is to do the above procedure, accompanied by an increase in current via a filter return or powerhead, which simulates the increased water volume/flow brought on by the influx of "rain."
Clever.

Many breeders will fast their fishes a few days, followed by a big binge of food after the temperature drop, apparently simulating the increased amount of food in the native waters when rains come.
Still other hobbyists will reduce the pH of their aquarium water to stimulate breeding. And I suppose the rationale behind this is once again to simulate an influx of water from rain or other external sources...
Weather, once again.

And another trick I hear from my Cory breeder friends from time to time is the idea of tossing in a few alder cones into the tank/vessel where their breeders' eggs are incubating.

This decades-old practice is justified by the assertion that the alder cones possess some type of anti-fungal properties...not entirely off base with some of the scientific research we've found about the allegedly anti-microbial/antifungal properties of catappa leaves and such...
And of course, I hear/read of recommendations to use the aforementioned catappa leaves, oak leaves, and Magnolia leaves for just this purpose...
Interesting.

Okay, cool.
Not really earth-shattering; however, it got me thinking about the whole idea of environmental manipulations as part of the routine "operation" of our botanical-mehtod aquariums.....Should we create true seasonal variations for our aquariums as part of our regular practice- not just when trying to spawn fishes? I mean, changing up lighting duration, intensity, angles, colors, increasing/decreasing water levels or flow?
With all of the high tech LED lighting systems, electronically controlled pumps; even advanced heaters- we can vary environmental conditions to mimic what occurs in our fishes' natural habitats during seasonal changes as never before. I think it would be very interesting to see what kinds of results we could get with our fishes if we went further into seasonal environmental manipulations than we have been able to before.
And of course, if we look at the natural habitats where many of our fishes originate, we see these seasonal changes having huge impact on the aquatic ecosystems. In The Amazon, for example, the high water season runs December through April.
And during the flooding season, the average temperature is 86 degrees F, around 12 degrees cooler than the dry season. And during the wet season, the streams and rivers can be between 6-7 meters higher on the average than they are during the dry season!

And of course, there are more fruits, flowers, and insects during this time of year- important food items for many species of fishes.
And the dry season? Well, that obviously means lower water levels, higher temperatures, and abundance of fishes, most engaging in spawning activity.
Mud and algal growth on plants, rocks, submerged trees, etc. is quite abundant in these waters at various times of the year. Mud and detritus are transported via the overflowing rivers into flooded areas, and contribute to the forest leaf litter and other botanical materials, coming nutrient sources which contribute to the growth of this epiphytic algae.

During the lower water periods, this "organic layer" helps compensate for the shortage of other food sources. When the water is at a high period and the forests are inundated, many terrestrial insects fall into the water and are consumed by fishes. In general, insects- both terrestrial and aquatic, support a large community of fishes.

So, it goes without saying that the importance of insects and fruits- which are essentially derived from the flooded forests, are reduced during the dry season when fishes are confined to open water and feed on different materials.

So I wonder...is part of the key to successfully conditioning and breeding some of the fishes found in these habitats altering their diets to mimic the seasonal importance/scarcity of various food items? In other words, feeding more insects at one time of the year, and perhaps allowing fishes to graze on detritus and biocover at other times?
And then, there are those fishes whose life cycle is intimately tied into the seasonal changes.
The killifishes.
Any annual or semi-annual killifish species enthusiast will tell you a dozen ways to dry-incubate eggs; again, a beautiful simulation of what happens in Nature...So much of the idea can be applicable to other areas of aquarium practice, right?

Yeah... I think so.
It's pretty clear that factors such as the air, water and even soil temperatures, atmospheric humidity, the water level, the local winds as well as climatic variables have profound influence on the life cycle and reproductive behavior on the fishes that reside in these dynamic tropical environments!
In my "Urban Igapo" experiments, we get to see a little microcosm of this whole seasonal process and the influences of "weather."

And of course, all of this ties into the intimate relationship between land and water, doesn't it?
There's been a fair amount of research and speculation by both scientists and hobbyists about the processes which occur when terrestrial materials like leaves and botanical items enter aquatic environments, and most of it is based upon field observations.
As hobbyists, we have a unique opportunity to observe firsthand the impact and affects of this material in our own aquariums! I love this aspect of our "practice", as it creates really interesting possibilities to embrace and create more naturally-functioning systems, while possibly even "validating" the field work done by scientists!

And of course, there are a lot of interesting bits of information that we can interpret from Nature when planning, creating, and operating our aquariums.
It goes without saying that there are implications for both the biology and chemistry of the aquatic habitats when leaves and other botanical materials enter them. Many of these are things that we as hobbyists observe every day in our aquariums!

Example?
A lab study I came upon found out that, when leaves are saturated in water, biofilm is at it's peak when other nutrients (i.e.; nitrate, phosphate, etc.) tested at their lowest limits. This is interesting to me, because it seems that, in our botanical method aquariums, biofilms tend to occur early on, when one would assume that these compounds are at their highest concentrations, right? And biofilms are essentially the byproduct of bacterial colonization, meaning that there must be a lot of "food" for the bacteria at some point if there is a lot of biofilm, right?
More questions...
Does this imply that the biofilms arrive on the scene and peak out really quickly; an indication that there is actually less nutrient in the water? Is the nutrient bound up in the biofilms? And when our fishes and other animals consume them, does this provide a significant source of sustenance for them?
Hmm...?

Oh, and here is another interesting observation:
When leaves fall into streams, field studies have shown that their nitrogen content typically will increase. Why is this important? Scientists see this as evidence of microbial colonization, which is correlated by a measured increase in oxygen consumption. This is interesting to me, because the rare "disasters" that we see in our tanks (when we do see them, of course, which fortunately isn't very often at all)- are usually caused by the hobbyist adding a really large quantity of leaves at once, resulting in the fishes gasping at the surface- a sign of...oxygen depletion?
Makes sense, right?
These are interesting clues about the process of decomposition of leaves when they enter into our aquatic ecosystems. They have implications for our use of botanicals and the way we manage our aquariums. I think that the simple fact that pH and oxygen tend to go down quickly when leaves are initially submerged in pure water during lab tests gives us an idea as to what to expect.
A lot of the initial environmental changes will happen rather rapidly, and then stabilize over time. Which of course, leads me to conclude that the development of sufficient populations of organisms to process the incoming botanical load is a critical part of the establishment of our botanical-method aquariums.
Fungal populations are as important in the process of breaking down leaves and botanical materials in water as are higher organisms, like insects and crustaceans, which function as "shredders." The “shredders” – the animals which feed upon the materials that fall into the streams, process this stuff into what scientists call “fine particulate organic matter.”

And that's where fungi and other microorganisms make use of the leaves and materials, processing them into fine sediments. Allochthonous material can also include dissolved organic matter (DOM) carried into streams and re-distributed by water movement.

And the process happens surprisingly quickly.
In studies carried out in tropical rainforests in Venezuela, decomposition rates were really fast, with 50% of leaf mass lost in less than 10 days! Interesting, but is it tremendously surprising to us as botanical-method aquarium enthusiasts? I mean, we see leaves begin to soften and break down in a matter of a couple of weeks- with complete breakdown happening typically in a month or so for many leaves.
And biofilms, fungi, and algae are still found in our aquariums in significant quantities throughout the process.
So, what's this all mean? What are the implications for aquariums?

I think it means that we need to continue to foster the biological diversity of animals in our aquariums- embracing life at all levels- from bacteria to fungi to crustaceans to worms, and ultimately, our fishes...All forming the basis of a closed ecosystem, and perhaps a "food web" of sorts for our little aquatic microcosms. It's a very interesting concept- a fascinating field for research for aquarists, and we all have the opportunity to participate in this on a most intimate level by simply observing what's happening in our aquariums every day!
We've talked about this very topic many times right here over the years, haven't we? I can't let it go.
Bioversity is interesting enough, but when you factor in seasonal changes and cycles, it becomes an almost "foundational" component for a new way of running our botanical-style aquariums.
Consider this:
The wet season in The Amazon runs from November to June. And it rains almost every day.
And what's really interesting is that the surrounding Amazon rain forest is estimated by some scientists to create as much as 50% of its own precipitation! It does this via the humidity present in the forest itself, from the water vapor present on plant leaves- which contributes to the formation of rain clouds.

Yeah, trees in the Amazon release enough moisture through photosynthesis to create low-level clouds and literally generate rain, according to a recent study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (U.S.)!
That's crazy.
But it makes a lot of sense, right?
Okay, that's a cool "cocktail party sound bite" and all, but what happens to the (aquatic) environment in which our fishes live in when it rains?
Well, for one thing, rain performs the dual function of diluting organics, while transporting more nutrient and materials across the ecosystem. What happens in many of the regions of Amazonia - and likewise, in many tropical locales worldwide-is the evolution of some of our most compelling environmental niches...

We've literally scratched the surface, and the opportunity to apply what we know about the climates and seasonal changes which occur where our fishes originate, and to incorporate, on a broader scale, the practices which our Corydoras-enthusiast friends employ on all sorts of fishes!
So much to learn, experiment with, and execute on.
Stay fascinated. Stay intrigued. Stay observant. Stay creative. Stay astute...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
Inception.
We've had a lot of requests lately to discuss how we start up our botanical method aquariums. Now sure, we've covered this topic before over the years; yet, as our practices have evolved, so has our understanding about why we do things the way that we do- and why it works.
Establishing a new botanical method aquarium is an exciting, fun, and interesting time. And the process of creating your aquarium is shockingly easy, decidedly un-stressful, and extremely engaging.
The main ingredients that you need are vision, a bit of knowledge, and... patience.
Bringing your tank from a clean, dry,"static display" to a living, breathing microcosm, filled with life is an amazing process. This, to me is really the most exciting part of keeping botanical method aquariums.

And how do we usually do it? I mean, for many hobbyists, we've been more or less indoctrinated to clean the sand, age water, add wood, arrange plants, and add fishes. And that works, of course. It's the basic "formula" we've used for over a century.
Yet, I'm surprised how we as a hobby have managed to turn what to me is one of the most inspiring, fascinating, and important parts of our aquarium hobby journey into what is more-or-less a "checklist" to be run through- an "obstacle", really- to our ultimate enjoyment of our aquarium.

When you think about it, setting the stage for life in our aquariums is the SINGLE most important thing that we do. If we utilize a different mind set, and deploy a lot more patience for the process, we start to look at it a bit differently.
I mean, sure, you want to rinse sand as clean as possible. You want make sure that you have a piece of wood that's been soaked for a while, and..
Wait, DO you?
I mean, sure, if you don't rinse your sand carefully, you'll get some cloudy water for weeks...no argument there.

And if you don't clean your driftwood carefully, you're liable to have some soil or other "dirt" get into your system, and more tannins being released, which leads to...well, what does it lead to?
I mean, an aquarium is not a "sterile" habitat. Let's not fool ourselves.
The natural aquatic habits which we attempt to emulate, although comprised of many millions of times the volumes of water volume and throughput that we have in our tanks- are typically not "pristine"- right? I mean, soils from the surrounding terrestrial environment carry with them decomposing matter, leaves, etc, all of which impact the chemistry, oxygen-carrying capacity, biological activity, and of course, the visual appearance of the water.

And that's kind of what our whole botanical-method aquarium adventure is all about- utilizing the "imperfect" nature of the materials at our disposal, and fostering and appreciating the natural interactions between the terrestrial and aquatic realms which occur.
Of course, much like Nature, our botanical-method aquariums make use of the "ingredients" found in the abundant materials which comprise the environment. And the "infusion" of these materials into the water, and the resulting biological processes which occur, are what literally make our tanks come alive.
And yeah, it all starts with the nitrogen cycle...
We can embrace the mindset that every leaf, every piece of wood, every bit of substrate in our aquariums is actually a sort of "catalyst" for sparking biodiversity, function, and yes- a new view of aesthetics in our aquariums.

I'm not saying that we should NOT rinse sand, or soak wood before adding it to our tanks. What I AM suggesting is that we don't "lose our shit" if our water gets a little bit turbid or there is a bit of botanical detritus accumulating on the substrate. And guess what? We don't have to start a tank with brand new, right-from-the-bag substrate.
Of course not.

We can utilize some old substrate from another tank (we have done this as a hobby for decades for the purpose of "jump starting" bacterial growth) which also has the side benefit of providing a different aesthetic as well!
And, you can/should take it further: Use that slightly algal-covered piece of driftwood or rock in our brand new tank...This gives a more "broken-in look", and helps foster a habitat more favorable to the growth of the microorganisms, fungi, and other creatures which comprise an important part of our closed aquarium ecosystems.
In fact, in a botanical-method aquarium, facilitating the rapid growth of such biotia is foundational.

It's perfectly okay for your tank to look a bit "worn" right from the start. Functional aesthetics once again! the look results from the function.
In fact, I think most of us actually would prefer that! It's okay to embrace this. From a functional AND aesthetic standpoint. Employ good husbandry, careful observation, and common sense when starting and managing your new aquarium.

So don't obsess over "pristine." Especially in those first hours.
The aquarium still has to clear a few metaphorical "hurdles" in order to be a stable environment for life to thrive.
I am operating on the assumption (gulp) that most of us have a basic understanding of the nitrogen cycle and how it impacts our aquariums. However, maybe we don’t all have that understanding. My ramblings have been labeled as “moronic” by at least one “critic” before, however, so it’s no biggie for me as said “moron” to give a very over-simplified review of the “cycling” process in an aquarium, so let’s touch on that for just a moment!

During the "cycling" process, ammonia levels will build and then suddenly decline as the nitrite-forming bacteria multiply in the system. Because nitrate-forming bacteria don't appear until nitrite is available in sufficient quantities to sustain them, nitrite levels climb dramatically as the ammonia is converted, and keep rising as the constantly-available ammonia is converted to nitrite.
Once the nitrate-forming bacteria multiply in sufficient numbers, nitrite levels decrease dramatically, nitrate levels rise, and the tank is considered “fully cycled.”
And of course, the process of creating and establishing your aquariums ecology doesn't end there.
With a stabilized nitrogen cycle in place, the real "evolution" of the aquarium begins. This process is constant, and the actions of Nature in our aquariums facilitate changes.
And our botanical-method systems change constantly.
They change over time in very noticeable ways, as the leaves and botanicals break down and change shape and form. The water will darken. Often, there may be an almost "patina" or haziness to the water along with the tint- the result of dissolving botanical material and perhaps a "bloom" of microorganisms which consume them.
This is perfectly analogous to what you see in the natural habitats of the fishes that we love so much. As the materials present in the flooded forests, ponds, and streams break down, they alter it biologically, chemically, and even physically.

It's something that we as aquarists have to accept in our tanks, which is not always easy for us, right? Decomposition, detritus, biofilms- all that stuff looks, well- different than what we've been told over the years is "proper" for an aquarium. And, it's as much a perception issue as it is a husbandry one. I mean, we're talking about materials from decomposing botanicals and wood, as opposed to uneaten food, fish waste, and such.
What's really cool about this is that, in our community, we aren't seeing hobbyists freak out over some of the aesthetics previously associated with "dirty!"
It's seen as a fundamental part of the evolution of the tank.
And soon, you'll see the emergence of elegant, yet simple life forms, such as bacterial biofilms and fungal growths. We've long maintained that the appearance of biofilms and fungi on your botanicals and wood are to be celebrated- not feared. They represent a burgeoning emergence of life -albeit in one of its lowest and (to some) most unpleasant-looking forms- and that's a really big deal.
Biofilms, as we've discussed ad nauseam here, form when bacteria adhere to surfaces in some form of watery environment and begin to excrete a slimy, gluelike substance, consisting of sugars and other substances, that can stick to all kinds of materials, such as- well- in our case, botanicals. It starts with a few bacteria, taking advantage of the abundant and comfy surface area that leaves, seed pods, and even driftwood offer.
The "early adapters" put out the "welcome mat" for other bacteria by providing more diverse adhesion sites, such as a matrix of sugars that holds the biofilm together. Since some bacteria species are incapable of attaching to a surface on their own, they often anchor themselves to the matrix or directly to their friends who arrived at the party first.
Tannin's creative Director, Johnny Ciotti, calls this period of time when the biofilms emerge, and your tank starts coming alive "The Bloom"- a most appropriate term, and one that conjures up a beautiful image of Nature unfolding in our aquariums- your miniature aquatic ecosystem blossoming before your very eyes!
The real positive takeaway here:
Biofilms and fungal growths are really a sign that things are working right in your aquarium! A visual indicator that natural processes are at work, helping forge your tank's ecosystem.

