- Continue Shopping
- Your Cart is Empty
Where the magic lies...
The botanical method aquarium niche is a bit weird, isn't it? Collectively, companies in our space tend to speculate a lot.
We make claims.
And we make recommendations..
And at best, they’re subjective guesses. Based upon our personal experince and perhaps the experiences of others.
Yet, wherever you turn in the botanical method aquarium world, speculation and generalizations are, well- rampant. How much tannin or other compounds are in a given botanical is, without very specific bioassays and highly specialized equipment- simply a guess on our part.

There is absolutely no proof or quantification of these assertions that is grounded in hard facts or rigorous, scientific research. I think about it a lot..For us to make recommendations based on concentrations of various compounds in a given botanical is simply irresponsible and not grounded in fact.
There is a lot of speculation. So-called "experts" in our area of specialization have, in all likelihood, done little beyond use the materials avialbel to us in aquairums. I'm not aware of anyone in our niche who runs a lab, or has performed disciplined scientific analysis on any of the materials that we as a hobby use every day.
This is not an "indictment" or secret reveal about our industry...it's just the way things are.
One of the things that we assert the most is "how much tannins" are in a given material. Okay...What is this based upon?
Generally, it's based upon the admittedly superficial observations that we make as hobbyists and "power users" of botanical materials. There are not awhole lot of other, more insightful observations that we CAN make, right?
Sure, we could tell you that, based upon our experience, a given wood type or seed pod will color the water a darker color than another.. but what does that mean, really?
Not that much.

I mean color of the water is absolutely not an indication of anything- other than the fact that tint producing types of tannins are present. It doesn’t tell you what the pH, dKH, or TDS of the water.. let alone, how much of what tannins are present…
Now, sure, it’s arguably correct that “tannins” are present in many botanical materials. However, the degree to which the tannins present in a given botanical or leaf can influence water chemistry is really speculative. Quite honestly, other than staining the water a distinctive brown color, it’s actually not entirely known by science what other influences that specific tannins impart to water.
So, to be quite honest, when we make general statements like “contains a lot of tannins” or “can lower pH”, many times we’re simply “spitballing…” Guessing. Assuming.
Now, don't get me wrong. I'm not trying to trash the many responsible, experienced vendors in our space. I am, however, attempting to make the point that a large part of what we assert about the materials we work with and sell is, well- speculative.
We make claims.
And we make recommendations..

I think the main thing which keeps the idea from really developing more in the hobby- knowing exactly how much of what to add to our tanks, specifically to achieve "x" effect- is that we as hobbyists simply don't have the means to test for many of the compounds which may affect the aquarium habitat.
At this point, it's really as much of an "art" as it is a "science", and more superficial observation- at least in our aquariums- is probably almost ("almost...") as useful as laboratory testing is in the wild. Even simply observing the effects upon our fishes caused by environmental changes, etc. is useful to some extent.

At least at the present time, we're largely limited to making these sort of "superficial" observations about stuff like the color a specific botanical can impart into the water, etc. It's a good start, I suppose.

Of course, not everything we can gain from this is superficial...some botanical materials actually do have scientifically confirmed impacts on the aquarium environment.
In the case of catappa leaves, for example, we can at least infer that there are some substances (flavonoids, like kaempferol and quercetin, a number of tannins, like punicalin and punicalagin, as well as a suite of saponins and phytosterols) imparted into the water from the leaves- which do have scientifically documented affects on fish health and vitality.

So, there's that.
The one area that we are not speculating or guessing is the ecology part. How botanical materials interact with the aquatic environment to form an ecosystem of organisms. And the most fundamental, most important "driver" of the whole thing is the process of decomposition.
Decomposition is how Nature processes botanical materials for use by the greater aquatic ecosystem. It's the first part of the recycling of nutrients that were used by the plant from which the botanical material came from. When a botanical decays, it is broken down and converted into more simple organic forms, which become food for all kinds of organisms at the base of the ecosystem.

In aquatic ecosystems, much of the initial breakdown of botanical materials is conducted by detritivores- specifically, fishes, aquatic insects and invertebrates, which serve to begin the process by feeding upon the tissues of the seed pod or leaf, while other species utilize the "waste products" which are produced during this process for their nutrition.
In these habitats, such as streams and flooded forests, a variety of species work in tandem with each other, with various organisms carrying out different stages of the decomposition process.

And it all is broken down into three distinct phases identified by ecologists.
It goes something like this:
A leaf falls into the water.
After it's submerged, some of the "solutes" (substances which dissolve in liquids- in this instance, sugars, carbohydrates, tannins, etc.) in the leaf tissues rather quickly. Interestingly, this "leaching stage" is known by science to be more of an artifact of lab work (or, in our case, aquarium work!) which utilizes dried leaves, as opposed to fresh ones.

Fresh leaves tend to leach these materials over time during the breakdown/decomposition process. It makes sense, because freshly fallen or disturbed leaves will have almost their full compliment of chlorophyll, sugars, and other compounds present in the tissues. (Hmm, a case for experimenting with "fresh" leaves? Perhaps? We've toyed with the idea before. Maybe we'll re-visit it?)
Cool experiments aside, this is yet another reason why it's not a bad idea to prep your leaves, because it will help quickly leach out many of the remaining sugars and such which could degrade water quality a bit in closed systems.
The second stage of the process is called the "conditioning phase", in which microbial colonization on the leaf takes place. They begin to consume some of the tissues of the leaf- at least, softening it up a bit and making it more palatable for the aforementioned detritivores. This is, IMHO, the most important part of the process. It's the "main event"- the part which we as hobbyists embrace, because it leads to the development of a large population of organisms which, in addition to processing and exporting nutrients, also serve as supplemental food for our fishes!
The last phase, "fragmentation", is exactly what it sounds like- the physical breakdown of the leaf by various organisms, ranging from small crustaceans and shrimp to fungi- and even fishes, collectively known as "shredders." It has been suggested by some ecologists that microbes might be more important than "shredders" in tropical streams.
Fauna composition differs between habitats, yet most studies I've found will tell you that Chironomidae ( insect larvae-think Bloodworms!) are the most abundant in many streams, pools, flooded forests, and "riffles" in the initial period of leaf breakdown!

The botanical material is broken down into various products utilized by a variety of life forms. The particles are then distributed downstream by the current and are available for consumption by a variety of organisms which comprise aquatic food webs.
Six primary breakdown products are considered in the decomposition process: bacterial, fungal and shredder biomass; dissolved organic matter; fine-particulate organic matter; and inorganic mineralization products such as CO2, NH4+ and PO43-.
An interesting fact: In tropical streams, a high decomposition rate of terrestrial materials has been correlated to high fungal activity...these organisms accomplish a LOT!

Interestingly, scientists have noted that the leaves of many tropical plant species tend to have higher concentrations of secondary compounds and more recalcitrant compounds than do leaves of temperate species. Why do you suppose this is?
Also, some researchers hypothesized that high concentrations of secondary compounds (like tannins) in many tropical species inhibit leaf breakdown rates in tropical streams...that may be why you see leaf litter beds that last for many years and become known features in streams and river tributaries!

There's a whole lot of stuff going on in the litter beds of the world, huh?
Of course, fungal colonization of wood and botanicals is but one stage of a long process, which occurs in Nature and our aquariums. And, for many hobbyists, once we see those first signs of fungal growths or biofilms, the majority of us tend to reach for the algae scraper or brush and remove as much of it as possible- immediately! And of course, this provides some "aesthetic relief" for some period of time- but it comes right back...because botanical materials will provide a continuous source of food and colonization sites for fungal growths!
And the idea of "circumventing" this stuff is appealing to many, but the reality is that you're actually interrupting the process. It's not a "phase" that your botanical method aquarium goes through. Rather, it's how the aquarium functions on a continuous basis. Siphon the stuff out- and it comes right back. Nature abhors a vacuum, and new growths will return to fill the void, thus prolonging the process.
Why fight it?
Alteration of the botanicals durning the decomposition process is done chemically via this microbial action; ultimately, the components of the botanicals/leaves (lignin, cellulose, etc.) are broken down near completely. In aquatic environments, photosynthetic production of oxygen ceases in plants, and organic matter and nutrients are released back into the aquatic environment.
All of these organisms work together- in essence, supporting each other via the processes which they engage in.

And, decomposition is a dynamic, fascinating process- part of why we find the idea of a natural, botanical-method system so compelling. Many of the organisms- from microbes to micro crustaceans to fungi- are almost never seen except by the most observant and keen-eyed hobbyist...but they're there- doing what they've done for eons.
They work slowly and methodically over weeks and months, converting the botanical material into forms that are more readily assimilated by themselves and other aquatic organisms.

The real cycle of life!
The ultimate result is the transformation to what ecologists call "coarse particulate organic matter" (C.P.O.M.) into "fine particulate organic matter" (F.P.O.M.), which may constitute an important food source for other organisms we call “deposit feeders” (aquatic animals that feed on small pieces of organic matter that have drifted down through the water and settled on the substrate) and “filter feeders” (animals that feed by straining suspended organic matter and small food particles from water).
And yeah, insect larvae, fishes and shrimp help with this process by grazing among or feeding directly upon the decomposing botanical materials..So-called "shredder" invertebrates (shrimps, etc.) are also involved in the physical aspects of leaf litter breakdown.
There's a lot of supplemental food production that goes on in leaf litter beds and other aggregations of decomposing botanical materials. It's yet another reason why we feel that aquariums fostering significant beds of leaves and botanicals offer many advantages for the fishes which reside in them!

The biggest allies we have in the process of decomposition of our botanicals in the aquarium are the smallest organisms: Microbes (bacteria, fungi, and protozoa, specifically)!
Interestingly, in some wild aquatic habitats, such as the famous Peat swamps of Southeast Asia, the decomposition of leaves which fall into these waters is remarkably slow. In fact, ecologists have observed that the leaves typically do not break down.
Why?
It's commonly believed that these low nutrient waters, which are high in tannins, and highly acidic, seem to impede microbial activity. This is seemingly at odds with the understanding that passive leaching of dissolved organic compounds (DOC) from leaf litter has been found to be a major source of energy in tropical stream habitats, fueling the microbial food chains which we are so fascinated by.
No doubt the water parameters have something to do with this. These are unique habitats. Here are a few stats from the peat swamps in which some studies on leaf decomposition were conducted:
Water temperature: 25C/77F-32C/89F
pH: 2.6-3.8
TDS: 89-134mg/l
Nitrate: <0.-0.2mg/l
Dissolved oxygen: 1.8-16mg/l
In the studies, leaves of native species found along the swamps submerged in the waters of the swamps lost very little biomass, which other leaves from trees did break down more substantially. This tends to rule out the generally-held theory that ecologists have which postulates that the slow decomposition rate in the peat swamps is due to the extreme conditions. Rather, as mentioned above, it's believed that the resistance to decomposition is due to the physical and chemical properties of the leaves which are found right along the swamps.

(image by Marcel Silvius)
The reason? Well, think about it.
Leaf litter in tropical peat swamp forests builds up into peat many feet deep over thousands of years, and thus impedes nutrient cycling. And when you think about it, inputs of nutrients into most peat swamps come solely from rainfall, because rivers and streams in the region don't always flow into the swamps. In such nutrient poor, highly acidic conditions, it is more beneficial for plants to protect their leaves, rather than to replace them when subjected to elements like wind, and herbivore damage (mostly by insects) with new growth.
And interestingly, bacteria and fungi are known to be responsible for leaf breakdown in the peat swamps, because ecologists typically don't encounter aquatic invertebrates in the peat swamp which are known to ingest leaf material!
Our friends, the fungi!
Yeah, those guys again. Yet, there just one group of a diverse biome of organisms which contribute to the function of our botanical method aquariums.
By studying and encouraging the growth of this diversity of organisms, and creating a multi-faceted microcosm of life in our tanks, I believe that we are contributing to an exciting progression of the art and science of aquarium keeping!
I'm fascinated by the "mental adjustments" that we need to make to accept the aesthetic and the processes of natural decay, fungal growth, the appearance of biofilms, and how these life forms affect what's occurring in the aquarium.
It's all a complex synergy of life and aesthetic.