About a year ago, had a discussion with our friend, Alex Franqui. His beautiful Igarape-themed aquarium pictured above, "bloomed" beautifully, with the biofilms, fungal growths, and sediments working together to create a stunning, very natural functioning- and appearing-ecosystem. He was not repulsed at all. Rather, he was awed and fascinated...He celebrated what was occurring in his tan. He has an innate understanding of the ecological process, and replaced "fear and loathing" with excitement.
Alex is a hardcore aquascaper, and to see him marveling and rejoicing in the "bloom" of biofilms in his tank is remarkable.
He gets it.
And it turns out that our love of biofilms is truly shared by some people who really appreciate them as food...Shrimp hobbyists! Yup, these people (you know who you are!) go out of their way to cultivate and embrace biofilms and fungi as a food source for their shrimp.

They get it.
And this makes perfect sense, because they are abundant in Nature, particularly in habitats where shrimp naturally occur, which are typically filled with botanical materials, fallen tree trunks, and decomposing leaves...a perfect haunt for biofilm and fungal growth!
Nature celebrates "The Bloom", too.

There is something truly remarkable about natural processes playing out in our own aquariums, as they have done for eons in the wild.
Time for a little thought experiment...
You're a fish.
Seriously. Make yourself a fish...for a second. (I think I'd be a Black Ghost Knife, FYI. What, you thought I'd be a Cardinal Tetra or something? Really? Sheesh!)

Your main goals in life are avoiding predators, finding food, and reproducing. The "finding food" part is what we're focusing on in this experiment.
Now, back to being you for a second.

Would you like to move into a house which didn’t have a refrigerator full of food? I wouldn’t, for sure. Unlike humans, fishes seem to have not lost their "genetic programming" for grazing and hunting for food. Let’s face it—most of the waking hours of aquatic animals are devoted to acquiring food and reproducing. They need to have some food sources available to "hunt and graze" for.
That’s reality.
So why not help accommodate our your animals’ needs by supplementing their prepared diet with some “pre-stocked” natural foods in their new home? You know, slow down, get things "going" a bit, and then add the fishes?
I’m not talking about tossing in a few frozen brine shrimp hours before the first fishes go in the tank—I’m talking about a deliberate, systematic attempt to cultivate some living food sources within the system before a fish ever hits the water! Imagine a “new” system offering numerous foraging opportunities for its new inhabitants!

in our world, that might mean allowing some breakdown of the botanicals, or time for wood or other botanicals to recruit some biofilms, fungi- even turf algae on their surfaces before adding the fishes to the aquarium.
“Scott. You’re being impractical here! It could take months to accomplish this. I’ve just spent tons of money and time setting up this tank and you want me to deliberately keep this tank devoid of fishes while the biofilms form and Daphnia reproduce?”
Yes. Seriously.
I am a bit crazy. I’ll give you that.
Yet, with my last few systems, this is exactly what I did.
Why?
Well, for one thing, it creates a habitat for sighs which is uniquely suited to their needs in a different way.
Think abut the way most fishes live. They spend a large part of their existence foraging for food. Even in the cozy, comfortable confines of the aquarium.
So, why not create conditions for them which help accommodate this instinctive behavior, and provide opportunities for supplemental (or primary!) nutrition to be available to them by foraging.
Now, I have no illusions about this idea of "pre-stocking" being a bit challenging to execute.
I’m no genius, trust me. I don’t have half the skills many of you do but I have succeeded with many delicate “hard-to-feed” fishes over my hobby “career.”
Any "secret" to this?
None at all. I'm simply really fucking patient.
Success in this arena is simply a result of deploying..."radical patience." The practice of just moving really slowly and carefully when adding fishes to new tanks.
A really simple concept.
I mean, to some extent, we already deploy this practice with our botanical-method tanks, right? The very process of creating a botanical-method aquarium lends itself to this "on board supplemental food production" concept. A concept that's pretty analogous to what occurs in Nature, right?

And one of the most important functions of many botanically-influenced wild habitats is the support of food webs. As we've discussed before in this blog, the leaf litter zones in tropical waters are home to a remarkable diversity of life, ranging from microbial to fungal, as well as crustaceans and insects...oh, and fishes, too! These life forms are the basis of complex and dynamic food webs, which are one key to the productivity of these habitats.
You can do this. You can foster such a "food web"- or the basis for one- in your aquarium!
Wait a minimum of three weeks—and even up to a month or two if you can stand it, and you will have a surprisingly large population of micro and macro fauna upon which your fishes can forage between feedings.
Having a “pre-stocked” system helps reduce a considerable amount of stress for new inhabitants, particularly for wild fishes, or fishes that have reputations as “delicate” feeders.
And think about it for a second.
This is really a natural analog of sorts. Fishes that live in inundated forest floors (yeah, the igapo again!) return to these areas to "follow the food" once they flood. In fact, other than the physical flooding itself, this pursuit of food sources is the key factor in the migration of fishes into these habitats.
So, what would some candidate organisms be for "pre-stocking" a botanical-style aquarium?
How about starting with (okay, sounding a bit commercial, I know, but...) the versatile Purple Non Sulphur Bacteria (PNSB), Rhodopseudomonas palustris- the species which forms our product, "Culture." PNSB are useful for their ability to carry out a particularly unusual mode of metabolism: "anaerobic photoheterotrophy."

In this process, they consume organic wastes while inhabiting moderately illuminated and poorly oxygenated microhabitats (patches of detritus, leaf litter beds, shallow depths of substrate, deeper pores of expanded clay media, etc.). In addition to helping to maintain an ecologically stable microhabitat, "Culture" provides a nutritious live food source for zooplankton as well as soil mesofauna.
Yeah, these guys form the "foundation" of your food chain! (And yeah, we'll have "Culture" back in stock soon...we're re-thinking the packaging to make the product more affordable!)
Next, perhaps some "starter cultures" of organisms like Paramecium, Euglena, etc. You know, "infusoria" from the old school aquarium literature. And then, small crustaceans like Daphnia, and copepods of various types.

Pure cultures of all of these organisms are available online from various biological supply houses. They're a fantastic source of biodiversity for your aquarium!
Of course, the more daring among you may want to introduce various worms, like "Black Worms" or Tubifex worms, if you can find clean cultures of them. For that matter, even "blood worms", which are actually the larval phase of the midge.
Some organisms, such as nematodes and chironomids ("Bloodworms!") will dig into the leaf structures and feed on the tissues themselves, as well as the fungi and bacteria found in and among them. These organisms, in turn, become part of the diet for many fishes.

These organisms, in turn, become part of the diet for many fishes.
Food Web.
And the resulting detritus (here we go again!) produced by the "processed" and decomposing plant matter is considered by many aquatic ecologists to be an extremely significant food source for many fishes, especially in areas such as Amazonia and Southeast Asia, where the detritus is considered an essential factor in the food webs of these habitats.
It performs the same function in an aquarium- if we allow it to.

And of course, if you observe the behavior of many of your fishes in the aquarium, such as characins, cyprinids, Loricariids, and others, you'll see that, in between feedings, they'll spend an awful lot of time picking at "stuff" on the bottom of the tank. In a botanical method aquarium, this is a pretty common occurrence, and I believe an important benefit of this type of system.
When you start seeing your fishes "graze" casually on the materials that pop up on your driftwood and botanicals, you start realizing that, although it might not look like the aesthetics we have had in mind in years past, it is a beautiful thing to our fishes!
You can do this.
Remember, it's all part of the game with a botanical-influenced aquarium. Understanding, accepting, and celebrating "The Bloom" is all part of that "mental shift" towards accepting and appreciating a more truly natural-looking, natural-functioning aquarium.

The "price of admission", if you will- along with the tinted water, decomposing leaves, etc., the metaphorical "dues" you pay, which ultimately go hand-in-hand with the envious "ohhs and ahhs" of other hobbyists who admire your completed aquarium when they see it for the first time.
Stay studious. Stay diligent. Stay observant. Stay patient...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
The "through line"
through line (N): "A common or consistent element or theme shared by items in a series or by parts of a whole."
I recently returned from another speaking gig.
This time, I was in St. Louis, Missouri, in the midwest of the U.S. I visited a club with some very advanced, super-talented hobbyists, some who are icons in various hobby specialities. It was a lot of fun, as they almost always are. However, this one- THIS trip- left me with some really profound revelations about the hobby which I'm still processing.
An added bonus is that I was able to visit the amazing botanical method aquariums of our friend, Melanie Holmes. It was beyond satisfying to see a truly talented hobbyist find Her way in the hobby, evolving from "traditional" planted aquascaped tanks into the botanical method.

Observing her work, it was easy to see how Her skill from one "genre" translated into our little speciality. The "through line" was a great understanding of the ecology of aquariums. Here tanks were a celebration of life, aesthetic, and ecology. Any one of them was among the best botanical-method aquariums ever created, IMHO.

I was also able to visit a fish room of a very advanced killifish breeder, and it was not only educational for me, it was enlightening...I took particular note of the techniques and approaches that he was utilizing to manage a large number of aquariums, and to keep a "work flow" of fishes going at all times.
Perhaps what was most memorable to me was how he made adjustments to his techniques, like inducing spawning, egg collection, incubation, and production of live foods.
His function-first approaches to light and temperature manipulation, egg collection, incubation approaches, and even how fry were reared- all demonstrated a keen understanding of the needs of his fishes, and an understanding of the environments- and environmental cues- which the fishes needed to trigger spawning events.

Although the process was more "methodical" than "natural", in that it involved sort of "deconstructing" how Nature works in the wild- all of the techniques he employed were simply practical and simple recreations of natural processes to accomplish what Nature does-just in a more "controlled" manner.
Killifish, IMHO, are the ultimate example of how fishes are intimately tied to their habitats. The techniques which modern killie keepers utilize to spawn their fish, incubate the eggs, and rear the resulting fry are a direct distillation of an understanding of this relationship.

Indeed, there was a "through line" of sorts, running from the wild savannah pools and forest streams of East Africa, to the tightly-controlled environment of this suburban St. Louis basement.

It was profound. It was inspiring. It was amazing.
Now, sure, I wasn't seeing fishes being kept in tanks with accumulations of leaf litter over a shallow sedimented substrate, with overhanging terrestrial vegetation. Literal recreations of their natural habitats. Rather, I was seeing the pragmatic application of "biotope replication!" Yeah, it doesn't always have to look like it to function like it!
A huge "unlock" for me, really.
What we've longed called "natural" in the aquairum hobby can take on more than one meaning. I mean, I have consistently railed on the use of the term "natural" when those "high concept", artistically-styled "Nature Aquariums" are proferred to us as "natural" for some very specific reasons; in particular, the fact that they are often touted as "looking just like Nature", an assertion which makes me want to vomit. They generally don't look like wild aquatic habitats.
They're simply beautiful aquariums, skillfully executed.

However, I really can't deny that, on a purely ecological level, they DO function like natural aquatic systems to a certain extent, relying on energy/nutritoinal inputs, and yielding growth of aquatic plants. It's just again, a sort of "deconstructed" approach.
I think that it's the "cultural arrogance" and embrace of the most superficial aspects of aquarium keeping, coupled with the constant assertion that these tanks "look like natural aquatic habitats" by the proponents who surround the "Nature Aquarium" movement, which has always turned me off about them.
Not the work itself.

The reality is that these systems do require the aquarist to reproduce natural processes to some extent in order to be successful. An understanding of the ecology of aquatic plants and their environment is necessary.
Another "through line" from Nature to aquarium...
And of course, there is what we call the "botanical method"- an approach that seeks to more literally recreate the ecology of wild aquatic ecosystems in the aquarium.

To a certain extent, it's the "oldest game in town" in the aquarium world- the approach which lovers of aquatic life centuries before us took to keeping fishes: Toss in some soil, leaves, twigs, and plants and attempt to recreate the wild aquatic habitat as accurately as possible. We incorporate these materials in our tanks because they're what's found in the environments from which our fishes come, right?

Yeah. An homage to Nature by attempting to replicate the function of Nature. And making the effort to understand the relationship between fishes and their habitats.
It's not some arcane idea, is it?

A "through line", for sure!
All we are doing with any aquarium, wether we are conscious of it or not- is attempting to reproduce the functions of natural aquatic ecosystems in our tanks.
The idea of creating a multi-tiered ecosystem, which provides a lot of the requirements needed to operate successfully with just a few basic maintenance practices, the passage of time, a lot of patience, and careful observation- is something that has been discussed, but rarely executed in the modern aquarium hobby until quite recently...

Why?
Not because it's difficult to execute.
Not because it's hard to grasp the underlying concepts.
It's because it's difficult to try something which seems so "contrary" to what we are constantly exposed to in social media and elsewhere. It means doing something which we may find uncomfortable, because we're told it's "dangerous" or "reckless" or "dirty" or whatever, by pundits who neither understand nor appreciate what it means to embrace a truly natural, ecological approach to aquarium keeping.

It means adopting a different outlook, accepting a different, yet very beautiful aesthetic. It's about listening to Nature instead of the dude on Instagram with the flashy, artistically-presented, gadget-driven tank. It's not always comfortable at first for some to try, and it initially seems like you're somehow doing things wrong.
Yet, executing this type of tank is about as basic as aquarium-keeping gets.
The difficult part is understanding that this is an extremely natural, ecologically beneficial process, and accepting that it does facilitate the appearance of some things that you might not be comfortable with initially (like, cloudy water, fungal threads, biofilms, decomposition...all that stuff!). Making those mental shifts to accept something different than what the aquarium hobby establishment has proffered as the way to go for generations...
Yet it's not that different than what our distant ancestors did when they set up what we now refer to as an "aquarium."
A through line...one which requires mental shifts and adoption of a long-term mindset.

You have to give things time to establish and settle.
It's about patience.
It's about faith.
Faith in Mother Nature, who's been doing this stuff for eons. Faith that you're doing something which embraces Nature's processes so fully.
The truest, straightest "through line" there is in the aquarium hobby.
Stay diligent. Stay curious. Stay observant. Stay patient. Stay engaged...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
Your fishes call it "food..."
If you've followed us for any length of time, you're well aware that we are not just pushing you to play with natural, botanical-method aquariums only for the pretty aesthetics.

I mean, yeah, they look awesome, but there is so much more to it than that. We are unapologetically obsessed with the function of these aquariums and the wild habitats which they attempt to represent!

And one of the most important functions of many botanically-influenced wild habitats is the support of what ecologists call food webs-a system of interlocking and interdependent food chains...in other words, "what eats what" in the aquatic ecosystem!
It's a fascinating field of study that plays beautifully into what we do in our botanical method aquariums.
As we've discussed before, the leaf litter zones in tropical waters are home to a remarkable diversity of life, ranging from microbial to fungal, as well as crustaceans and insects...oh, and fishes, too! These life forms are the basis of complex and dynamic food webs, which are one key to the ecological "productivity" of these habitats.

By researching, developing, and managing our own botanically-influenced aquaria, particularly those with leaf litter beds, we may be on the cusp of finding new ways to create "nurseries" for the rearing of many fishes!
At least upon superficial examination, our aquarium leaf litter/botanical beds seem to function much like their wild counterparts, creating an extremely rich "microhabitat" within our aquariums. And initial reports form those of you who breed and rear fishes in your intentionally "botanically-stocked" aquariums are that you're seeing great color, more regularity in spawns, and higher survival rates from some species.
I don't believe that this is mere coincidence.

We're just beginning here, and the future is wild open for huge hobbyist-level contributions that can lead to some serious breakthroughs in understanding how food webs develop in aquariums!

Maybe we will finally overcome generations of fear over detritus and fungi and biofilms- the life-forms and "by-products" which literally "power" the aquatic ecosystems we strive to duplicate in our aquariums.
There is something tantalizing to me about the idea of our fishes being able to supplement what we feed them by foraging in the aquarium. To some extent, virtually every aquairum has some microorganisms, algae, etc. which fishes can "snack on" in between our feedings. Yet, botanical-method aquariums, with their abundance of decomposing leaves and the ecology which they foster, take this to a whole different level.
I'm particularly fascinated with the idea of the fry of our fishes being able to sustain themselves or supplement their diets substantially, with what is produced inside the little habitat we've created in our tanks! A botanical method aquarium is, I believe, an ideal "nursery" for many species of fishes to begin their lives, and the experience of many of my fish-breeding friends who have played with this idea successfully helps to prove my thesis.

Let's consider some of the types of food sources that our fishes might utilize in the wild habitats that we try so hard to replicate in our aquariums, and perhaps develop a greater appreciation for them when they appear in our tanks. Perhaps we will even attempt to foster and utilize them to our fishes' benefits in unique ways?

One of the important food resources in natural aquatic systems are what are known as macrophytes- aquatic plants- which grow in and around the water, emerged, submerged, floating, etc. Not only do macrophytes contribute to the physical structure and spatial organization of the water bodies they inhabit, they are primary contributors to the overall biological stability of the habitat, conditioning the physical parameters of the water. Of course, anyone who keeps a planted aquarium could attest to that, right?

One of the interesting things about macrophytes is that, although there are a lot of fishes which feed directly upon them, in this context, the plants themselves are perhaps most valuable as a microhabitat for algae, zooplankton, and other organisms which fishes feed on. Small aquatic crustaceans seek out the shelter of plants for both the food resources they provide (i.e.; zooplankton, diatoms) and for protection from predators (yeah, the fishes!).

I have personally set up a couple of systems recently to play with this idea- botanical-influenced planted aquariums, and have experimented with going extended periods of time without feeding my fishes who lived in these tanks- and they have remained as fat and happy as when they were added to the tanks…

Something is there- literally!
Perhaps most interesting to us botanical-method aquarium people are epiphytes. These are organisms which grow on the surface of plants or other substrates and derive their nutrients from the surrounding environment. They are important in the nutrient cycling and uptake in both nature and the aquarium, adding to the biodiversity, and serving as an important food source for many species of fishes.

In the case of our aquatic habitats, like streams, ponds, and inundated forests, epiphytes are abundant, and many fishes will spend large amounts of time foraging the biocover on tree trunks, branches, leaves, and other botanical materials. Although most animals use leaves and tree branches for shelter and not directly as a food item, grazing on this epiphytic growth is very important.
Some organisms, such as nematodes and chironomids ("Bloodworms!") will dig into the leaf structures and feed on the tissues themselves, as well as the fungi and bacteria found in and among them. These organisms, in turn, become part of the diet for many fishes.

And the resulting detritus produced by the "processed" and decomposing pant matter is considered by many aquatic ecologists to be an extremely significant food source for many fishes, especially in areas such as Amazonia and Southeast Asia, where the detritus is considered an essential component of the food webs in these habitats.

And of course, if you observe the behavior of many of your fishes in the aquarium, such as characins, cyprinids, Loricarids, and others, you'll see that in between feedings, they'll spend an awful lot of time picking at "stuff" on the bottom of the tank. In a botanical style aquarium, this is a pretty common occurrence, and I believe an important benefit of this type of system.

I am of the opinion that a botanical-method aquarium, complete with its decomposing leaves and seed pods, can serve as a sort of "buffet" for many fishes- even those who's primary food sources are known to be things like insects and worms and such. Detritus and the organisms within it can provide an excellent supplemental food source for our fishes!
Just like in Nature.

It's well known by scientists that in many habitats, like inundated forest floors, etc., fishes will adjust their feeding strategies to utilize the available food sources at different times of the year, such as the "dry season", etc. And it's also known that many fish fry feed actively on bacteria and fungi in these habitats...so I suggest once again that a botanical method aquarium could be an excellent sort of "nursery" for many fish species!

You'll often hear the term "periphyton" mentioned in a similar context, and I think that, for our purposes, we can essentially consider it in the same manner as we do "epiphytic matter." Periphyton is essentially a "catch all" term for a mixture of cyanobacteria, algae, various microbes, and of course- detritus, which is found attached or in extremely close proximity to various submerged surfaces. Again, fishes will graze on this stuff constantly.

And then, of course, there's the “allochthonous input” that we’ve talked about so much: Foods from the surrounding environment, such as flowers, fruits, terrestrial insects, etc. These are extremely important foods for many fish species that live in these habitats. We mimic this process when we feed our fishes prepared foods, as stuff literally "rains from the sky!" Now, I think that what we feed to our fishes directly in this fashion is equally as important as how it's fed.

I'd like to see much more experimentation with foods like live ants, fruit flies, and other winged insects. Of course, I can hear the protests already: "Not in MY house, Fellman!" I get it. I mean, who wants a plague of winged insects getting loose in their suburban home because of some aquarium feeding experiment gone awry, right?
That likely wouldn't go over well with just about any significant other in the "non-aquarium" world, right?

That being said, I would encourage some experimentation with ants and the already fairly common wingless fruit flies. Sure, you can just catch some ants outside and drop them into your tank...or you could culture them...Remember those "Ant Farms" that some of us had when we were kids?

Can you imagine one day recommending an "Ant Farm" as a piece of essential aquarium food culturing equipment? It's at least as wacky as culturing peanut beetle larvae or microworms, and not nearly as messy!
Why not, right? 😆
And of course, easier yet- we can simply foster the growth of potential food sources that don't fly or crawl around- they just arise when botanicals and wood and stuff meet water...We just need to not wipe them out as soon as they appear! Damn, using the collection and feeding of winged insects as an opposite example sure makes fungal growths and biofilms more palatable, right?

As many of you may know, I've often been sort of amused by the panic that many non-botanical-style-aquarium-loving hobbyists express when a new piece of driftwood is submerged in the aquarium, often resulting in an accumulation of fungi and biofilm.
I realize this stuff can look pretty shitty to many of you, particularly when you're trying to set up a super-cool, "sterile high-concept" aquascaped tank.
That being said, I think we need to let ourselves embrace this stuff and celebrate it for what it is: Life. Sustenance. Diversity. Foraging.
I think that those of us who maintain botanical method aquariums have made the "mental shift" to understand, accept, and even celebrate the appearance of this stuff.

We learn to appreciate it by looking to Nature.
Natural habitats are absolutely filled with this stuff...in every nook and cranny. On every rock, branch, seed pod, and leaf. It's like the whole game here- an explosion of life-giving materials, free for the taking...
A priceless natural resource.

It's why, a long time ago, I learned to not be put off by the mere appearance of these life forms when they showed up in my early botanical method aquariums. They are literally the drivers of underwater ecology- a priceless resource which Nature happily deposits into our aquariums.

A true gift from Nature.
Yet, for a century or so in the hobby, our first instinct is to reach for the algae scraper or siphon hose, and lament our misfortune with our friends.
It need not be this way. Its appearance in our tanks is a blessing.
Really.
You call it "mess." I call it a blessing. Your fishes call it “food."
Another "mental shift", I suppose...one which many of you have already made, no doubt. Or, I hope you have..or can.
The ability to appreciate this stuff- to move beyond the fear, loathing, and disdain which many hobbyists have for it-is to truly grow as a hobbyist. In fact, the oft-quoted, absurdly mis-interpreted and applied (to the point where it's almost a mockery) statement by none other than the late Akashi Amano that, "To know Mother Nature is to love her smallest creations..." sums this up perfectly.
Yeah, he got it.
You can, too.

Now look, I'm not saying that your tank has to be packed with biofilms, fungal growth, decomposing leaves, and detritus in order to provide all of these benefits to your fishes. However, I am suggesting that, as hobbyists, we should to allow some amount of this material to accumulate in our tanks.
Remember, the presence of these materials does not signify some "problem" with your aquarium, as is so easy to conclude.
Rather, their presence indicates that your aquarium is functioning very much like a natural aquatic ecosystem. That it's doing what Nature has done for eons. To disrupt the process by aggressively siphoning out every gram of detritus, scraping off every bit of fungal growth or biofilm actually inhibits or even completely disrupts processes which can benefit your tank in manifold ways.
Not only do fungal growths and biofilms serve as a supplemental food resource for our fishes, they help "filter" the water by processing nutrients. And a large part of their "fuel" is the leaf litter, seed pods, wood, and the detritus which occurs as a result of their decomposition.

Yeah, we talk about this a lot around here, I know.
However, it's such an important part of our philosophy and methodology that it cannot be stated often enough.
And the sooner we embrace this stuff, the sooner we begin to realize the lasting benefits that it can bring to our aquariums!
Stay confident. Stay bold. Stay curious. Stay diligent. Stay studious...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
Perpetual darkness...
Okay, that was an admittedly "dark"-sounding title, but it's perfectly appropriate for today's topic...How to get- and keep- your water as tinted as possible. Or, at least, what materials would do the best job in terms of "color production."
We as a group are kind of obsessed with this.

And yeah, it's a good question!
Now, first off- let's all remember that the color of the water has absolutely NO relationship to its pH or carbonate hardness. It just doesn't. You can have water that looks super dark brown, yet has a pH of 8.5 or whatever. And conversely, it's just as possible to have crystal clear blue-white water that's soft, and has a pH of 4.5. We have to get beyond the social media-style "blackwater" definition, which seems to be, "If the water is tinted, it's a blackwater aquarium!"
Now, look, if you just want the nice color but could care less about the pH and hardness, that's fine. For the benefit of the hobby as a whole, please don't perpetuate the confusing narrative about blackwater aquariums by telling others that you have "blackwater." You have a "tinted" aquairum.
And that's just fine.

So, yeah-I'm not going to launch into a long drawn out description today about how ecologists define "blackwater" and what specific chemical characteristics make it up- we've covered it enough over the years...you can deep dive here or elsewhere to get that.

Okay, micro-rant over. Let's get back to the topic.
Remember, this piece is not about how to make blackwater...It's a little more superficial than that...it's about creating an aquarium with color and maintaining it.
First off, one of the "keys" to getting your color that lovely brown is to select the right types and quantities of botanical materials to assist. Now, I'll be the very first to raise my hand and call BS on anyone who claims to have a perfect "recipe" for how many Catappa leaves per liter or whatever you must use to achieve a specific color. Sure, you could come up with some generic recommendations, but they're not always applicable to every tank or situation.
Yes...there are simply so many variables in the equation- many which we probably haven't even considered yet-that it would be simply guessing. Just like Nature, to some extent...
What I can do is recommend some materials which we have found over the years to generally impart the most reliable and significant color to water. In no particular order, I'll give you my thought on a few of my personal faves. There are a lot more, but these are some that consistently show up on my "fave" list.
Wood
Yep, you heard me. One of the very best sources of tint-producing tannins in our aquariums is wood. I've told you many times, wood imparts tannins, lignin, and all sorts of other "stuff" from the exterior surfaces and all of those nooks and crannies that we love so much into the water.
Ahh...the tannins.
Now, I don't know about you, but I'm always amused (it's not that hard, actually) by the frantic posts on aquarium forums from hobbyists that their water is turning brown after adding a piece of wood. I mean- what's the big deal?
Oh, yeah, not everyone likes it...I forgot that. 😂
The reality, though, as you probably have surmised, is that wood will continue to leach tannins to a certain extent pretty much for as long as it's submerged. As a "tinter", I see this as a great advantage in helping establish and maintain the blackwater look, and to impart humic substances that are known to have health benefits for fishes.
Some wood types, like Mangrove ( a wood we don't have at the moment), tend to release more tannins than others over long periods of time. Other types, like "Spider Wood", will release their tannins relatively quickly, in a big burst. Some, such as Manzanita wood, seem to be really "dirty", and release a lot of materials over long periods of time. All will recruit fungal growths and bacterial biofilms.
And the biocover on the wood is a unique functional aesthetic, too, as we rant on and on about here!

Bark
I'm a huge fan of tree bark to impart not only color, but beneficial tannins into the water. Because of its composition and structure, bark tends to last a very long time when submerged, and tends to impart a lot of color to the water over the long term.
And to be quite honest, almost all of the bark products we've played with over the years seem to work equally as well. The real difference in bark is the "form factor" (appearance) and the color that they impart to the water over time. Some, such as Red Mangrove bark or Cutch bark, will impart a much deeper, reddish-brown tint to the water than say, an equal quantity of catappa bark. And our soon-to-be-released Ichnocarpus bark really packs in this reddish brown color! You're gonna love this stuff!

Ounce for ounce, gram for gram, I've always felt that various types of bark always impart the most color to the water over almost any other materials.
"Skyfruit Pods"
These are very interesting, woody pods, derived from the outer "valve" of the fruit of the Swietenia macrophylla tree, which hails from a wide range of tropical locales (although native to Brazil), and are just the sort of thing you'd find floating or submerged in a tropical jungle stream. Often called "Skyfruit" by locals in the regions in which they're found because they hang from the trees- a name we fell in love with!
These botanicals can leach a terrific amount of tannins, akin to a similar-sized piece of Mopani wood or other driftwood. They are known to be full of flavonoids, saponins, and other humic substances, which have known positive health effects on fishes. Like bark, it lasts a good long time and recruits some biofilms and fungal growths for good measure.

Live Oak Leaves/Magnolia Leaves
Despite their humble North American origins, these leaf types impart more color, ounce per ounce, than just about any of our fave tropical leaves. And they both last very long time...Like, I've had specimens of live oak leaves stay intact for several months!
It's really important to think of leaves as not just a "coloring agent" for your water, but as a sort of biological support mechanism for your burgeoning ecosystem. They actively recruit fungi, bacterial biofilms, and other microorganisms which enrich the overall aquatic environment in your tank.

Cones
Alder cones (Aalnus glutinosa and Alnus incana) and Birch cones (Betula occidentalis), have been widely utilized by aquarium hobbyists in Europe for some time. Betta and ornamental shrimp breeders are fond of the tannins released into the water by these cones, and their alleged anti fungal and antibacterial properties. There has also been much study by hobbyists about the pH reduction attributes of these cones, too.
A study done a few years back by a Swedish hobbyist using from one to six cones in a glass containing about 10 ounces of tap water, with a starting ph of around 8.12, was able to affect a drop to 6.74 with one cone after about two weeks, 4.79 with 2 cones after two weeks, and an amazing 3.84 with 6 cones after the same time period! The biggest part of the drop in pH occurred in the first 12 hours after immersion of the cones!

Now, I'm the last guy to tell you that a bunch of cones is the perfect way to lower pH, but this and other hobby-level studies seem to have effectively have demonstrated their ability to drive pH down in "malleable" (soft) water...
Coconut-based products (Coco Curls, "Fundo Tropical", "Substrato Fino")
There's something about coconuts...The materials which are derived from the husks of coconuts seem to produce a significant amount of tannins and impart color to the water. Of course, "Substrate Fino" and "Fundo Tropical" are smaller, or finer-textured materials which work primarily as "substrate enhancers", and not strictly as "color-producing agents", because there is an initial "burst", which subsides over time.
Now, one of the novel applications for these finer botanical materials to take advantage of their color producing ability is to place them in a fine mesh filter bag and allow water to flow around or through them, like filter media. Essentially, a more sustainable alternative to the old peat moss trick...

Oak Twigs
For an interesting look and some nice color, I'm a big fan of oak twigs. Oak has a nice bark which imparts a deep brownish/yellow color to the water and it's quite distinctive. There is a reason why our "Twenty Twigs" packs are pretty popular, and it's not just because you get a bunch of cool sticks!

When mixed with leaves and/or other botanical materials, not only do you get an incredible "framework" for a cool ecosystem, you get an incredible aesthetic as well!

Now, this is an absolutely cursory list.. I could have easily listed 10 or more items. No doubt, some of you hardcore enthusiasts are screaming at your screens now: "WTF Fellman, you didn't include_______!"
And of course, that's the beauty of natural materials...There are numerous options!
Another note on the colors to expect from various botanical materials. As you might suspect, many of the lighter colored ones will impart a correspondingly lighter tint to the water. And, some leaves, such as Guava or Loquat, also impart a more yellowish or golden color to the water, as opposed to the brownish color which Jackfruit and Catappa are known for.

A lot of you ask about things that impact how long the water retains it's tint.
This kind stuff is a big deal for us- I get it! Many hobbyists who have perhaps added some catappa leaves, "blackwater extracts", or rooibos tea to their water contact me asking stuff like why the water doesn't stay tinted for more than a few days. Now, I'm flattered to be a sort of "clearing house" for this stuff, but I must confess, I don't have all the answers.
So, "Why doesn't my water stay tinted, Scott?"
Well, I admit I don't know. Well, not for certain, anyways!
I do, however, have some information, observations, and a bunch of ideas about this- any of which might be literally shot to pieces by someone with the proper scientific background. However, I can toss some of these seemingly uncoordinated facts out there to give our community some stuff to "chew on" as I offer my ideas up.
Now, perhaps it starts with the way we "administer" the color-producing tannins.
Like, I personally think that utilizing leaves, bark, and seed pods is perhaps the best way to do this. I'm sure that you're hardly surprised, right? Well, it's NOT just because I sell these material for a living...It's because they are releasing tannins, humic substances, and other compounds into the water "full time" during their presence in the aquarium as they break down. A sort of "on-board" producer of these materials, with their own "half life" (for want of a better term!).
And, they also perform an ecological role, providing locations for numerous life forms (like fungal growths) surface area upon which to colonize. They become part of the ecosystem itself. A few squirts of "blackwater extracts" won't do that, right?