And we have to accept Nature's input here.
Nature dictates the speed by which this decomposition process occurs. We set the stage for it- but Nature is in full control.
Nuance. Art. Challenge. Fascination.
Beyond the pretty looks. That's where the real magic lies.
Stay engaged. Stay curious. Stay dedicated. Stay observant. Stay open-minded...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
Fools rush in...
Recently, I've been fielding a lot of questions from new hobbyists.
Not just new to the botanical method aquarium world- new to the aquarium hobby altogether!
On first thought, my answer is, "Fuck, no! You have to understand the basics of the hobby first."
Ouch. A bit quick and decisive, right? And perhaps a bit contrary to the realities of what we do and experience with botanical method aquariums.

I mean, I've often touted how I feel that, once these systems are established, they are remarkably stable, relatively easy-to-maintain aquariums., right?
Of course, there are some real qualifiers here.
The first being, "After the system is established."
Establishing a botanical-method aquarium, blackwater, brackish, or otherwise- certainly requires some basic understanding of the principles of aquarium management. Specifically, the nitrogen cycle, an understanding of water quality assessment and management, and stocking.
You need to understand a little about the ecology of natural aquatic systems; how they function, evolve, and why the look the way that they do.

Yet, you CAN learn all of these things. You can google and study and even listen to our podcast and read our blog.
Facts. Processes. Techniques.
And then, there are some things you can't really "teach"- like patience. You need, well- a shitload of it...in the aquarium hobby in general, yet especially in the natural, botanical-method aquarium sector. And the "patience" part? I feel that it's seminal. Foundational.
Essential.
I don't think you can "teach" that.

I mean, perhaps you can be taught about why patience is so important.
We can provide some expectations and explanations of how these systems establish, appear, and operate over time. We can offer guidelines about "best practices" and procedures.
However, the best teacher, as with so many things- is experience. You have to dive in and do it. Beginner, intermediate, advanced- you have to DO.
Perhaps some things might be easier to an outright beginner; someone who has no preconceived notions about how an aquarium is "supposed to look", or what is considered "natural", "beautiful", etc. There is a beautiful, almost innocent objectivity that we bring to the game when we are flat-out beginners, right? We have little basis for comparison, other than our own observations and personal tastes.
And that's actually an advantage, in some respects, IMHO.
In my opinion, the hobby has been- for better or worse- influenced by schools of thought which seem to dogmatically dictate what is "good", "bad", and "correct." And, in a strange sort of way, hobbyists who stray off of the generally accepted, well-trodden paths established by our hobby forefathers are often greeted with skepticism, cynicism, and sometimes, outright disdain!

That blows, IMHO.
And then there is the other end of the spectrum: The splashy, often vapid, sometimes downright bizarre presentation of the aquarium hobby found on social media.
One trend I've noticed that's fueled by social media is an almost fetishization of showing only the "finished product" of gorgeous, pristine aquascaped tanks, with maybe just a little sampling of "construction" pics (usually just staged shots of products or "unboxing" stuff- read that, "shilling" for manufacturers, btw), but little mention of the actual process; the challenges, the "ugly" parts- the work- of establishing one of these aquariums.
The result of this superficial ("dumbed down") presentation of aquariums conveys the message that it's just all about buying stuff, artfully arranging some materials, and POW! Finished awesome tank. Shit, it's so easy- why isn't YOUR tank this cool and sexy?
It often results in frustration for the everyday hobbyist, who can't seem to figure out why his or her tank isn't exactly like the one on the 'gram.
Sure, the fundamentals of aquarium keeping and the mindset behind establishing successful systems isn't as "sexy" or 'gram-ready as pics of the finished product, but to operate from the position that everyone who sees these tanks has that underlying knowledge already is at best "glossing over" the realities, and at worst, downright irresponsible.
We've gotta talk more anbout process. About how these tanks work, the philosophy and methodology behind them, and about how to establish and maintain them. The beginner needs to see this stuff.

To jump into any aquarium- botanical-filled or otherwise- without having basic knowledge about stuff like the nitrogen cycle, fish stocking protocols, and husbandry techniques- is flat-out stupid, IMHO.
Now, I realize not everyone wants to- and can- produce content about aquarium keeping fundamentals, but maybe just touching on a few basics now and then would be cool.
I challenge all of my fellow hobbyists who are influential in this social-media-powered world to commit to touching on some of these underlying themes, challenges, and expectations on occasion when featuring your amazing work. Just taking a few seconds to explain this stuff; even posting just one pic in your feed showing a tank cycling, or with the plants not looking perfect, or the water not crystal clear- can go a long, long way to gently give a dose of reality and expectation management in the splashy world of aquascaped aquariums.

Now, I realize that there is plenty of material out there on "how to start an aquarium" or whatever- but I think it needs refreshing, updating, FEATURING- for a new generation of hobbyists who are getting the bulk of their information from Facebook forums, Instagram feeds, and YouTube shorts. It's important for the future of the hobby. It will assure more people get in- and STAY in the hobby. We need to evolve how we present the concepts as much as we need to evolve the concepts themselves.
Sadly, it has to be reinforced constantly.
I can't tell you how many times a week I answer questions like, "I just received my Enigma Pack! Can I just add this stuff to my 5-gallon tank? What do I need to do..?" And I have a freakin' website with gigabytes of stuff on this very topic and other related topics, accumulated over years! And we're evolving this too. I had to check my ego a bit, and accept that not everyone likes to read a daily blog. So I started this podcast in 2019.
Getting some of the fundamental messages across required us to adapt.
We all need to evolve. More succinctly, we need to preach the underlying fundamental stuff...but in an evolved way.
Part of the reason we've spent so much time over the past few years in this blog/podcast chatting about the processes, the pitfalls, and the expectations you should have when establishing the systems we advocate is to give everyone a very clear picture of what's actually involved.
Makes sense. We are literally asking you to dump dead plant materials into your aquarium and let them decompose. To NOT touch on all of this fundamental stuff and discuss the potential issues would have been irresponsible at every level.
So, yeah- getting back to the initial point of this whole thing- I believe that you certainly CAN start with a botanical-style natural aquarium for your first project, but you absolutely need to familiarize yourself with the fundamentals of aquarium practice. And you CAN be successful.
Of course, you just can't delude yourself into thinking that it's a simple matter of tossing leaves and twigs into a tank, filling it up, and BAM! "Instant Borneo" or whatever. Like, the nitrogen cycle, formation of biofilms, environmental stability, etc. don't apply to you... Yeah, there are a LOT of neophyte hobbyists- end experienced ones, for that matter-who harbor such beliefs! I've talked to quite a few over the years. And, based on 'gram reality, apparently, there IS no "nitrogen cycle"- just cool finished tanks, so...