The continuous release of tint-producing compounds from botanical materials keeps things more-or-less constant. And, if you're part of the "school" which leaves your botanicals in your aquarium to completely break down, you're certainly getting maximum value out of them! And if you are continuously adding/replacing them with new ones as they completely or partially break down, you're actively replenishing and adding additional "tint-producing" capabilities to your system, right?
There is another way to "keep the tint" going in your tanks, and it's pretty easy. Now, those of you who know me and read my rambling or listen to "The Tint" podcast regularly know that I absolutely hate shortcuts and "hacks" in the aquarium hobby. I preach a long, patient game and letting stuff happen in its own time...
Nonetheless, there ARE some that you can employ that don't make you a complete loser, IMHO.😆
When you prepare your water for water changes, it's typically done a few days to a week in advance, so why not use this time to your advantage and "pre-tint" the water by steeping some leaves in it? Not only will it keep the "aesthetics" of your water ( can you believe we're even talking about "the aesthetics of water?") consistent (i.e.; tinted), it will already have humic substances and tannins dissolved into it, helping you keep a more stable system.
Obviously, you'd still check your pH and other parameters, but the addition of leaves to your replacement water is a great little "hack" that you should take advantage of. (Shit, I just recommended a "hack" to you...)
It's also a really good way to get the "look" and some of the benefits of blackwater for your system from the outset, especially for those of you heathens that like the color of blackwater and despise all of the decomposing leaves and seed pods and stuff!
So, if you're just setting up a brand new aquarium, and have some water set aside for the tank, why not use the time while it's aging to "pre-tint" it a bit, so you can have a nice dark look from day one? It's also great if you're setting up a tank for an aquascaping contest or other same-day club event that would make it advantageous to have a tinted tank immediately.

I must confess that yet another one of the more common questions we receive here from hobbyists is, "How can I get the tint in my tank more quickly?"- and this is definitely one way!
How many botanicals to use to accomplish this?
Well, that's the million dollar question.
Who knows?
It all gets back to the (IMHO) absurd "recommendations" that have been proffered by vendors over the years recommending using "x" number of leaves, for example, per gallon/liter of water. There are simply far, far too many variables- ranging from starting water chem to pH to alkalinity, and dozens of others- which can affect the "equation" and make specific numbers unreliable at best.

We did, too, in the early days of Tannin. And it was kind of stupid really. There just is no hard-and-fast answer to this. Every situation is different. You need to kind of go with your instinct. Go slowly. Evaluate the appearance of your water, the behaviors of the fishes...the pH, hardness, TDS, nitrate, phosphate, or other parameters that you like to test for.
It's really a matter of experimentation.

I'm a much bigger fan of "tinting" the water based on the materials in the aquarium. Letting Nature have at it. The botanicals will release their "contents" at a pace dictated by their environment. And, when they're "in situ", you have a sort of "on board" continuous release of tannins and humic substances based upon the decomposition rate of the materials you're using, the water chemistry, etc.
Replacement of botanicals, or addition of new ones, as we've pointed out many times, is largely a subjective thing, and the timing, frequency, and extent to which materials are removed or replaced is dependent upon multiple factors, ranging from base water chemistry to temperature, to the types of aquatic life you keep in the tank (ie; xylophores like certain Plecos, or strongly grazing fishes, like Headstanders, will degrade botanicals more quickly than in a tank full of characins and such).
(The part where Scott bashes the shit out of the idea of using "blackwater extracts" and Rooibos tea. This could get nasty!)
If you haven't heard of it before, there is this stuff called Rooibos tea, which, in addition to bing kind of tasty, has been a favored "tint hack" of many hobbyists for years. Without getting into all of the boring details, Rooibos tea is derived from the Aspalathus linearis plant, also known as "Red Bush" in South Africa and other parts of the world.

(Rooibos, Aspalathus linearis. Image by R.Dahlgr- used under CC-BY S.A. 2.5)
It's been used by fish people for a long time as a sort of instant "blackwater extract", and has a lot going for it for this purpose, I suppose. Rooibos tea does not contain caffeine, and and has low levels of tannin compared to black or green tea. And, like catappa leaves and other botnaicals, it contains polyphenols, like flavones, flavanols, aspalathin, etc.
Hobbyists will simply steep it in their aquariums and get the color that they want, and impart some of these substances into their tank water. I mean, it's an easy process. Of course, like any other thing you add to your aquarium, including leaves and botanicals, it's never a bad idea to know the impact of what you're adding.
Like using botanicals, utilizing Rooibos tea bags in your aquarium requires some thinking, that's all.
The things that I personally dislike about using tea or so-called "blackwater extracts" are that you are simply going for an effect, without getting to embrace the functional aesthetics imparted by adding leaves, seed pods, etc. to your aquarium as part of its physical structure and ecology, and that there is no real way to determine how much you need to add to achieve______.
Obviously, the same could be said of botanicals, but we're not utilizing botanicals simply to create brown water or to target specific pH parameters, etc. We're trying to create an ecology that is similar to what you'd see in such habitats in Nature.

Yet, with tea or commercial blackwater extracts, you sort of miss out on replicating a little "slice of Nature" in your aquarium. The building of an ecosystem. Which is why we call this the botanical method. It's not a "style" of aquascaping! And of course, it's fine if your goal is just to color the water, but it's more of an aesthetically-focused aquarium at that point.
I also understand that some people, like fish breeders who need bare bottom tanks or whatever- like to condition water without all of the leaves and twigs and nuts we love. They want the humic substances and tannins, but really don't need/want the actual leaves and other materials in their tanks.
And, when it comes to tea and these commercial extracts, I don't think the stuff lasts all that long. I personally believe that the tint-producing tannins in "tea" are potentially taken up quickly by substrate materials, filter media, etc. And unless you're keeping tea bags in your tank on a continuous basis, you'll always experience some "color loss" after some period of time.
Yes it works to impart some color and tannins. Creating infusions or extracts is useful, if you understand their purpose and limitations. They have a place in the hobby for sure.
It's why we got into the game with our botanical-based "Shade" products. We're currently sold out and are working with our supplier on a reformulated version. Seems as though we need to make a "darker" mix!

On the other hand, if you're trying to replicate the look and function (and maybe some of the parameters) of THIS:

You won't achieve it by using THIS:

It's simply another shortcut.
Not good or bad. Just a way to get the end "effect" faster, and without the other collateral benefits we discussed.
And look, I understand that we are all looking for the occasional shortcuts and easier ways to do stuff. And I realize that none of what we proffer here at Tannin is an absolute science. It's likely more of an "art" at this point, with a little science behind it.
Think about it: There is no current way available to the hobby to test for "x" types or amounts of tannins (of which there are hundreds of types) in aquariums. I mean, there are tannin test kits, but they're used for wine making and such...Perhaps there is some tangential application for our purposes, but I'm not really sure what practical information. we could extract from the results.
And, I have not found a study thus far which analyzed wild habitats (say, Amazonia) for tannin concentrations and specific types, so we have no real model to go on.

The best we can do is create a reasonable facsimile of Nature.
And, in Naturę, a lot of the tint in blackwater environments comes from dissolved fulvic and humic acids from...soils. Yeah, geology is the key, IMHO, to truly "realistic" blackwater habitats. This is why I've been very picky on sourcing the materials and figuring out recipes for our NatureBase sediment substrates. They are intended to support these types of systems.

Understanding substrates and their role in both the physical environment and the ecology of our aquariums is still a wildly under-appreciated concept in the aquarium hobby, IMHO. We'll keep coming back to this in the future, I'm certain.
And keeping the water tinted is something that many botanical method aquarists are interested in. This wonderful "collateral benefit" of our approach is something that's easy to get addicted to!
Now, all of these ideas are okay to impart some color to your water. Some do more, as we've discussed ad nauseam. And none of them will work to full advantage if your aquarium is removing them as fast as you're imparting them into the water. So, go easy on chemical filtration media like carbon. I didn't say NOT to use them...Just don't use a ton of them! Use less than what the manufacturer recommends.
What about plants?

Well, I have a theory about plants and tannins...
First off, as you know by now, you absolutely can keep plants in blackwater aquariums. We've talked about this a million times over the years. And yet, interestingly, you can't always keep "blackwater conditions" (at least, color-wise) in planted aquariums! There has been much geeky discussion on this topic.
Tannin are interesting things. Think about this:
Tannins are known to bind up heavy metals and minerals. The roots of aquatic plants prefer to take up bound-up minerals and metals...So, another theory of mine is that heavily planted tanks do actually remove some of the visual "tint" (ie; the tannins) from the water via uptake from their roots.
Make sense? Maybe?
Okay, I could go on and on all day throwing out all sorts of theories and unsubstantiated (via lab tests and rigorous studies, anyways) ideas on this topic...But I think I gave you enough here to get the party started. I encourage you to do some homework. We need to ask these questions to people who really understand the chemistry here. I think that there might be some good answers out there.
And, back to the "color thing" to close on here...
I admit, visual "tint" is probably THE single most superficial aspect of what we experience with botanical-method aquariums- but the most obvious, and likely the most impactful to the casual hobbyist or observer.

It's just as important to understand the collateral benefits of utilizing botanical materials- a subject we've discussed dozens of times here. However, in the end, it's the look of your aquarium that is what you have to experience each and every day, and if having an understanding of which materials can bring you the aesthetic experience you're after in a more effective way- well, then this is a worthwhile discussion, right?
I think that it is.
Stay curious. Stay resourceful. Stay enthusiastic. Stay observant. Stay appreciative. Stay tinted...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
Heading to the bottom...Again!
Time to hit on another of my fave topics regarding botanical method aquariums; one that we've talked about before- yet one that is still new and exciting to many of us, and perhaps clouded at times with a lot of misinformation, too.
We're talking about botanically-supplemented substrates!
For far too long in the aquarium hobby, I think that we've treated aquairum substrates as simply an afterthought. I mean, there are all sorts of sands and gravels on the market today, but I think that we sort of take them for granted- or at the very least, we treat them as a "requirement" when setting up a tank, and move on to other, more "exciting stuff": "Sand added, check. Time to select the wood!"
That sort of thing.
One of the most "liberating" things we've seen in the botanical-method aquarium niche is our practice of utilizing the bottom itself to become a feature aesthetic point in our aquariums, as well as a functional mechanism for the inhabitants.

"Oh, shit, he's talking about that 'functional aesthetic' thing again!"
Yeah. Yes I am. 😎
Because I think that there are a lot of "missed opportunities" to do something cool with substrates in our tanks. Opportunities to make it a much more important part of the aquarium.
When you look at it from our rather biased perspective, and from a strictly aesthetic sense, the bottom itself becomes a big part of the aesthetic appeal of the aquarium. You may not focus on it, observationally, but it's hugely important. And of course, I see the bottom of the aquarium as more than just sand or whatever. Rather, it's a important component of the aquarium habitat, with the botanical materials placed upon or mixed into the substrate- or, in some cases, becoming the substrate!
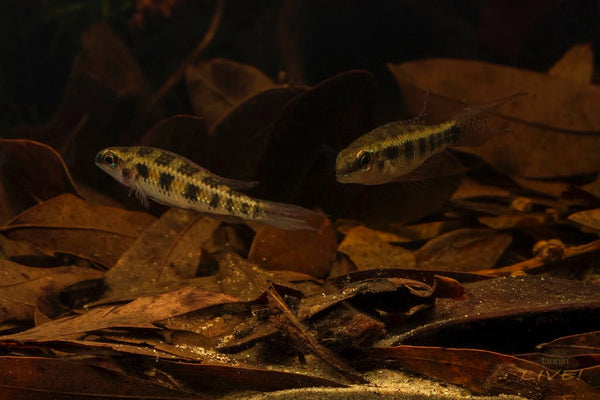

These materials form an attractive, texturally varied "microscape" of their own, creating color and interest. In addition to be being comprised of the usual sands and gravels, we can be adding bits of botanicals, root pieces, twigs, leaves, etc. into the mix.
Why?
Again, the focus isn't just on aesthetics.
It's about creating a habitat for the fauna which help "run" our tanks!
Much like in Nature, the materials that we place on the bottom of the aquarium will become an active, integral part of the ecosystem. From a "functional" standpoint, bottoms comprised of supplemented with a variety of botanical materials form a sort of "in-tank refugium", which allows small aquatic crustaceans, fungi, and other microorganisms to multiply and provide supplemental food for the aquarium, as we've touched on before.
So, the idea of creating rich, diverse botanical-influenced substrates for the purpose of infusing tannins, humic substances, and other compounds- as well as creating a "matrix" for the growth and propagation of beneficial micro and microfauna is pretty appealing to me.
Using a botanically-infused substrate to create a unique, ecologically diverse, functional, and aesthetically interesting affect on the aquarium- even one that doesn't have aquatic plants in it- is a sort of different approach.
Functionality. Interest. Aesthetics. Stability. They're all there!

Nature provides no shortage of features which can provide inspiration for unique aquariums.

Think about the materials which accumulate on and in the substrates of natural aquatic habitats, and why they accumulate in the first place. Well, typically, in addition to soils and leaves, you'll see sediments, pieces of plant roots, bits of twigs and bark, and the occasional seed pod. Almost all of this material arrives in these bodies of water from the surrounding terrestrial environment.
Some of it is present on forest floors, and when nearby streams overflow, inundating the once dry floor, these materials become part of the aquatic environment, influencing both the structure and the ecology of the habitat. Other materials, like sediments, are the product of hydrology and erosion- rocks ground down over eons by water; or soils- which find their way into streams during periods of intense rain, with the resulting material distributed over vast distances by current.
The beauty of Nature is that She uses pretty much everything that is thrown at Her. Fishes and other organisms feed directly upon some of this material, or on the other life forms (small crustaceans, insects, fungal growths) which live among it. The bottom of streams and other becomes a vibrant, ecologically diverse habitat, which supports a tremendous amount of life at many levels.
And we just throw bag of aquarium sand or gravel on the bottom of our tanks...and move on!
Shit. Really?
Like, WTF is a matter with us fish geeks? There is HUGE opportunity here! We need to give a lot more thought to what goes on the bottom of our aquariums! Instead of becoming a literal "placeholder" in our tanks, substrate should become the ecological "backbone"- and a (functionally aesthetic) foundation of our miniature aquatic ecosystems- just like it is in Nature!

Now, the first "pushback" we hear from critics of this type of approach in aquariums is that it will result in all sorts of problems- ranging from suppressed pH to high levels of nitrates, or even pockets of hydrogen sulfide and other nasty stuff accumulating.
I think that this is an incredible over-reaction and grounded in not fully thinking through why we are creating substrates like this in the first place.
In Nature, the leaf litter "community" of fishes, insects, fungi, and microorganisms is really important to the overall tropical environment, as it assimilates terrestrial material into the blackwater aquatic system (and, by doing this, acts to reduce the loss of nutrients to the forest which would inevitably occur if all the material which fell into the streams was washed downstream...)
The key point: These materials foster the development of life forms which process it. Stuff is being used by life forms.

It's the same in our aquariums.
And bits of botanical materials and such not only provide a physical substrate upon which these organisms can grow and multiply as they process it- they provide a sort of "on board nutrient processing center" within the aquarium.
If you approach this "substrate enrichment" idea holistically, rather than just from some warped aesthetic mindset, creating and managing such a system is not at all difficult or dangerous. In fact, you don't really need to give it all that much thought in a well-managed aquarium, once it's set up.
I realize that experimenting with these unusual substrates requires not only a sense of adventure, a direction, and some discipline- but a willingness to accept and deal with an entirely different aesthetic than what we know and love. And this also includes pushing into areas and ideas which might make us uncomfortable, not just for the way they look, but for what we are told might be possible risks.
One of the things that many hobbyists ponder when we contemplate creating deep, botanical-heavy substrates, consisting of leaves, sediment, bark, and other botanical materials is the "buildup of hydrogen sulfide", CO2, and other undesirable compounds within the substrate.

Well, sure, I can't entirely "diss" fellow hobbyists for having this fear. It does make sense that if you have a large amount of decomposing material in an aquarium, then some of these compounds are likely to accumulate in heavily-"active" substrates. The big "bogeyman" that we all seem to zero in on in our "sum of all fears" scenarios - the one which keyboard warriors on the forums will pounce on- is an accumulation of deadly hydrogen sulfide, which results from bacterial breakdown of organic matter in the total absence of oxygen.

Let's think about this for just a second.
In a botanical bed with materials placed on the substrate, or loosely mixed into the top layers, will it all really "pack down" enough to the point where there is a complete lack of oxygen and we develop a significant amount of this reviled compound in our tanks? Are we managing tanks in such a way as to encourage no circulation whatsoever?
I think that we're more likely to see some oxygen in this layer of materials, and in fact, I can't help but speculate- and it IS just speculation- that actual de-nitirifcation (nitrate reduction), which lowers nitrates while producing free nitrogen, might actually be able to occur in a "deep botanical" bed.
And it's certainly possible to have denitrification without dangerous hydrogen sulfide levels. As long as even very small amounts of oxygen and nitrates can penetrate into the substrate this will not become an issue for most systems. I have yet to see a botanical-method aquarium where the material has become so "compacted" as to appear to have no circulation whatsoever within the botanical layer.
Now, sure, I'm not a scientist, and I base this on close visual inspection of numerous aquariums, and the basic aquarium-standard chemical tests I've run on my systems under a variety of circumstances. As one who has made it a point to keep my botanical method aquariums in operations for very extended time frames, I think this is significant. The "bad" side effects we're talking about should manifest over these longer time frames...and they just haven't.
Yeah- in my experience, based on literally a lifetime of playing with all sorts of combinations of materials in dozens and dozens of my aquariums' substrates ('cause I've always been into that stuff!), I cannot attribute a single environmental lapse, let alone, a "tank crash", as a result of such additions.