As those of us in this game already know, it's a process.
A journey. A learning curve.
One that acknowledges that success is entirely achievable for those who make the effort to study, familiarize themselves with the basics; one that is almost guaranteed to kick the shit out of you if you leap without learning.
It doesn't matter if you're an innocent neophyte, unfamiliar with this stuff - or even a seasoned hobbyist with decades of experience. You CAN be a "beginner"- and one who's quite successful. We, as a community just need to continue to do some of the "heavy lifting" to help everyone along!
Expectations need to be set.
As we all know, leaves and botanicals simply don't last indefinitely; they begin to soften and decompose shortly after they're added to the aquarium. Depending upon the particular botanical in question, they can last from a few weeks (as in the case of Catappa leaves, for example) to many months (the "harder" pods, like Carinaina or Sterculia pods.).
And of course, that means that we need to accept the idea that most botanicals are "consumables" for all intents and purposes, much like activated carbon, filter pads, etc.- and need periodic replacement.
Leaves, for example, should be "topped off" regularly to continue to contribute to the ecological function of the aquarium. Just like in a real tropical stream or other body of water, as materials decompose or wash downstream, the physical appearance" and other characteristics, like water movement, etc. will change over time. And the fishes will adapt, too- finding new "territories", spawning sites, and feeding locations. These are very natural behaviors which you just won't see in a more traditional "static" aquascape.

Expectations. Evolutions. Changes.
Part of the game that beginners and advanced hobbyists alone need to accept.
By regularly replacing the botanical materials in your aquarium, you're constantly "evolving" or "editing" the habitat, creating a truly dynamic display for your fishes. And if you look at your botanical method aquarium over several months or longer, for example, you'll see this clearly. Now, Nature does a certain percentage of this for us, because, as mentioned above- stuff decomposes, softens, breaks down, etc. And this results in subtle (or not-so-subtle) changes over time, wether we intervene or not.

Sure, the basic "structure" of the aquascape will likely be the same- but the smaller-scale "niches" within the tank, as well as the colors, textures and "negative space" within the habitat will vary and "evolve." Similar, in some respects to a planted aquarium, a botanical system can be "pruned" to keep a rough "form", yet it will evolve in subtle ways on it's own, despite our interventions.
This fascinates me.
And there is that concept of when the aquarium is "finished."

Over the years, I've found that the thrill of starting up a new aquarium never faces. However, one of the things that I'm realizing is that I've never been in any particular hurry to get my tank "finished."
I mean, I don't think a tank is ever really "finished"- it's more like the system reaches some level of function and appearance that you may have envisioned before your started the project, and you tell yourself, "yeah- this is what I wanted..."
My aquarium hobby "philosophy" is predicated on one simple idea:
"Radical patience!"
What's "radical" about patience?
Is there some special meaning to this? Well, not really. It's as much about common sense as anything, actually. Yeah, common sense. However, in today's "insta"- world, the concept of taking the time to establish an aquarium is sort of...radical- as is the patience required to go slowly and steadily.
That is- not jumping right into something...taking a bit of time- or even a long time- to allow your aquariums to "run in" and develop before pushing them along.
I mean, why are we always in such a hurry to get fishes in?
Having set up more than a few systems in my time, I never seem to be surprised at my own true hobbyist-style impatience!
Let’s face it—once we get the plumbing done, the lighting tweaked, leaks sealed, and aquascaping set, we’re all seemingly hell-bent on getting some fishes in there! I mean—we’ve waited so long for “first water” in the tank that it’s time to enjoy the fruits of our labor.
It's like we need to get the fishes in there right away…even just a few, right?

Can’t really blame us, huh?
However, there may be some compelling reasons to wait just a bit longer…
Would you like to move into a house which didn’t have a refrigerator full of food? I wouldn’t, for sure. Unlike humans, fishes seem to have not lost their "genetic programming" for grazing and hunting for food. Let’s face it—most of the waking hours of aquatic animals are devoted to acquiring food and reproducing. They need to have some food sources available to "hunt and graze" for.
That’s reality.
So, unleashing a group of fishes into an almost "sterile" aquarium seems decidedly at odds with this evolutionary adaptation which our fishes have. Yet, from a strictly human perspective, most of us would rather have parts of our vital organs snipped off before we'd wait several weeks or more to add fishes to our new aquariums...
As a reefer, my patience has really evolved over the years. My friends have finally learned to stop asking me "How's the tank looking?" after it has been set up for a few weeks, because they know damn well by now that my tank looks essentially the same as it did the day I set it up..at least, from an animal stocking perspective! I simply don't start adding tons of animals until the system has evolved to the point where it's "ready" IMHO.

This approach actually has its origin in my youth.
Like now, I was really into fish. However, with limited funds, I often had to do things in stages...It could literally take months to get a tank set up as I accumulated the funds. SO, sometimes, the then would be filled, "scared", and just...sit. And this was after taking a few months to get to that stage! it actually was such a regular process to me that it kind of became a habit. I mean, I was (and still am) pretty adverse to getting a tank up and running and populated in just a few days.
I feel like I'm rushing things too much.
Interestingly, Nature sort of supports this approach! With reef tanks, or the natural, botanical method aquariums we play with here, this "latency period" when the tank is "running in" gives the ecology of the tank a chance to establish itself. The microfauna which make up the foundation of our closed ecosystems will colonize and multiply, umolested and unhurried, during this time.