A well-managed substrate, in which uneaten food and fish feces are not allowed to accumulate to excess, and in which regular nutrient export processes are embraced, rather than decimated by constant interference (ie; siphoning) it's not an issue, IMHO. When other good practices of aquarium husbandry (ie; not overcrowding, overfeeding, etc.) are empIoyed, a botanically-"enriched" substrate can enhance- not inhibit- the nutrient processing within your aquarium and help maintain high water quality for extended periods of time.
Like many of you, I have always been a firm believer in some forms of nutrient export being employed in every single tank I maintain. Typically, it's regular water exchanges. Not "when I think about it', or "periodically", mind you.
Nope, it's weekly.
Now look, I'm not saying that you can essentially disobey all the common sense husbandry practices we've come to know and love in the hobby (like not overcrowding/overfeeding, etc.) and just change the water weekly and everything's good. And I'm not suggesting that the only way to succeed with adding botanical materials to the substrate is to employ massive effort at nutrient export; the system otherwise teetering on a knife's edge, with disaster on one side and success on the other.
It's not that binary.
Our aquariums are more resilient than that. If we set them up to be. Common sense aquarium management, with an eye towards how natural aquatic systems work, is key, IMHO.
Of course, an aquarium is NOT a stream, river, etc. However, the same processes and "rules" imposed by Nature that govern the function of these wild ecosystems apply to our little glass and acrylic boxes. It's simply a matter of nuance in management and understanding how these wild habitats work on a basic level.
I'd love to keep us in the mindset of thinking about our aquariums as little "microcosms", not just "aquatic dioramas."
Think about this: The idea of a substrate "enriched" with botanical materials is completely in line with the practices of a "dirted" planted aquarium. In our case, not only will there be an abundance of material for microorganisms and crustaceans to forage and multiply among, trace elements and essential plant nutrients will also be present in such a substrate. And, of course there will be the constant addition of tannins and humic substances into the water, which provide many known benefits for fishes as well.
The best of both worlds, I think.
Again, it's not about creating a cool Instagram-ready "look."
It's about trying to create an entire aquatic ecosystem.

Embracing and fostering not just the look, but the very processes and functions which take place in natural aquatic systems. Is it as simple as crushing some leaves, adding some coconut-based material, covering it up with sand and you have an "instant tropical stream?" No, of course not. There is no such "magic bullet!" You need to look at things sort of "holistically"- with an eye towards nutrient export and long-term maintenance.
For those of you who are adventurous, experimental, diligent, and otherwise engaged with managing and observing your aquariums, I think this process offers amazing possibilities. Not only will you gain some fascinating insights and the benefits of "on-board" nutrient export/environmental "enrichment"- you will also get the aesthetics of a more natural-looking substrate as well. (Let's face it, no matter how "function first" we feel that we are, everyone likes a nice-looking aquarium, right?)

So, the best way to "enrich" (for want of a better term) your substrate is to add the botanical materials and sediments before you fill the tank up with water. In the case of leaves, bits of botanicals, etc., you'd want to have boiled/steeped them previously, so that they are rid of any surface contaminants, and to assure that their tissues are saturated enough to get them to sink immediately upon submersion.
There is no set "process" for this, other than to mix these materials into the upper layers of substrate as you add them. You will just sort of know when you've achieved the look and texture that pleases you (that's the "aesthetic" part!), and take comfort in knowing that just about any amount of these materials that you're adding to your system will help accomplish the "functional" aspect.
Once your substrate is in place, Nature takes over and the materials develop that lovely "patina" of fugal growth, biofilms and microbial colonization, and start breaking down. Some may be moved about by the grazing activities of resident fishes, or otherwise slowly redistributed around the aquarium.
A literal "active substrate", indeed! Yet, something that is fascinating and beautiful for those who give the idea a shot!
At this point, I have to admit that there are many hobbyists who will never find any sort of appeal whatsoever in a botanically-enriched substrate, dark and complex, filled with all sorts of "stuff" besides just sand. The so-called "Nature Aquarium" cult crowd, or the truly "artistic" aquascaping people, for example, will likely never approve of this idea, because it looks "dirty" to them, and because some of the aesthetic and management "work" is being "ceded" to Nature. They need to be in control.
I admit, the simple practice of adding "botanical stuff" into our aquariums is not some "high concept thing." However, the impacts on the water chemistry and overall aquatic environment- not to mention, on our fishes- are profound, fascinating, and real!
Being careful and taking the time to clean, prepare, and add botanicals to your aquarium in a measured manner always yields a better outcome. Going slowly also gives you the opportunity to address any issues that you might have before they become critical, especially when you're experimenting with some of these ideas.
It just makes sense to be patient. The rewards are so great.
From a maintenance standpoint, it's pretty straightforward. You monitor your environmental parameters regularly, and conduct routine water exchanges, taking care not to siphon aggressively from the substrate. You simply don't want to disrupt the very processes within the substrate that you're trying to foster. And trust me, your fishes will spend a lot of time foraging among it.

Much like what occurs spontaneously in Nature, the materials that we deliberately place on the bottom of the aquarium will become an active, integral part of the ecosystem.
Like so many things we discuss here, I admit that simply don't have all the answers about every aspect of botanically-supplemented substrates. There is a ton to learn! That's part of the joy of this process- sort of figuring out why and how it works as you're enjoying the success!
Playing with ideas like botanically supplemented substrates truly pushes the boundaries between what we do al the time in the hobby, and those outer regions where few have tread before. There will be challenges, discoveries..and rewards for taking this road less travelled.
And that's part of the fun, isn't it?
Stay creative. Stay brave. Stay curious. Stay diligent...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
Along the way.
Our approach to aquarium keeping is as much a "mindset" as it is a practice. And, although the practical techniques are relatively easy to grasp and execute, the philosophical components can be confusing and seem a bit contradictory at times.
We preach radical patience, yet completely embrace the idea of dramatically changing things within the greater "mindset."
Huh? Wtf?
Yeah, you should just do what feels right to you.
And sometimes, that means creating an aquarium which doesn't look anything like you'd want it to until long after it's been established. Other times, it means tearing stuff apart immediately and "re-directing" your tank based on a different vision.

Yet, I always urge you to take a slightly longer view of what''s going on in your tank. Not to rush to completely tear your aquarium apart just because it doesn't seem to be getting to where you want it to go right after you set it up.
Stuff takes time.
Looking back on some of my favorite tanks that I've executed in the past few years, it becomes increasingly obvious to me that these systems really didn't completely hit that "look and feel" that I want until long after they'd evolved naturally...however long that took. It seems that , in the botanical-method aquarium, stuff needs to acquire a "patina" of biofilm, a "stain" from the tannins, and decomposition of botanical materials needs to really begin before one of these systems turns "functional" as well.



That's part of why using aesthetics only as an evaluation criteria for a successful botanical-method aquairum falls a bit short, IMHO.
I mean, every new botanical-method tank likely looks cool to a broader swatch of the aquarium world from day one, if you're just using superficial aesthetics as your metric...But the long-established ones stand out for what they really are. After 4-6 months, that's when things get really special. After Nature has done a lot of the real "work" on the tank.
The decomposition of materials in water impacts our aesthetics greatly, as we all know by now. And that is what's so intriguing. The crisp leaves and dry, lifeless twigs that you submerge will evolve into a dynamic, ever-changing microcosm.
Every tank can get there.
Simply by exercisng patience, and letting your aquarium be.

I've long held that perhaps my fave botanical-method aquarium of all was the one I did about 3 years ago..an aquarium utilizing mangrove wood, extensive leaf litter, and catappa bark throughout. This is probably the only tank in recent years that I've truly regretted changing and moving on from! 😂
I knew what it was I wanted from the tank at the start, but it didn't look like much at first...It would have tested a lot of people's faith if they saw it in it's early stages! 
It literally looked like shit for the first couple of months of it's existence: Slightly tinted water, a contrived-looking "campfire-like" wood stack, bare sand, and mostly intact botanical materials. I had to do a bunch of "iterations" with the hardscape to get it where I wanted it. It looked quite "contrived" at points, but I knew instinctively that if I waited it out, let Nature do Her thing- that the potential was huge in this tank.
Sure enough, a few months in, biofilms started forming. The wood acquired that "patina" we talk about so much. Leaves and botanicals broke down...And the water took on perhaps the most earthy-looking, deeply mysterious color I've seen in a botanical-influenced blackwater aquarium.
By some standards, the water in the tank could be described as almost "turbid"- taking on an appearance as though there were fine materials in the water column. Yet, the tank had a real magical appearance with the lighting; the fishes were as colorful, relaxed and happy as any I've ever seen, and the water parameters were spot-on and consistent for as long as the tank was set up.
The essence of "wabi-sabi", for sure. Transience, the ephemeral aspects of our botanicals...the wonders of Nature, embraced.
It just took a little time.
I could have "intervened" at a number of junctures- trying to "circumvent" these aesthetic "deviations" while the tank was evolving. However, I knew not to. I knew that the long-term gains from letting this system evolve would far exceed any "relief" I'd gain from siphoning out the biofilms, removing decomposing leaves, and clearing the water.
And, as usual- Nature delivered...because I didn't get in Her way.
We've done this numerous times with similar results. Inauspicious starts.

Botanical-method aquariums typically require more time to evolve than more "conventional" aquariums do. They are dependent upon the development of a specialized ecology, which includes fostering organisms like fungal growths and biofilms.This process can be "expedited" or manipulated a bit, but to achieve truly meaningful and beneficial results, you just can't rush stuff!
You can't interrupt it, either.
When you do, as we've learned, results can be, well- "different" than they would be if you allow things to continue on at their own pace. Not necessarily always "bad"- just not as good as what's possible if you relax and let Nature run Her course without interruption. Following a plan is never a bad idea; it can lead to some exciting destinations.

However, the ability to "pivot" and "go with the flow" is really important, too.
It's not always a bad idea to switch things around if you're suddenly inspired to do so. What I hate to see is when hobbyists attempt to "intervene" on the processes which are occurring in the tank- like the recruitment of biofilms and fungal growths, the breakdown of leaves, etc. THAT'S a problem, imho. You can change the "overall theme" without irrevocably interrupting Nature's processes.
Yeah, there IS a certain kind of "intervention" which I occasionally embrace myself. As I've previously discussed here, on occasion, I'll start to execute on an idea I've had, and very early (or sometimes, not so early) in the process, I'll completely lose interest in it for whatever reason (it can be anything from "not feeling it!" to "I hate that I can't hide that heater!"), and the desire to abort and move on to something else on my "to do list" beckons.
In general, however, I play a really long game.
One which acknowledges that the fact that our botanical-method aquariums evolve over very long periods fo time, not reaching the state that we perhaps envisioned for many months. My actions reflect this mindset. Unless there is some major emergency, about the only thing that I might do is to add a few more botanicals, re-arrange some wood, or just wait it out.
Of course, if you really are "not feeling it" (it happens!), does it mean tearing the whole thing apart and starting over?

No!
You can change the "look" or aesthetic direction of an aquairum- fairly significantly- without disrupting its function.
One of the things I've done a lot in recent years when making big changes to aquariums is to keep the substrate layers from my existing tanks and "build on them." It makes a ton of sense, really. Why waste this goodness, just because the "theme" of the "new" tank is different than the existing one?
Your South American-themed tank won't be that much different if you change up the "hardscape" to turn it into s Southeast Asian-themed tank, while leaving the substrate layer intact, right?

In other words, I'm taking advantage of the well-established substrate layers, complete with their sediments, decomposing leaves and bits of botanicals, and simply building upon them with some additional substrate and leaves. I've done this many times over the years- and I'm sure a lot of you have, too-it's hardly a "game-changing" practice, but it's something not everyone talks about.
I believe that preserving and building upon an existing substrate layer provides not only some biological stability (ie; the nitrogen cycle), but it has the added benefit of maintaining some of the ecological diversity and richness created by the beneficial fuana and the materials present within the substrate.

I know many 'hobby old timers" might question the safety- or the merits-of this practice, mentioning things like "disturbing the bacterial activity" or "releasing toxic gasses", etc. A lot of 'em would rather have you simply remove this stuff altogether. It's "all or nothing" for them! I'm not sure how leaving the substrate layer intact is problematic. It doesn't "die." I believe that particular belief is steeped in "aquarium mythology", conflates a lot of different ideas and topics, and has generally been misapplied and misunderstood over the years.
I simply have never experienced any issues of this nature from this practice. Well maintained systems generally are robust and capable of evolving from such disturbances. And we're not really "disturbing" the substrate when we preserve it, are we? Moving around a few pieces of wood or rock might cloud the water a bit, but it's not wholesale disturbance of the substrate.
I see way more benefits to this practice than I do any potential issues.

Since I tend to manage the water quality of my aquariums well, if I say so myself, I have never had any issues, such as ammonia or nitrite spikes, by doing this- in fresh or saltwater systems. It's a logical way of maintaining stability and continuity- even in an arguably disruptive and destabilizing time!

This idea of a "perpetual substrate"- keeping the same substrate layer "going" in successive aquarium iterations- is just one of those things I believe that we can do to replicate Nature in an additional way.
Huh?
Well, think about it for just a second. In Nature, the substrate layer in rivers, streams, and yeah, flooded forests and pools tends to not completely wash away during wet/dry or seasonal cycles.
Oh sure, some of the material comprising the substrate layer may get carried away by currents or other weather dynamics, but for the most part, a good percentage of the material- and the life forms within it- remains when the water recedes. Wind and weather add additional materials to the now terrestrial environment, which become part of the aquatic habitat when the waters return.

So, by preserving the substrate from the previous iteration of your aquarium, and perhaps "refreshing" it a bit with some new materials (ie; sand, sediment, gravel, leaves, and botanicals), you're essentially mimicking some aspects of the way Nature functions in these wild habitats!
And, from an aquarium management perspective, consider the substrate layer a living organism (or "collective" of living organisms, as it were), and you're sure to look at things a bit differently next time you "re-do" a tank!


I suppose, one could view the process of "perpetuating" the substrate almost like persuing "eternal youth"- it's not entirely possible to achieve, but you can easily embrace the idea of renewal and continuity within your aquarium. It's a very natural process. Perhaps it's even beneficial in some way over the long term?
Things change in Nature, some things are utilized elsewhere, and other things are preserved in situ. Nothing goes to waste.

Rather, stuff gets "folded" into the changing ecosystem. Leaves on the forest floor become a lush ecological niche for fungal growth and bacteria, and a grazing substrate for fishes when submerged. Tree branches become "attachment points" for epiphytic plants, sponges, and other aquatic life forms.

Nature is very efficient. We should take a cue from Her! "Disruption" is often a form of renewal and evolution in Nature.
Patience, as always, is the key ingredient here. Of course, this is a hobby, and it should be fun...and you should feel free to change stuff up if it's not. However, make it a point to consider your actions in the "big picture", and it takes on a greater significance.
You need to have an understanding that you're creating a dynamic environment, not simply an "aquascape." And it's constantly evolving- even when you're not ripping it apart! It's anything but "static"-sort of like a planted aquarium, but in reverse (rather than plants growing, the botanicals are, for want of a better word "diminishing")! At any given time, you'll have materials like leaves in various states of decomposition, seed pods, slowly softening, breaking down, and recruiting biofilms and a "patina" of fungal growth.

It begs the most fundamental of questions about our botanical method practice:
What happens over time in a botanical method aquarium? What changes occur along the way?
Well, typically, at its simplest, as most of you who've played with this stuff know, the botanicals will begin to soften and break down. Botanical materials are the very definition of the word "ephemeral." Nothing lasts forever, and botanicals are no exception! Pretty much everything we utilize- from Guava leaves to oak twigs- starts to soften and break down over time.

Most of these materials should be viewed as"consumables"- meaning that you'll need to replace them over time if you want maintain some environmental consistency. Again, perfectly analogous to what occurs in Nature.
You're not an "aquascaper" in the classic hobby sense when you play with these types of systems. Rather, you're a a sort of "superintendent" to Nature, helping Her do what she has done for eons. You're not simply an idle "passenger," either- you play an active role in conceiving, setting up, and maintaining such a system. You need to take some cues from Nature, and that often means simply standing by and observing as she does Her work and goes through Her process.
You learn. You evolve with your aquarium, on a very real level.

Sometimes, it requires intervention on your part- at least in your own mind, perhaps. Other times, it simply involves sitting back, letting things unfold, and observing patiently.
Watching a display aquarium evolve and sort of "find itself" naturally over time is proving to be one of the most enjoyable discoveries I've made in the hobby in decades. It's a mindset that I actually had in my youth- by necessity, because I had very limited resources except for time- yet lost as I grew into adulthood and "evolved" in the hobby. With more skills and economic resources, I could "do more"- but the reality is that it wasn't always the right thing.
It took me a few decades after hitting so-called "advanced" hobbyist status before it really hit me that, by simply studying the function of natural ecosystems, all of the answers I needed to be successful as an aquarist were right there! I just needed to figure out which questions to ask.
I'm still deep in that process, decades later!

By understanding that my aquariums are governed by the same "laws" which apply to natural aquatic ecosystems, and developing and following simple practices and husbandry routines to embrace this, and monitoring what's occurring in the tank (as opposed to constantly trying to intervene to "pre-empt" what we in the hobby have commonly perceived to be problems), I've personally had more beautiful, healthy and stable aquariums, and...more success than ever before.

Accepting that there is most definitely an elegant, yet complex ecological "dance" in our aquariums, and becoming an "active monitor" instead of an "active intervener" has added an enjoyable and rewarding aspect to my love of the hobby.
I think that this approach to the "dance" not only makes you a more engaged hobbyist, it gives you a remarkable appreciation for the long term evolution of an aquarium; an appreciation for the pace by which Nature operates, and the direction in which your aquarium ultimately goes.

By doing this, you get the enjoyment of seeing the "evolution" every day! Observing and enjoying the subtle nuances of your aquarium at every stage of its existence. With my "go slow" mindset and practice, the differences are subtle in the short term- the "payoffs" really more apparent over the longer term.
Again, it's okay to make changes- even significant ones- to the "theme" of your aquarium. However, it's simply not good practice to interfere with the processes which allow it to become what Nature ( and YOU, too, if you're honest with yourself) wants it to become.
I know, it does feel a bit "yin" and "yang"- like I'm pulling from both sides- telling you, on one hand, that it's okay to make significant changes to a tank, while simultaneously urging you to deploy extreme patience and an almost "sit back and relax" approach...These seemingly diametrically opposite actions actually work really well together when you have the "common denominator" of good intentions, vision, careful actions, and an appreciation for what Nature can do if we let Her.

This philosophy, like so many things I ask you to consider here- doesn't always seem to make any sense.
Until it does.
Be kind to yourself- and to Nature.
Trust that She'll guide your aquarium effectively along the way to its ultimate potential. She won't let you down. Even if you take a slight detour now and again.
Stay confident. Stay observant. Stay curious. Stay patient....
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
For the love of weird substrates...
One of the "cornerstones" of our botanical-method aquarium practice is the use of substrate. Specifically, substrate materials which can influence- or make it easier to influence- water chemistry in the aquarium, as well as to help foster a "microbiome" of small organisms which will provide ecological diversity for the system.
Substrates, IMHO, are one of the most often-overlooked components of the aquarium. We tend to just add a bag of "_____________" to our tanks and move on to the "more exciting" stuff like rocks and "designer" wood. It's true! Other than planted aquarium enthusiasts, the vast majority of hobbyists seem to have little more than a passing interest in creating and managing a specialized substrate or associated ecology.

A real pity, especially for those of us who are interested in botanical-method aquariums, which replicate natural aquatic habitats where soils and geology play a HUGE role in influencing the environmental parameters of these ecosystems. And in the hobby, we've largely overlooked the benefits and possibilities which specialized substrates can offer.
So I started to experiment with materials to recreate some of the characteristics of wild aquatic habitats which fascinated me. And an obsession was born.
I started playing with substrates mainly because I couldn't find exactly what I was looking for on the market. This is not some indictment of the major substrate manufacturers out there...I LOVE almost all of them and use and happily recommend ones that I like. I'm obsessed with substrates. I think that the companies which produce them are among the coolest of the cool aquatics industry brands. If I wasn't doing this botanical thing with Tannin, I'd probably have started a company that specializes in substrates for aquariums. Seriously.
And the fact is, the major manufacturers need to market products that more than like 8 people are interested in. It's unreasonable to think that they'd devote precious resources to creating a product that would be geared to such a tiny target.
And of course, being one of those 8 people who are geeked-out about weird substrates, I decided that I'd "scratch my own itch" (as we did with the botanical thing..) and formulate and create some of my own. Thus, the NatureBase product line was born!
I realized that the specialized world which we operate in embraces some different ideas, unusual aesthetics, and is fascinated by the function of the environments we strive to replicate. These are important distinctions between what we are doing with substrates at Tannin, and what the rest of the aquarium hobby is doing.

Our NatureBase line is not intended to supersede or completely replace the more commonly available products out there as your "standard" aquarium substrate, because: a) they're more expensive, b) they're not specifically "aesthetic enhancements", c) they are not intended to be planted aquarium substrates, and d) because of their composition, they'll add some turbidity and tint to the aquarium water, at least initially (not everyone could handle THAT!)

So, right there, those factors have significantly segmented our target market...I mean, we're not trying to be the aquarium world's "standard substrate", they weren't formatted to grow aquatic plants, we're not marketing them just for the cool looks, and we can't emphasize enough that they will make your water a bit turbid when first submerged. If you have fishes which dig, or which like to "work" the substrate, you may see a near-continuous turbidity in your aquarium!
Oh, joy.
Those factors alone will take us out of contention for large segments of the market!

This is important to grasp.
I mean, these substrates are intended to be used in more natural, botanical-style/biotope-inspired aquariums. Our first two releases, "Igapo" and "Varzea", are specific to the creation of a type of "cyclical" terrestrial/aquatic feature. They do exactly what I wanted them to do, and they were specifically intended for use in specialized set ups, like the "Urban Igapo" idea we've been talking about for a long time here, as well as brackish water mangrove environments, etc.
Let's touch on the "aesthetic" part for a minute.
Most of our NatureBase substrates have a significant percentage of clays and sediments in their formulations. These materials have typically been something that aquarists have avoided, because they will cloud the water for a while, and often impart a bit of color. We also have some botanical components in a few of our substrates, because they are intended to be "terrestrial" substrates for a while before being flooded...and when this stuff is first wetted, some of it will float.
And that means that you're going to have to net it out, or let your filter take it out. You simply won't have that "issue" with your typical bag of aquarium sand!
Shit, you're probably just frothing right now, waiting to cloud and dirty up your aquariums with this stuff, huh?

No?
I can't for the life of me figure out why not? ;)
Remember, some of these substrates were formulated for a very specific purpose: To replicate the terrestrial soils which are seasonally inundated in the wild. As such, these products simply won't look or act like your typical aquarium substrate materials!
Scared off completely yet? I hope not.
Why include sediments and clays in our mixes?
Well, for one thing, sediments are an integral part of the natural substrates in the habitats from which our fishes come. So, they're integral to our line. In fact, I suppose you'd best classify NatureBase products as "sedimented substrates."

Think about this: Many of our favorite habitats are forest floors and meadows which undergo periodic flooding cycles in the Amazon, which results in the creation of aquatic habitats for a remarkable diversity of fish species.

Depending on the type of water that flows from the surrounding rivers, the characteristics of the flooded areas may vary. Another important impact is the geology of the substrates over which the rivers and streams pass. This results in differences in the physical-chemical properties of the water.
In the Amazon, areas flooded by rivers of black or clear waters, with acid pH and low sediment load, in addition to being nutritionally poor, are called “igapó."

The flooding often lasts for several weeks or even several months, and the plants and trees need special biochemical adaptations to be able to survive the lack of oxygen around their roots. We've talked about this a lot here over the years.

Forest floor soils in tropical areas are known by soil geologists as "oxisols", and have varying amounts of clay, sediments, minerals like quartz and silica, and various types of organic matter. So it makes sense that when flooded, these "ingredients" will have significant impact on the aquatic environment. This "recipe" is not only compositionally different than typical "off-the-shelf" aquarium sands and substrates- it looks and functions differently, too.
YOU DON'T RINSE THEM BEFORE USE!
You CAN wet them right away; you don't have to do a "wet/dry season" igapo-style tank with them. However, you should be ready for some cloudy water for a week or more! And again, if you have fishes which like to "work" the substrate, it will be a near-constant thing, the degree to which it will be is based on the habits of the fishes you keep.

And that's where a lot of people will metaphorically "leave the room."Turbid, darker water is a guaranteed "freak out" for a super-high high percentage of aquarists.
So, yeah, you'll have to make a mental shift to appreciate a different look and function.
And many hobbyists simply can't handle that. I've been extremely up front with this stuff since the introduction of these substrates, to ward off the, "I added NatureBase to my tank and it looks like a cloudy mess! This stuff is SHIT!" type of emails that inevitably come when people don't read up first before they purchase the stuff. (And trust me- the fact that you're even reading this blog, or listening to this podcast puts you in the tiniest minority of aquarium hobbyists!)

Let's talk a bit about how to "live" with these substrates.
There are a lot of different ways to use these substrates in all sorts of tanks. I mean, if you want some of the benefits and want to geek out and experiment with them, you can use a "sand cap" of whatever conventional substrate you prefer on top, and likely limit the turbidity somewhat, much like the practice of aquarists who employ "dirted" substrates do.
Oh, and the plant thing...
We're asked a LOT if these substrates can grow aquatic plants. Now, although they were intended to facilitate the growth of terrestrial plants, like grasses, the fact is, both our customers and ourselves have seen pretty damn good plant growth in tanks using this stuff!

Our Igapo and Varzea substrates mimic sandy acidic soils that have a low nutrient content. And, as you know, the color and acidity of the floodwater is due to the acidic organic humic substances (tannins) that dissolve into it. The acidity from the water translates into acidic soils, which makes sense, right?
Now, I admit, I am NOT a geologist, and I'm not expert in soil science. I know enough to realize that, in order to replicate the types of habitats I am fascinated with, it required different materials. If you ask me, "Will this fish do well with this materials?" or, "Can I grow "Cryptocoryne in this?", or "Does this make a good substrate for shrimp tanks?" I likely won't have a perfect answer. Sorry.
Periodically, plant enthusiasts will ask me about the "cation exchange capacity" of our substrate. Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC) is the ability of a material to absorb positively-charged nutrient ions. This means the substrate will hold nutrients and make them available for the plant roots, and therefore, plant growth. CEC measures the amount of nutrients, more specifically, positivity changed ions, which a substrate can hold onto/store for future use by aquatic plants.

Thus, a "high CEC" is important to many aquatic plant enthusiasts in their work. While it means that the substrate will hold nutrients and make them available for the plant roots. it doesn't indicate the amount of nutrients the substrate contains.
For reference, scientists measure cation exchange capacity (CEC) in milliequivalents per 100 grams ( meq/100g).
To really get "down and dirty" to analyze substrates scientifically, CEC determinations are often done by a process called "Method 9081A of EPA SW- 846." What the....? CEC extractions are often also analyzed on ICP-OES systems. A rather difficult and pretty expensive process, with equipment and methods that are not something casual hobbyists can easily replicate!
As you might suspect, CEC varies widely among different materials. Sand, for instance, has a CEC less than 1 meq/100 g. Clays tend to be over 30 meq/100 g. Stuff like natural zeolites are around 100 meq/100g! Soils and humus may have CEC up to 250 meq/100g- that's pretty serious!
What nutrients are we talking about here? The most common ones which come into play in the context of CEC are iron, potassium, calcium and magnesium. So, if you're into aquatic plants, high CEC is a good thing!
Of course, this is where the questions arise around the substrates we play with.
It makes sense, right?

Our "Nature Base" substrates do contain materials such as clays and silts, which could arguably be considered "higher CEC" materials, because they're really fine- and because higher surface area generally results in a higher CEC. The more surface area there is, the more potential bonding sites there are for the exchange to take place. Alas, nothing is ever exactly what we hope it should be in this hobby, and clays are often not all that high in their CEC "ratings."
Now, the "Nature Base" substrates are what we like to call “sedimented substrates”, because they are not just sand, or pellets of fired clays, etc. They are a mix of materials, and DO also have some terrestrial soils in the mix, too, which are also likely higher in CEC. And no, we haven't done CEC testing with our substrates...It's likely that in the future, some enthusiastic and curious scientist/hobbyist might just do that, of course!
Promising, from a CEC standpoint, I suppose!
However, again, I must emphasize that they were really created to replicate the substrate materials found in the igapo and varzea habitats of South America, and the overall habitat- more "holistically conceived"-not specifically for plant growth. And, in terrestrial environments like the seasonally-inundated igapo and varzea, nutrients are often lost to volatilization, leaching, erosion, and runoff..

So, it's important for me to make it clear again that these substrates are more representative of a terrestrial soil. Interestingly, the decomposition of detritus and leaves and such in our botanical-method aquariums and "Urban Igapo" displays is likely an even larger source of “stored” nutrients than the CEC of the substrate itself, IMHO. Thus, they will provide a home for beneficial bacteria- breaking down organics and helping to make them more available for plant growth.
Perhaps that's why aquatic plants grow so well in botanical-method aquariums?

Yeah, the stuff DOES grow aquatic and riparian plants and grasses quite well, in our experience! Yet, again- I would not refer to them specifically as "aquatic plant substrates." They're not being released to challenge or replace the well-established aquatic plant soils out there. They're not even intended to be compared to them!

Remember, our "Igapo" and "Varzea" substrates are intended to start out life as "terrestrial" materials, gradually being inundated as we bring on the "wet season." And because of the clay and sediment content of these substrates, you'll see some turbidity or cloudiness in the water. It won't immediately be crystal-clear- just like in Nature. That won't excite a typically planted aquarium lover, for sure.

I can't stress it often enough: With our emphasis on the "wholistic" application of our substrate, our focus is on the "big picture" of these closed aquatic ecosystems.
I'll be the first to tell you that, while I have experimented with many species of plants, inverts, and fishes with these substrates, I can't tell you that every single fish or plant will like them. You'll simply have to experiment!
Well, shit- that's not something that you typically hear an aquarium hobby brand tell you to do with their products every day, huh? Like, I'm not going to make all sorts of generalized statements about everything I think that these products can do. It would be very unhelpful. I'd rather focus on how they perform in the types of systems in which they were intended to work in, and what the possible downsides could be!

The whole point here is that these substrates are perfect for a whole range of applications. They're not "the greatest substrates ever made!" or anything like that. However, they are super useful for replicating the soils of some of our favorite aquatic habitats.
And for doing some of those geeky experiments that we love so much. So, that pretty much covers the "sedimented" substrate thing for now. Let's talk about "alternative" substrates for a bit...
PT.2 : "ALTERNATIVE SUBSTRATES" AND THE "DANGERS" FROM WITHIN?
In my experience, and in the reported experiences from hundreds of aquarists who play with botanical materials breaking down in and on their aquariums' substrates, undetectable nitrate and phosphate levels are typical for this kind of system. When combined with good overall husbandry, it makes for incredibly stable systems.
I've been thinking through further refinements of the "deep botanical bed"/sand substrate relationship. I've been spending a lot of time researching natural aquatic systems and contemplating how we can translate some of this stuff into our closed system aquaria.

Now, I realize, when contemplating really deep aggregations of substrate materials in the aquarium, that we're dealing with closed systems, and the dynamics which affect them are way different than those in Nature, for the most part.

And I realize that experimenting with these unusual approaches to substrates requires not only a sense of adventure, a direction, and some discipline- but a willingness to accept and deal with an entirely different aesthetic than what we know and love. And this also includes pushing into areas and ideas which might make us uncomfortable, not just for the way they look, but for what we are told might be possible risks.
One of the things that many hobbyists ponder when we contemplate creating deep, botanical-heavy substrates, consisting of leaves, sand, and other botanical materials is the possible buildup of hydrogen sulfide, CO2, and other undesirable compounds within the substrate.

Well, it does make sense that if you have a large amount of decomposing material in an aquarium, that some of these compounds are going to accumulate in heavily-"active" substrates. Now, the big "bogeyman" that we all seem to zero in on in our "sum of all fears" scenarios is hydrogen sulfide, which results from bacterial breakdown of organic matter in the total absence of oxygen.

Let's think about this for just a second.
In a botanical bed with materials placed on the substrate, or loosely mixed into the top layers, will it all "pack down" enough to the point where there is a complete lack of oxygen and we develop a significant amount of this reviled compound in our tanks? I just don't think so. I think that we're more likely to see some oxygen in this layer of materials, and I can't help but speculate- and yeah, it IS just speculation- that actual de-nitirifcation (nitrate reduction), which lowers nitrates while producing free nitrogen, might actually be able to occur in a "(deep) botanical" bed.
And it's certainly possible to have denitrification without dangerous hydrogen sulfide levels. As long as even very small amounts of oxygen and nitrates can penetrate into the substrate, this will not become an issue for most systems. I personally have yet to see a botanical-method aquarium where the material has become so "compacted" as to appear to have no circulation whatsoever within the botanical layer.
Now, sure, I'm not a scientist, and I base this on the management of, and close visual inspection of numerous aquariums, as well as the basic chemical tests I've run on my systems under a variety of circumstances. As one who has made it a point to keep my botanical-method aquariums in operation for very extended time frames, I think this is significant. The "bad" side effects we're talking about should manifest over these longer time frames...and they just haven't.