I believe that it gives an aquarium a greater degree of long term success.
And there is a lot to be said for simply doing nothing when you're experiencing something like cloudy water, for example. Yes, your aquarist instinct is screaming at you to do something, but the reality is that it's SOOOO much better to simply "wait it out" and let Nature sort things.
Remember: THERE IS NO RUSH!! THERE IS NO "FINISH LINE!"
It all starts with an idea...and a little bit of a "waiting game..." and a belief in Nature; a trust in allowing the natural processes which have guided our planet and its life forms for eons to develop to the extent that they can in our aquariums.
Rituals we engage in, and stages that we go through with our aquariums are remarkably analogous to the processes which occur in Nature...
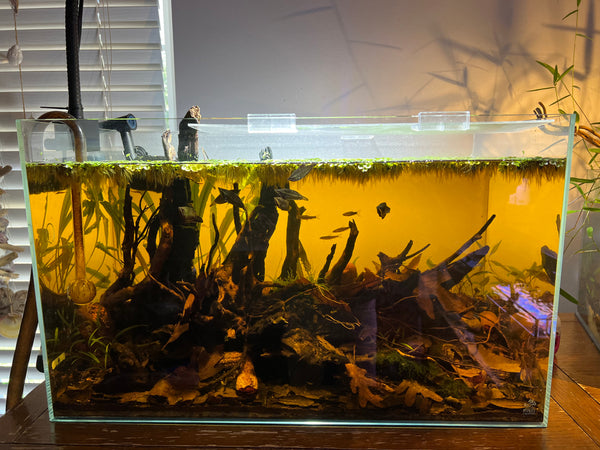

Yeah, think about it for a second:
A tree falls in the (dry) forest.
Wind and gravity determine it's initial resting place (you play around with positioning your wood pieces until you get 'em where you want, and in a position that holds!). Next, other materials, such as leaves and perhaps a few rocks become entrapped around the fallen tree or its branches (we set a few "anchor" pieces of hardscaping material into the tank).

Then, the rain come; streams overflow, and the once-dry forest floor becomes inundated (we fill the aquarium with water).
It starts to evolve. To come alive in a new way.

The action of water and rain help set the final position of the tree/branches, and wash more materials into the area influenced by the tree (we place more pieces of botanicals, rocks, leaves, etc. into place). The area settles a bit, with occasional influxes of new water from the initial rainfall (we make water chemistry tweaks as needed).

Fungi, bacteria, and insects begin to act upon the wood and botanicals which have collected in the water (kind of like what happens in our tanks, huh? Biofilms are beautiful...).

Gradually, the first fishes begin to "follow the food" and populate the area (we add our first fish selections based on our stocking plan...).

The aquatic habitat is enriched by the decomposition of leaves, wood, and botanical materials, creating new food supplies, spawning locales, and biological stability.

It continues from there. Get the picture? Sure, I could go on and on drawing parallels to every little nuance of tank startup, but I think you know where I'm going with this stuff...
Yet, when we think about our aquariums this way, the parallels are striking, aren't they?

And the thing we must deploy at all times in this process is patience. And an appreciation for each and every step in the process, and how it will influence the overall "tempo" and ultimate success of the aquarium we are creating.
When we take the view that we are not just creating an aquatic display, but a habitat for a variety of aquatic life forms, we tend to look at it as much more of an evolving process than a step-by-step "procedure" for getting somewhere.

Taking the time to consider, study, and savor each phase is such an amazing thing, and I'd like to think- that as students of this most compelling aquarium hobby niche, that we can appreciate the evolution as much as the "finished product" (if there ever is such a thing in the aquarium world).
It all starts with an idea...and a little bit of a "waiting game..." and a belief in nature; a trust in the natural processes which have guided our planet and its life forms for eons.
Fools rush in. Smart hobbyists enjoy the process.
The appreciation of this process is a victory, in and of itself, isn't it? The journey- the process- is every bit as enjoyable as the destination, I should think.
Stay excited. Stay enthralled. Stay observant. Stay appreciative...Stay patient...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
"Opportunistic habitats", and the parallels between Nature and the Aquarium.
One of the more remarkable things about the botanical-method aquarium approach is that it offers us a unique insight into the operation of many wild aquatic habitats. These habitats are tremendously influenced by their surrounding terrestrial environment. The very soils which make up the substrate, and the fallen tree trunks, leaves, and seed pods present in the water cement the relationship between land and water.

The "operating system" of a botanical method aquairum, as we've discussed many times before, is literally driven by the presence of these materials.
A few days ago, I was doing a small water exchange in one of my personal botanical method aquariums, and I reached in to move a seed pod away from the siphon hose (so that it wouldn't block it), and it promptly disintegrated in my fingers! Another botanical did its job, gradually releasing tannins, humic substances, and other compounds into the water over the months, until finally decomposing back into its (likely) near-inert constituent parts.
This is the essence of what we call have called "habitat enrichment" over the years-the imparting of beneficial substances and materials into the overall aquatic environment via botanical materials. Of course, as we've reiterated before here, we can't say exactly what they are imparting, and how much.
We can conclude via observation, that they are contributing...something...to the aquatic environment.
This submerged botanical, like many others in the tank, contributed greatly to the microbiome of the system. Fishes foraged upon its surfaces, shrimp consumed its lignin-rich tissues, and fungal growths, biofilms, and microorganisms flourished on its matrix of interstitial surfaces.