And then there's the question of nitrate.
Although not the terror that ammonia and nitrite are known to be, nitrate accumulation is something a lot of hobbyists are concerned with. As nitrate accumulates, fish will eventually suffer some health issues. Ideally, we strive to keep our nitrate levels no higher than 5-10ppm in our aquariums.
As a reef aquarist, I was always of the "...keep it as close to zero as possible." mindset, until I realized that corals just grow better with the presence of some nitrate! This was especially evident in my large scale coral grow-out raceways.

It seems that 'zero" nitrate is not always the most realistic or achievable target in a heavily-botanical-laden aquarium, although I routinely see undetectable nitrate reading in my tanks. You have a bit more "wiggle room", IMHO, however, before concern over fish health is a factor. Now, when you start creeping towards 50ppm, you're getting closer towards a number that should alert you.
It's not a big "stretch" from 50ppm to more potentially detrimental readings of 75ppm and higher...
And then you get towards the range where health issues could manifest themselves in your fishes. Now, many fishes will not show any symptoms of nitrate poisoning until the nitrate level reaches 100 ppm or more. However, studies have shown that long-term exposure to moderate concentrations of nitrate stresses fishes, making them more susceptible to disease, affecting their growth rates, and inhibiting spawning in many species.
At those really high nitrate levels, fishes will become noticeably lethargic, and may have other health issues that are obvious upon visual inspection, such as open sores or reddish patches on their skin. And then, you'd have those "mysterious deaths" and the sudden death (essentially from shock) of newly-added fishes to the aquarium, because they're not acclimated to the higher nitrate concentrations.
Okay, that's scary stuff. However, high nitrate concentrations are not only manageable- they're something that's completely avoidable in our aquairums.

Quite honestly, even in the most heavily-botanical-laden systems I've played with, I have personally never seen a higher nitrate reading than around 5ppm. Often, as I mentioned above, they're undetectibIe on hobby-level test kits. I attribute this to common sense stuff: Good quality source water (RO/DI), careful stocking, feeding, good circulation, not disturbing the substrate, and consistent basic aquarium husbandry practices (water exchanges, filter maintenance, etc.).
Now, that's just me.
I'm no scientist, certainly not a chemist, but I have a basic understanding of maintaining a healthy nitrogen cycle in the aquarium. And I am habitual-perhaps even obsessive- about consistent maintenance. Water exchanges are not a "when I get around to it" thing in my aquarium management "playbook"- they're "baked in" to my practice.

So yeah, although nitrate is something to be aware of in botanical-method aquariums, it's simply not an ominous cloud hanging over our success.
Relatively shallow sand or substrate beds seem to be optimal for denitrification, and many of us employ them for the aesthetics as well. Light "stirring" of the top layers, if you're concerned about any potential "dead spots" is something that is permissible, IMHO. Any debris stirred up can easily be removed mechanically by filtration, as mentioned above.
But that's it.

Of course, as we already discussed, you don't have to go crazy siphoning the shit (literally!) out of your sand every week, essentially decimating populations of beneficial microscopic infauna -or interfering with their function- in the process.
What I am starting to feel more and more confident about is postulating that some form of denitrification occurs in a system with a layer of leaves and botanicals as a major component of the tank.
Now, I know, I have little rigorous scientific information to back up my theory, other than anecdotal observations and even some assumptions. However, there is always an example to look at- Nature.
Of course, Nature and aquariums differ, one being a closed system and the other being "open." However, they both are beholden to the same laws, aren't they? And I believe that the function of the captive leaf litter bed and the wild litter beds are remarkably similar to a great extent.

The thing that fascinates me is that, in Nature, leaf litter beds perform a similar function; that is, fostering biodiversity, nutrient export, and yes- denitrification. Let's take a little look at a some information I gleaned from the study of a natural leaf litter bed for some insights.
In a slow-flowing wild Amazonian stream with a very deep leaf litter bed, observations were made which are of some interest to us. First off, oxygen saturation was 6.7 3 mg/L (about 85% of saturation), conductivity was 13.8 microsemions, and pH was 3.5.

Some of these parameters (specifically the very low pH) are likely difficult to obtain and maintain in the aquarium, but the interesting thing is that these parameters were stable throughout a months-long investigation.
Oxygen saturation was surpassingly low, given the fact that there was some water movement and turbulence when the study was conducted. The researchers postulated that the reduction in oxygen saturation presumably reflects respiratory consumption by the organisms residing in the litter, as well as low photosynthetic generation (which makes sense, because there is no real algae or plant growth in the litter beds).
And of course, such numbers are consistent with the presence of a lot of life in the litter beds.

Microscopic investigation confirmed that the leaf litter was heavily populated with fungi and other microfauna. There was also a significant amount of fish life. Interestingly, the fish population was largely found in the top 12"/30cm of the litter bed, which was estimated to be about 18"/45cm deep. The food web in this type of habitat is comprised largely of fungal and bacterial growth which occurs in the decomposing leaf litter.
Okay, I"m throwing a lot of information here, and doing what I hope is a slightly better-than-mediocre attempt at tying it all together. The principal assertions I'm making are that, in the wild, the leaf litter bed is a very productive place, and has a significant impact on its surroundings, and that it's increasingly obvious to me that many of the same functions occur in an aquarium utilizing leaf litter and botanicals.

"Enriching" a substrate with botanicals, or composing an entire substrate of botanicals and leaves is a very interesting and compelling subject for investigation by hobbyists.
So, three areas of potential investigation for us:
*Use of botanicals and leaves to comprise a "bed" for bacterial growth and denitrification.
*Understanding the chemical/physical impact of the botanical "bed" on an aquarium. (ie, pH, conductivity, etc.)
*Utilization of a botanical bed to create a supplemental food source for the resident fishes.
We've also touched on the idea of a leaf litter/botanical bed as "nursery" for fry, something more and more hobbyists/breeders are confirming is a logical "go-to" thing for them.
Interesting semi-anecdotal observations from my friends in the know suggest that the biofilms for decaying leaves form a valuable secondary food for the fry of fishes such as Discus, Uaru, (after they’re done feeding on their parent’s exuded slime coat) and even Loricariid catfishes. And I've seen juvenile fishes of a variety of species "appear" from my botanical-rich aquariums over the years, fat and happy, apparently deriving some nutrition from the fungi, bacteria, and small crustaceans which live in, on, and among the leaf litter bed.

My own experience with creating leaf-litter-bed-focused aquariums has proven that supplemental food production for the resident fishes is a real "thing" that we need to consider. It's a valid and very exciting approach to creating a functional closed aquatic ecosystem.

We talk about the concept of "substrate enhancement" or "enrichment" a lot in the context of aquatic botanicals (we tend to use the two terms interchangeably).
Again, we're not talking about "enrichment" in the same context as say, planted aquarium guys, with materials put into the substrate specifically for the benefit of plants. However, the addition of botanical and other materials CAN create a sort of organic "mulch" which benefits many aquatic plants!

Rather, "enrichment" in our context refers to the addition of botanical materials for creating a more natural-appearing, natural-functioning substrate- one which provides a haven for microbial life, as well as for small crustaceans, biofilms, and even algae, to serve as a foraging area for our fishes and invertebrates.
We've found over the years of playing with botanical materials that substrates can be really dynamic places, and benefit from the addition of leaves and other materials. For many years, substrates in aquarium were really just sands and gravels. With the popularity of planted aquariums, new materials, like soils and mineral additives, entered into the fray.
With the botanical-method aquarium starting to gain in popularity, now you're seeing all sorts of materials added on and in the substrate...for different reasons of course.
I think the big takeaway is that we should not be afraid to experiment with the idea of mixing various botanical materials into our substrates, particularly if we continue to embrace solid aquarium husbandry practices.
In my opinion, richer, botanically-enhanced substrate provides greater biological diversity and stability for the closed system aquarium.
Is it for everyone?
Not for those not willing to experiment and be diligent about monitoring and maintaining water quality. Not for those who are superficially interested, or just in it for the unique aesthetics it affords.
However, for those of you who are adventurous, experimental, diligent, and otherwise engaged with managing and observing your aquariums, I think it offers amazing possibilities. Not only will you gain some fascinating insights and the benefits of "on-board" nutrient export/environmental "enrichment"- you will also get the aesthetics of a more natural-looking substrate as well.

Like so many things we do in our niche, the "weird" alternative and botanical-enriched substrate approaches are fascinating, dynamic, and potentially ground-breaking for the aquarium hobby. For the adventurous, diligent, and observant aquarist, they present numerous opportunities to learn, explore, and create amazing, function-first aquatic ecosystems.
Who's in?
Stay creative. Stay observant. Stay diligent. Stay thoughtful...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
Anything goes? Well, sort of...
The garden suggests there might be a place where we can meet Nature halfway."-Michael Pollan
It's long been suggested that an aquarium is sort of like a garden, right? And, to a certain extent it is. Of course, we can also allow our tanks to evolve on a more-or-less "random" path than the word "garden" implies...

Perhaps one of the most liberating things about our botanical-method aquariums is that there is no set "style" that you have to follow to "arrange" botanical materials in your tank.
When you look at those amazing pictures of the natural habitats we love so much, you're literally bombarded with the "imperfection" and apparent randomness that is Nature. Yet, in all of the "clutter" of an igarape flooded forest, for example, there is a quiet elegance to it. There is a sense that everything is there for a reason- and not simply because it looks good. It IS perfect. Can't we bring this sense to our aquariums?
I think we can...simply by meeting Nature halfway.

To a certain extent, it's "anything goes" in terms of adding materials to represent the wild habitats. I mean, when you think about flooded forest floors and rainforest streams, you're talking about an aggregation of material from the forest that has accumulated via wind, rain, and current. The influences on the "design" are things like how something arrives into the water, and how it gets distributed by water movement.
Nature offers no "style guide."
Rather, she offers clues, based on her processes.
I mean, sure, you could and should certainly use some aesthetic thought in the concept, but when you're trying to recreate what in Nature is a more-or-less random thing, you probably don't want to dwell too much on the concept! You don't want to over-think "random" too much, right? Rather, put your effort into selecting suitable materials with which to do the job.

For a bit more context, just think for just a second, about the stems and branches that we love so much in our aquascaping. Those of us who obsessively study images of the wild tropical habitats we love so much can't help but note that many of the bodies of water which we model our aquariums after are filled with tree branches and stems.
Since many of these habitats are rather ephemeral in nature, they are only filled up with water part of the year. The remainder of the time, they're essentially dry forest floors.

And what accumulates on dry forest floors?
Branches, stems, leaves, and other materials from trees and shrubs. When the waters return, these formerly terrestrial materials become an integral part of the (now) aquatic environment. This is a really, really important thing to think of when we aquascape or contemplate how we will use botanical materials like the aforementioned stems and branches.
They impact both function and aesthetics of an aquarium...Yes, what we call "functional aesthetics" rears its head again!

There is no real rhyme or reason as to why stuff orients itself the way it does once submerged. There are numerous random factors involved.
I mean, branches fall off the trees, a process initiated by either rain or wind, and just land "wherever." Which means that we as hobbyists would be perfectly okay just literally tossing materials in and walking away! Now, I know this is actually aquascaping heresy- Not one serious 'scaper would ever do that...right?
On the other hand, I'm not so sure why they wouldn't!
I mean, what's wrong with sort of randomly scattering stems, twigs, and branches in your aquascape? It's a near-perfect replication of what happens in Nature. Now, I realize that a glass or acrylic box of water is NOT nature, and there are things like "scale" and "ratio" and all of that shit that hardcore 'scapers will hit you over the head with...
But Nature doesn't give a fuck about some competition's "rules"- and Nature is pretty damn inspiring, right? There is a beauty in the brutal reality of randomness. I mean, sure, the position of stones in an "Iwagumi" is beautiful...but it's hardly what I'd describe as "natural."
Natural looks...well, like what you'd see in Nature.

It's pretty hardcore stuff.
And it's all part of the reason that I spend so damn much time pleading with you- my fellow fish geeks- to study, admire, and ultimately replicate natural aquatic habitats as much as you do the big aquascaping contest winners' works. In fact, if every hobbyist spent just a little time studying some of these unique natural habitats and using them as the basis of their work, I think the hobby would be radically different.
When hobbyists interpret what they see in wild aquatic habitats stats more literally, the results are almost always stunning. And contest judges are starting to take notice...

I think that there would also be hobby success on a different level with a variety of fishes that are perhaps considered elusive and challenging to keep. Success based on providing them with the conditions which they evolved to live in over the millennia, not a "forced fit" its what works for us humans.
More awareness of both the function and the aesthetics of fascinating ecological niches, such as the aforementioned flooded forests, would drive the acceptance and appreciation of Nature as it is- not as we like to "edit" and "sanitize" it.
Taking this approach is actually a "stimulus" for creativity, perhaps in ways that many aquarists have not thought of.
There are a lot of aquatic habitats in Nature which are filled with tangles of terrestrial plant roots, emergent vegetation, fallen branches, etc., which fill small bodies of water almost completely.

These types of habitats are unique; they attract a large populations of smaller fishes to the protection of their vast matrix of structures. Submerged fallen tree branches or roots of marginal terrestrial plants provide a large surface area upon which algae, biofilm, and fungal growth occurs. This, in turn, attracts higher life forms, like crustaceans and aquatic insects. Sort of the freshwater version of a reef, from a "functionality" standpoint, right?
Can't we replicate such aquatic features in the aquarium?
Of course we can!
This idea is a fantastic expression of "functional aesthetics." It's a "package" that is a bit different than the way we would normally present an aquarium. Because we as hobbyists hesitate to densely pack an aquarium like this, don't we?
Why do you think this is?
I think that we hesitate, because- quite frankly- having a large mass of tangled branches or roots and their associated leaves and detritus in the cozy confines of an aquarium tends to limit the number, size, and swimming area of fishes, right? Or, because its felt that, from an artistic design perspective, something doesn't "jibe" about it...

Sure, it does limit the amount of open space in an aquarium, which has some tradeoffs associated with it.
On the other hand, I think that there is something oddly compelling, intricate, and just beautiful about complex, spatially "full" aquatic features. Though seldom seen in aquarium work, there is a reason to replicate these systems. And when you take into account that these are actually very realistic, entirely functional representations of certain natural habitats and ecological niches, it becomes all the more interesting!

What can you expect when you execute something like this in the aquarium?
Well, for on thing, it WILL take up a fair amount of space within the tank. Of course. Depending upon the type of materials that you use (driftwood, roots. twigs, or branches), you will, of course, displace varying amounts of water.
Flow patterns within the aquarium will be affected, as will be the areas where leaves, detritus and other botanical materials settle out. You'll need to understand that the aquarium will not only appear different- it'll function differently as well. Yet, the results that you'll achieve- the more natural behaviors of your fishes, their less stressful existence- will provide benefits that you might not have even realized possible before.
This is something which we simply cannot bring up often enough. It's transformational in our aquarium thinking.
The "recruitment" of organisms (algae, biofilms, epiphytic plants, etc.) in, on, and among the matrix of wood/root structures we create, and the "integration" of the wood into other "soft components" of the aquascape- leaves and botanicals is something which occurs in Nature as well as in the aquairum.
This is an area that has been worked on by hobbyists rather infrequently over the years- mainly by biotope-lovers. However, embracing the "mental shifts" we've talked about so much here- allowing the growth of beneficial biocover, decomposition, tinted water, etc.- is, in our opinion, the "portal" to unlocking the many secrets of Nature in the aquarium.

The extraordinary amount of vibrance associated with the natural growth on wood underwater is an astounding revelation. However, our aesthetic sensibilities in the hobby have typically leaned towards a more "sterile", almost "antispetic" interpretation of Nature, eschewing algae, biofilm, etc.
However, a growing number of hobbyists worldwide have began to recognize the aesthetic and functional beauty of these natural occurances, and the realism and I think that the intricate beauty of Nature is starting to eat away at the old "sterile aquascape" mindset just a bit!

And before you naysayers scoff and assert that the emerging "botanical method" aquarium is simply an "excuse for laziness", as one detractor communicated to me not too long ago, I encourage you once again to look at Nature and see what the world underwater really looks like. There is a reason for the diversity, apparent "randomness", and success of the life forms in these bodies of water.
What is it?

It's that these materials are being utilized- by an enormous community of organisms- for shelter, food, and reproduction. Seeing the "work" of these organisms, transforming pristine" wood and crisp leaves into softening, gradually decomposing material, is evidence of the processes of life.