The "end" of this botanical's "service life" was symbolic, in a way, of what takes place in our aquariums: Fungi, bacteria, algae...indeed, the water itself all conspire to erode, degrade, and ultimately, decompose these materials...a real "cycle of life." As I continued with my weekly maintenance, I siphoned out a few stray pieces of broken-down leaves and added some new ones.
Adding new botanicals serves the multifold purpose of resupplying the organisms at the base of the microbiome with a new food source, keeping the water visually "tinted", the physical environment consistent, and the look and vibe of the tank "fresh"- so similar to what goes on in Nature, when old leaves break down, and new ones fall into bodies of water to take their place.
New leaves and botanical materials are a sort of a biological/chemical "shot in the arm" for our aquariums.

Some of the most amazing comments we receive after sharing underwater pics of the wild habitats of Amazonia and elsewhere are from hobbyists who, at first, thought that some of these pics were from someones' aquarium! In a few instances, some of the close ups of botanical-themed aquaria are virtually indistinguishable from wild scenes!
This is a real turning point in the history of natural aquarium keeping, IMHO. One in which the function of the aquariums we are creating trumps the aesthetics...or, perhaps better put- the function and natural processes drive the aesthetics..and it's an incredible replication of what you'd encounter in Nature!

By facilitating these natural processes within the aquairum- not resisting them, we've fostered in an entirely new approach to creating truly "natural" aquairums in the hobby!
Blurring the lines between Nature and the aquarium, at the very least, from an aesthetic sense- and in many aspects, from a "functional" sense, proves just how far today's hobbyists have come...how damn good you are at what you do. And how much more you can do when you turn to Nature as an inspiration, and embrace it for what it is.
Many of our most incredible natural aquariums are replications of what I like to call "opportunistic habitats"- or habitats which arise in Nature because of some specific events or occurrences, like seasonal inundation, sediment accumulation, and fallen trees.
Yeah, trees.
It’s not uncommon for a tree to fall in the rain forest, with punishing rain and saturated ground conspiring to easily knock over anything that's not firmly rooted. When these trees fall over, they often fall into small streams, or in the case of the varzea or igapo environments in The Amazon that I'm totally obsessed with, they fall and are submerged in the inundated forest floor when the waters return.

And of course, they immediately impact their (now) aquatic environment, fulfilling several functions: Providing a physical barrier or separation from currents, offering territories for fishes to spawn in, providing a substrate for fungi and biofilms to multiply on, a space for leaves to accumulate, and places for fishes forage among, and hide in.
An entire community of aquatic life forms uses the fallen tree for many purposes. And the tree trunks and parts will last for many years, fulfilling this important role in the aquatic ecosystems they now reside in each time the waters return.
What an incredible dynamic!

Let's focus on this "ecological component" for just a bit. Let's review what happens when a tree falls...literally!

Shortly after falling into the water, fungi and other microorganisms act to colonize the surfaces, and biofilms populate the bark and exposed surfaces of the tree. Over time, the tree will impart many chemical substances, (lignin, humic acids, tannins, sugars, etc.) into the water as the bark breaks down and the tree itself softens.
In aquatic ecosystems, much of the initial breakdown of botanical materials is conducted by detritivores- specifically, fishes, aquatic insects and invertebrates, which serve to begin the process by feeding upon the tissues of the seed pod or leaf, while other species utilize the "waste products" which are produced during this process for their nutrition.
In these habitats, such as streams and flooded forests, a variety of species work in tandem with each other, with various organisms carrying out different stages of the decomposition process.

The fallen tree literally brings new life to the waters.
I can't stress enough how interesting and important this transformation of the terrestrial environment to the aquatic one is. It helps explain so much of why the aquatic habitats look and function the way they do, and how they impact the life forms which make use of them.

The materials that comprise the tree are known in ecology as "allochthonous material"- something imported into an ecosystem from outside of it. (extra points if you can pronounce the word on the first try!) We've talked about that stuff for a while now, right?
Yeah.
And of course, in the case of fallen trees, this includes includes leaves, fruits and seed pods that fall, or are washed into the water along with the branches and trunks that topple into the stream.

All of this can be replicated, to a certain extent, in the confines of an aquarium. You just need to use some larger pieces of wood or branches.
Now, there are many aquarists who would make the case that you can't make big, gnarly pieces of wood "work" in an aquarium because of their impact on "ratio" and "proportion", etc... You know, the "artistic" part.
And to these types, I gently admonish you to check out the works of some talented 'scapers, like our friend, Mitch Mazur, who have made that now-famous "mental shift" to work with Nature in an artistic interpretation...

These pleas and "look what HE did!" sort of arguments are almost a "prerequisite" of late when I talk about any idea that has an "aesthetic" component to it, because the self-appointed "guardians of aquascaping style" seem to come out of the woodwork (lol) after these discussions, reciting dozens of well-rehearsed reasons why the concept won't work, rather than even trying to do something similar.
It's weird.
To that, of course, I call, "Bullshit!"

Yeah, a big piece of wood or dense aggregation of smaller pieces in an aquarium does create some challenges, but most of them are in our head. Hell, Takashi Amano himself did a few amazing tanks with huge pieces of wood years ago. Remember?
And of course, when we utilize a large piece of wood (relative to the aquarium's water volume), it has a chemical and physical impact on the aquatic environment that is...hey- sort of similar to that which occurs in Nature, right?
Yeah.
Function and aesthetics are linked. In Nature, and in the aquarium!

And, look- I'm not telling you to turn your back on the modern popular aquascaping scene; to disregard or dismiss the brilliant work being done by aquascapers around the world, to completely eschew aesthetics, or to develop a sense of superiority and snobbery, and conclude that everyone who loves that kind of stuff is a sheep...
Noooooo.
Not at all.
I'm simply the guy who's passing along the gentle reminder from Nature that we have this great source of inspiration that literally "works!" Rejoice in the fact that Nature offers an endless variety of beauty, abundance, and challenge- and that it's all there, free for us to interpret it as we like. It's not all perfect "rule of thirds" or flawless layouts and such.
Lots of places in Nature, beautiful though they may be, are a bit "rougher around the edges" than some aquarists seem to want to accept. Not all, but some.

And the rest of us?
We see the beauty in the apparent chaos and randomness.
We just happen to like things bit more, well- "natural" than others...
Stay creative. Stay thoughtful. Stay intrigued. Stay studious. Stay open-minded.
Blur the lines.
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
Inception.
We've had a lot of requests lately to discuss how we start up our botanical method aquariums. Now sure, we've covered this topic before over the years; yet, as our practices have evolved, so has our understanding about why we do things the way that we do- and why it works.
Establishing a new botanical method aquarium is an exciting, fun, and interesting time. And the process of creating your aquarium is shockingly easy, decidedly un-stressful, and extremely engaging.
The main ingredients that you need are vision, a bit of knowledge, and... patience.
Bringing your tank from a clean, dry,"static display" to a living, breathing microcosm, filled with life is an amazing process. This, to me is really the most exciting part of keeping botanical method aquariums.

And how do we usually do it? I mean, for many hobbyists, we've been more or less indoctrinated to clean the sand, age water, add wood, arrange plants, and add fishes. And that works, of course. It's the basic "formula" we've used for over a century.
Yet, I'm surprised how we as a hobby have managed to turn what to me is one of the most inspiring, fascinating, and important parts of our aquarium hobby journey into what is more-or-less a "checklist" to be run through- an "obstacle", really- to our ultimate enjoyment of our aquarium.

When you think about it, setting the stage for life in our aquariums is the SINGLE most important thing that we do. If we utilize a different mind set, and deploy a lot more patience for the process, we start to look at it a bit differently.
I mean, sure, you want to rinse sand as clean as possible. You want make sure that you have a piece of wood that's been soaked for a while, and..
Wait, DO you?
I mean, sure, if you don't rinse your sand carefully, you'll get some cloudy water for weeks...no argument there.

And if you don't clean your driftwood carefully, you're liable to have some soil or other "dirt" get into your system, and more tannins being released, which leads to...well, what does it lead to?
I mean, an aquarium is not a "sterile" habitat. Let's not fool ourselves.
The natural aquatic habits which we attempt to emulate, although comprised of many millions of times the volumes of water volume and throughput that we have in our tanks- are typically not "pristine"- right? I mean, soils from the surrounding terrestrial environment carry with them decomposing matter, leaves, etc, all of which impact the chemistry, oxygen-carrying capacity, biological activity, and of course, the visual appearance of the water.

And that's kind of what our whole botanical-method aquarium adventure is all about- utilizing the "imperfect" nature of the materials at our disposal, and fostering and appreciating the natural interactions between the terrestrial and aquatic realms which occur.
Of course, much like Nature, our botanical-method aquariums make use of the "ingredients" found in the abundant materials which comprise the environment. And the "infusion" of these materials into the water, and the resulting biological processes which occur, are what literally make our tanks come alive.
And yeah, it all starts with the nitrogen cycle...
We can embrace the mindset that every leaf, every piece of wood, every bit of substrate in our aquariums is actually a sort of "catalyst" for sparking biodiversity, function, and yes- a new view of aesthetics in our aquariums.

I'm not saying that we should NOT rinse sand, or soak wood before adding it to our tanks. What I AM suggesting is that we don't "lose our shit" if our water gets a little bit turbid or there is a bit of botanical detritus accumulating on the substrate. And guess what? We don't have to start a tank with brand new, right-from-the-bag substrate.
Of course not.

We can utilize some old substrate from another tank (we have done this as a hobby for decades for the purpose of "jump starting" bacterial growth) which also has the side benefit of providing a different aesthetic as well!
And, you can/should take it further: Use that slightly algal-covered piece of driftwood or rock in our brand new tank...This gives a more "broken-in look", and helps foster a habitat more favorable to the growth of the microorganisms, fungi, and other creatures which comprise an important part of our closed aquarium ecosystems.
In fact, in a botanical-method aquarium, facilitating the rapid growth of such biotia is foundational.
It's perfectly okay for your tank to look a bit "worn" right from the start. Functional aesthetics once again! the look results from the function.
In fact, I think most of us actually would prefer that! It's okay to embrace this. From a functional AND aesthetic standpoint. Employ good husbandry, careful observation, and common sense when starting and managing your new aquarium.

So don't obsess over "pristine." Especially in those first hours.
The aquarium still has to clear a few metaphorical "hurdles" in order to be a stable environment for life to thrive.
I am operating on the assumption (gulp) that most of us have a basic understanding of the nitrogen cycle and how it impacts our aquariums. However, maybe we don’t all have that understanding. My ramblings have been labeled as “moronic” by at least one “critic” before, however, so it’s no biggie for me as said “moron” to give a very over-simplified review of the “cycling” process in an aquarium, so let’s touch on that for just a moment!

During the "cycling" process, ammonia levels will build and then suddenly decline as the nitrite-forming bacteria multiply in the system. Because nitrate-forming bacteria don't appear until nitrite is available in sufficient quantities to sustain them, nitrite levels climb dramatically as the ammonia is converted, and keep rising as the constantly-available ammonia is converted to nitrite.
Once the nitrate-forming bacteria multiply in sufficient numbers, nitrite levels decrease dramatically, nitrate levels rise, and the tank is considered “fully cycled.”
And of course, the process of creating and establishing your aquariums ecology doesn't end there.
With a stabilized nitrogen cycle in place, the real "evolution" of the aquarium begins. This process is constant, and the actions of Nature in our aquariums facilitate changes.
And our botanical-method systems change constantly.
They change over time in very noticeable ways, as the leaves and botanicals break down and change shape and form. The water will darken. Often, there may be an almost "patina" or haziness to the water along with the tint- the result of dissolving botanical material and perhaps a "bloom" of microorganisms which consume them.
This is perfectly analogous to what you see in the natural habitats of the fishes that we love so much. As the materials present in the flooded forests, ponds, and streams break down, they alter it biologically, chemically, and even physically.