When you accept that seed pods, leaves, and other botanical materials are somewhat ephemeral in nature, and begin to soften, change shape, accrue biofilms and even a patina of algae- the idea of "meeting Nature halfway" makes perfect sense, doesn't it?
You're not stressing about the imperfections, the random patches of biofilm, the bits of leaves that might be present in the substrate. Sure, there may be a fine line between "sloppy" and "natural" (and for many, the idea of stuff breaking down in any fashion IS "sloppy")- but the idea of accepting this stuff as part of the overall closed ecosystem we've created is liberating.
Sure, we can't get every functional detail down- every component of a food web- every biochemical interaction...the specific materials found in a typical habitat- we interpret- but we can certainly go further, and continue to look at Nature as it is, and employ a sense of "acceptance"- and randomness-in our work.

I'm not telling you to turn your back on the modern popular aquascaping scene; to disregard or dismiss the brilliant work being done by aquascapers around the world, or to develop a sense of superiority or snobbery, and conclude that everyone who loves this stuff is a sheep...
Noooooo.
Not at all.
I'm simply the guy who's passing along the gentle reminder from Nature that we have this great source of inspiration that really works! Rejoice in the fact that Nature offers an endless variety of beauty, abundance, and challenge- and that it's all there, free for us to interpret it as we like. Without aesthetic rules, rigid standards, and ratios. The only "rules" are those which govern the way Nature works with materials in an aquatic environment.
A botanical-method aquarium features, life, death, and everything in between.
It pulses with the cycle of life, beholden only to the rules of Nature, and perhaps, to us- the human caretakers who created it.
But mainly, to Nature.
The processes of life which occur within the microcosm we create are indifferent to our desires, our plans, or our aspirations for it. Sure, as humans, we can influence the processes which occur within the aquarium- but the ultimate outcome- the result of everything that we did and did not do- is based solely upon Nature's response.

In the botanical-style aquarium, we embrace the randomness and unusual aesthetic which submerged terrestrial materials impart to the aquatic environment. We often do our best to establish a sense of order, proportion, and design, but the reality is that Nature, in Her infinite wisdom borne of eons of existence, takes control.
It's a beautiful process. Seemingly random, yet decidedly orderly.
Think about that for a bit.
Stay curious. Stay bold. Stay creative. Stay thoughtful...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
Specialized diets, "Leopard Frogs", and re-thinking assumptions...
I'm fascinated by the dietary preferences of fishes. How they've evolved over eons to consume various items found in their environments; how many fishes became "specialists" as an adaptation to the habitats in which they live.
And, as an aquarist who derives great pleasure from seeing his fishes "live off the land" and consume foods from the aquarium environment in which they reside, I really find some of the seunderlying feeding strategies fascinating. One of the more interesting examples is the consumption of wood by various species of fishes.

We read a lot about fishes which eat wood and wood-like materials.
Of course, the ones that come immediately to mind are the Loricariidae, specifically, Panaque species. Now, I admittedly am the last guy who should be authoritatively discussing the care of catfishes, having maintained maybe a couple dozen or so species during a lifetime of aquarium keeping. However, I do understand a little bit about their diets and the idea of utilizing wood- and botanical materials- in the aquarium for the purpose of supplementing our fishes' diets!

And of course, I'm equally fascinated by the world of biofilms, decomposition, microorganism growth and detritus...And this stuff plays right into that!
Now, the idea of xylophagy (the consumption and digestion of wood) is of course, a pretty cool and interesting adaptation to the environment from which these fishes come from. And as you'd suspect, the way that wood is consumed and digested by these fishes is equally cool and fascinating!

It's thought by ichthyologists that the scraping teeth and highly angled jaws of the Loricariidae are a perfect adaptation to this feeding habit of "scraping" wood. And of course, it's even argued among scientists that these fishes may or may not actually digest the wood they consume! While scientists have identified a symbiotic bacteria which is found in the gut of these fishes that helps break down wood components, it's been argued by some the the fishes don't actually digest and metabolize the wood; indeed deriving very little energy from the wood they consume!
Hmmm...
In fact, a lab study by Donovan P. German was described in the November, 2009 Journal of Comparative Physiology, in which several species were fed wood and found to actually digest it quite poorly:
"...in laboratory feeding trials, (Pterygoplichthys cf. nigrolineatus and Hypostomus pyrineusi) lost weight when consuming wood, and passed stained wood through their digestive tracts in less than 4 hours. Furthermore, no selective retention of small particles was observed in either species in any region of the gut. Collectively, these results corroborate digestive enzyme activity profiles and gastrointestinal fermentation levels in the fishes’ GI tracts, suggesting that the wood-eating catfishes are not true xylivores such as beavers and termites, but rather, are detritivores like so many other fishes from the family Loricariidae."
Did you see that? Detritioves. Like, they're taking in wood to get other stuff out of the deal... And detritus is comprised of stuff like macrophytes, algae, and particulate organic carbon.
Hmm...
And this little nugget from the same study: "...The fishes consumed 2–5% of their body mass (on a wet weight basis) in wood per day, but were not thriving on it, as Pt. nigrolineatus lost 1.8 ± 0.15% of their body mass over the course of the experiment, and Pt. disjunctivus lost 8.4 ± 0.81% of their body mass."
Oh, that's weird.
Yet, anatomical studies of these fishes showed that the so-called "wood-eating catfishes" had what physiologists refer to as "body size-corrected intestinal lengths" that were 35% shorter than the detritivore species. What does this mean? Could they have perhaps had at one time- and subsequently lost- their ability to digest wood?
Maybe?
Arrgh!

And to make it even weirder, check out this passage from a study by Lujan, Winemiller, and Armbruster:
"Loricariids have a dense endoskeleton and are covered with dermal plates composed primarily of calcium phosphate, giving them a high physiological demand for dietary phosphorus. Paradoxically, the rivers and streams inhabited by loricariids as well as the detritus and biofilm that most loricariids consume tend to be highly Phosporus deficient."
The same study noted that, "Loricariids as a whole are largely unable to digest lignocellulose, and instead derive most nutrients and energy from easily digestible breakdown products (e.g., disaccharides and dipeptides) that are produced during microbial degradation of submerged, decomposing wood."
Oh, interesting!
I think it's yet another case of us as hobbyists drawing innocent conclusions based on anecdotal or superficial observations. I mean,"... they're munching on my wood, therefore, they must be 'eating' it!"

Now, to the point of the argument that most loricariids are primarily detritivores, consuming a matrix of biofilm, algal growth, microorganisms, and (for want of a better word) "dirt"- what does this mean to us as hobbyists? Well, for one thing, this has made them remarkably adaptable fishes in the aquarium. They will definitely rasp at wood", but according to the studies I just cited, they are not "eating" it, per se.
Now, my personal experience with Loricariidae is nothing like many of yours, and an observation I've made over the years is at best anecdotal- but interesting:
If you follow "The Tint", you know I've had a years-long love affair with Peckolotia compta aka "L134 Leopard Frog"- a beautiful little fish that is filled with charms. Well, I recall, are years back, that my first specimen seemed to have vanished into the ether following a re-configuration/rescape of my home blackwater/botanical-method aquarium. I thought somehow I either lost the fish during the re-scape, or it died and subsequently decayed without my detecting it... Pretty upsetting either way, but I couldn't find any trace of it!

For almost three months, the fish was M.I.A., just....gone.
And then one, day- there she was, poking out from the "Spider Wood" thicket that formed the basis of my newer hardscape! To say I was overjoyed was a bit of an understatement, of course! And after her re-appearance, she was out every day. She looked just as fat and happy as when I last saw her in the other 'scape...which begs the question (besides my curiosity about how she evaded detection)- What the fuck was she feeding on during this time?
Well, I suppose it's possible that some bits of frozen food (I fed frozen almost exclusively at that time) got away from my population of hungry characins and fell to the bottom...However, I'm pretty fastidious- and the other fishes (characins) were voracious mid-water-column feeders! To think that any appreciable amount got away from the hungry hoard was a bit hopeful. I believed at the time (and now am fully convinced) that it was more likely the biofilms, fungal growth, and perhaps some of the compounds from surface tissues of the "Spider Wood" I used in the hardscape that she was feeding on.
"Spiderwood" (aka Azalea root) stuff does recruit significant biological growth on it's surfaces when submerged , and curiously, in this tank, I noticed that, during the first few months, the wood seemed to never accumulate as much of this stuff as I had seen it do in past tanks which incorporated it!
I attributed this to perhaps some feeding by a population of Nanostomus eques, which have shown repeatedly in the past to feed on the biofilm or "aufwuchs" accumulating on the wood.
I'm sure that was a valid observation, but they were actively taking prepared foods as the bulk of their diet, so I have a hard time that they solely were responsible.
There was also a layer of Live Oak leaves distributed throughout the booth of the wood matrix, which, although they break down very slowly compared to other leaves we use, DO ultimately soften over time and break down over time. Since they are rather "durable", they do accumulate a lot of fungal growth and biofilms on their surfaces.

Interestingly, in this tank, I was finding little tiny amounts of very broken-down leaves, which I attributed to decomposition, but thinking back on it, looks more like the end product of "digestion" by someone!
I don't think I ever saw my L134 consuming prepared food. When I did observe her activities, she was seemingly "grazing" away at the wood surfaces and on botanicals...That's all the proof that I needed to confirm my theory that she's pretty much 100% detritivorous, and that the botanical-method aquariums she's resided in provide a sufficient amount of this material for her to consume.
To this day, I've never seen her eat prepared foods!
I have since acquired three captive-bred specimens from my friend, master breeder Sumer Tiwari, and this group has been seen to take prepared food on occasion. At the very least, adding some pellets or frozen foods seems to initial some kind of response in the fish, wether they appear to eat it or not.
So, back the the whole "xylophore thing"... After reading the studies I mentioned, I think that in the aquarium, as well as in the wild, much of what we think is actually "consumption" of the wood by the fishes is simply incidental- as in, the fishes are trying to eat the biocover and detritus on the surface tissues of the wood, and perhaps obtain some nutrition from the compounds contained in the softer portions of the wood. They apparently do a pretty good job (with their specialized mouthparts) of rasping away the surface tissues of the wood!
So, yeah- apparently, some of the wood may pass through the digestive tract of the catfishes, but it's passed without metabolizing much from it...perhaps like the way chickens consume gravel, or whatever (don't they? City boy here! WTF do I know about chickens!)...or the way some marine Centropyge angelfishes "nibble" on corals in their pursuit of algae, detritus, and biofilms.

Again, my perusal of German's scientific paper seems to support this theory:
"Catfishes supplement their wood diet with protein-rich detritus, or even some animal material to meet their nitrogen requirements. Although I did not observe animal material in the wood-eating catfish guts, Pt. disjunctivus did consume some animal material (including insects parts, molluscs, and worms), and all three species consumed detritus."
And finally, the "clincher", IMHO: "The low wood fiber assimilation efficiencies in the catfishes are highly indicative that they cannot subsist on a wood only diet."
Boom.

I mean, it's just one paper, but when he's talking about isotopic tracing of materials not consistent with digestion of wood in the guts of Loricariids, I think that pretty much puts the "eats wood" thing to bed, right? His further mention that, although some cellulose and lignin (a component of wood and our beloved botanicals!) was detected in the fish's fecal material, it was likely an artifact of the analysis method as opposed to proof that the fishes derived significant nutrition from it.
So what does all of this stuff mean to us?
Well, for one thing, once again- detritus/biofilm/fungal growths = good. Don't loathe them. Love them.
Your fishes apparently do.
I think it means that, as hobbyists probably knew, theorized, and discussed for a long time- that the Loricariids consume detritus, biofilms, and prepared foods when available. This is not exactly earth-shattering or new.
However, I think understanding that our botanical-method aquariums can- and do- provide a large amount of materials from which which these and other fishes can derive significant nutrition furthers my assertion that this type of system is perfect for rearing and maintain a lot of specialized feeders.

Materials like the harder-"shelled" botanicals (ie; "Skyfruit" pods, Cariniana pods, Mokha pods, bark, etc.) tend to recruit significant fungal growths and biofilms, and accumulate detritus in and on their surfaces. And of course, as they soften, some fishes apparently rasp and "consume" some of them directly, likely passing most of it though their digestive systems as outlined in the cited study, extracting whatever nutrition is available to them as a result. This is likely the case with leaves and softer botanicals as well.
Incidental consumption.

The softer materials might also be directly consumed by many fishes, although the nutrition may or may not be significant. However, the detritus, fungal, and microorganism growth as a result of their decomposition is a significant source of nutrition for many fishes and shrimps.
Detritivores (of which the amount of species in the trade is legion), have always done very well in botanical-method aquariums, and the accumulation of biofilms and microbial growth is something that we've discussed for a long time. By their very nature, the structure and decomposition of botanical materials make the "functional aesthetics" of our aquariums an important way to accommodate the natural feeding behaviors of our fishes.
So, the answer to the question (literally!), "Who has the (literal) guts for this stuff?" is quite possibly, "everyone!"
Now, while while we're on the subject of loricariids, a further scan of scientific literature revealed some interesting things about what these fishes are actually taking in when they "graze" in the wild. It's kind of eye opening, to me. One study revealed that loricariids consumed five principal items: sponges, organic detritus, bryophytes, bryozoans and sediment.
Wood is definitely part of the equation somewhere, but for the species examined in one of the studies I found (Rhinelepis aspera, Hypostomus regani, H. ternetzi, H. maragaritifer, H. microstomus, and Megalancistrus aculeatus) the gut content analysis was quite revealing:
The food spectrum of R. aspera is primarily "organic detritus and small quantities of sediment"; with few periphytic organisms. Although H. regani was found to consume large quantities of organic detritus as well, it also consumed "plant detritus, various sediment, and periphytic organisms" (i.e.; bryozoans, sponges and aquatic insect larvae). Bryozoans and sponges, huh?
Wow! Freshwater sponges...
The study indicated that bryozoans and organic detritus were the main food food of H. ternetzi, which, according to the gut contents of a number of individuals, tended to consume more sediment, rotifers, chironomids (i.e.; "Bloodworms'), gastropods and harpacticoids than the other species.
Harpactoids...you mean, like "copepods?" Stuff we as reefers feed all the time? H. margaritifer was found to ingest plant material. Other periphytic organisms such as insect larvae, and those bryozoans and sponges contributed to the diet of H. margaritifer.

And it gets more interesting still...
Sponges- I can't let that go.
Sponges were the principal food resource of H. microstomus and M. aculeatus, along with a healthy does of chironomids, various gastropods, Trichoptera (insects), and some bryozoans also consumed. Diets of these two fishes were composed of larger-sized items, with the finer organic detritus and such being less important than it was to the other species in the study.
This kind of information is tantalizing. It's compelling.
And what really gets me going is learning that some of our favorite, most beloved fishes are consuming large quantities of materials that I doubt any freshwater aquarist adds to his/her arsenal of foodstuffs. We're really good at feeding our catfishes baby vegetables and stuff, while typically overlooking many species' surprisingly high dietary dependency on items like insects, bryozoans, harpactoid copepods, and interestingly...sponges!

While we kind of always knew that these fishes ingested wood and "stuff", it's interesting to see what they're actually eating in the wild...especially the "stuff"- and configuring our aquariums and the supplemental and primary feeding opportunities available to the fishes accordingly.
We have some interesting, yet perhaps overlooked possibilities to provide some of these items.
In fact, there are a number of marine aquarium-purposed foods (typically targeted at certain marine angelfishes, many of which consume significant quantities of sponge) which contain sponges in their formulation. One of my favorite is Ocean Nutrition's "Angel Formula." Granted, these foods contain stuff like mussels, and other marine foods, and the sponges included are marine sponges, but I can't help but wonder if these are that morphologically or nutritionally different/palatable to the fishes than a freshwater/tree sponge would be?

Could the next great frozen Loricarid food include sponges? And we DO have harpactoid copepods available live, and in a variety of other formats intended for marine fishes and corals...Interestingly, I remember that the big "knock" by us reefers, for a long time, about some of these copepods was that they were "freshwater" varieties, and therefore didn't have the "correct" nutritional profile for marine organisms.
Hmm. We're talking about freshwater fishes here, right? Yeah.
So, like, why the hell haven't we been feeding these foods to our freshwater fishes all of these years?

Try some of these foods with your loricariids..and other fishes as well. What's to lose?
Oh, I can hear the objections:
"Impractical!"
Is it?. Online ordering is really cool. It might just catch on.
"Too much work!"
Really? C'mon. Ever cultured Grindal Worms or wingless fruit flies? THAT is "too much work" by definition.
"This is ridiculous; No need to experiment with these wacky foods. We're doing just fine now with Zucchini and stuff! Stupid."
Urghhhhh. "If man was meant to fly, he'd have wings..."
To not experiment is stupid, IMHO.
Don't be stupid. And I mean that in the kindest way possible. Don't just accept "what works" as "the way."
Push forward. Experiment. Fail quickly, or move forward rapidly with success. Play a hunch or two. Try something different. This is how advances in the hobby are made. This is how breakthroughs happen.
You gotta try.
Stay studious. Stay curious. Stay observant. Stay engaged. Stay resourceful...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics


