It's something that we as aquarists have to accept in our tanks, which is not always easy for us, right? Decomposition, detritus, biofilms- all that stuff looks, well- different than what we've been told over the years is "proper" for an aquarium. And, it's as much a perception issue as it is a husbandry one. I mean, we're talking about materials from decomposing botanicals and wood, as opposed to uneaten food, fish waste, and such.
What's really cool about this is that, in our community, we aren't seeing hobbyists freak out over some of the aesthetics previously associated with "dirty!"
It's seen as a fundamental part of the evolution of the tank.
And soon, you'll see the emergence of elegant, yet simple life forms, such as bacterial biofilms and fungal growths. We've long maintained that the appearance of biofilms and fungi on your botanicals and wood are to be celebrated- not feared. They represent a burgeoning emergence of life -albeit in one of its lowest and (to some) most unpleasant-looking forms- and that's a really big deal.
Biofilms, as we've discussed ad nauseam here, form when bacteria adhere to surfaces in some form of watery environment and begin to excrete a slimy, gluelike substance, consisting of sugars and other substances, that can stick to all kinds of materials, such as- well- in our case, botanicals. It starts with a few bacteria, taking advantage of the abundant and comfy surface area that leaves, seed pods, and even driftwood offer.
The "early adapters" put out the "welcome mat" for other bacteria by providing more diverse adhesion sites, such as a matrix of sugars that holds the biofilm together. Since some bacteria species are incapable of attaching to a surface on their own, they often anchor themselves to the matrix or directly to their friends who arrived at the party first.
Tannin's creative Director, Johnny Ciotti, calls this period of time when the biofilms emerge, and your tank starts coming alive "The Bloom"- a most appropriate term, and one that conjures up a beautiful image of Nature unfolding in our aquariums- your miniature aquatic ecosystem blossoming before your very eyes!
The real positive takeaway here:
Biofilms and fungal growths are really a sign that things are working right in your aquarium! A visual indicator that natural processes are at work, helping forge your tank's ecosystem.

About a year ago, had a discussion with our friend, Alex Franqui. His beautiful Igarape-themed aquarium pictured above, "bloomed" beautifully, with the biofilms, fungal growths, and sediments working together to create a stunning, very natural functioning- and appearing-ecosystem. He was not repulsed at all. Rather, he was awed and fascinated...He celebrated what was occurring in his tan. He has an innate understanding of the ecological process, and replaced "fear and loathing" with excitement.
Alex is a hardcore aquascaper, and to see him marveling and rejoicing in the "bloom" of biofilms in his tank is remarkable.
He gets it.
And it turns out that our love of biofilms is truly shared by some people who really appreciate them as food...Shrimp hobbyists! Yup, these people (you know who you are!) go out of their way to cultivate and embrace biofilms and fungi as a food source for their shrimp.

They get it.
And this makes perfect sense, because they are abundant in Nature, particularly in habitats where shrimp naturally occur, which are typically filled with botanical materials, fallen tree trunks, and decomposing leaves...a perfect haunt for biofilm and fungal growth!
Nature celebrates "The Bloom", too.

There is something truly remarkable about natural processes playing out in our own aquariums, as they have done for eons in the wild.
Time for a little thought experiment...
You're a fish.
Seriously. Make yourself a fish...for a second. (I think I'd be a Black Ghost Knife, FYI. What, you thought I'd be a Cardinal Tetra or something? Really? Sheesh!)

Your main goals in life are avoiding predators, finding food, and reproducing. The "finding food" part is what we're focusing on in this experiment.
Now, back to being you for a second.

Would you like to move into a house which didn’t have a refrigerator full of food? I wouldn’t, for sure. Unlike humans, fishes seem to have not lost their "genetic programming" for grazing and hunting for food. Let’s face it—most of the waking hours of aquatic animals are devoted to acquiring food and reproducing. They need to have some food sources available to "hunt and graze" for.
That’s reality.
So why not help accommodate our your animals’ needs by supplementing their prepared diet with some “pre-stocked” natural foods in their new home? You know, slow down, get things "going" a bit, and then add the fishes?
I’m not talking about tossing in a few frozen brine shrimp hours before the first fishes go in the tank—I’m talking about a deliberate, systematic attempt to cultivate some living food sources within the system before a fish ever hits the water! Imagine a “new” system offering numerous foraging opportunities for its new inhabitants!

in our world, that might mean allowing some breakdown of the botanicals, or time for wood or other botanicals to recruit some biofilms, fungi- even turf algae on their surfaces before adding the fishes to the aquarium.
“Scott. You’re being impractical here! It could take months to accomplish this. I’ve just spent tons of money and time setting up this tank and you want me to deliberately keep this tank devoid of fishes while the biofilms form and Daphnia reproduce?”
Yes. Seriously.
I am a bit crazy. I’ll give you that.
Yet, with my last few systems, this is exactly what I did.
Why?
Well, for one thing, it creates a habitat for sighs which is uniquely suited to their needs in a different way.
Think abut the way most fishes live. They spend a large part of their existence foraging for food. Even in the cozy, comfortable confines of the aquarium.
So, why not create conditions for them which help accommodate this instinctive behavior, and provide opportunities for supplemental (or primary!) nutrition to be available to them by foraging.
Now, I have no illusions about this idea of "pre-stocking" being a bit challenging to execute.
I’m no genius, trust me. I don’t have half the skills many of you do but I have succeeded with many delicate “hard-to-feed” fishes over my hobby “career.”
Any "secret" to this?
None at all. I'm simply really fucking patient.
Success in this arena is simply a result of deploying..."radical patience." The practice of just moving really slowly and carefully when adding fishes to new tanks.
A really simple concept.
I mean, to some extent, we already deploy this practice with our botanical-method tanks, right? The very process of creating a botanical-method aquarium lends itself to this "on board supplemental food production" concept. A concept that's pretty analogous to what occurs in Nature, right?

And one of the most important functions of many botanically-influenced wild habitats is the support of food webs. As we've discussed before in this blog, the leaf litter zones in tropical waters are home to a remarkable diversity of life, ranging from microbial to fungal, as well as crustaceans and insects...oh, and fishes, too! These life forms are the basis of complex and dynamic food webs, which are one key to the productivity of these habitats.
You can do this. You can foster such a "food web"- or the basis for one- in your aquarium!
Wait a minimum of three weeks—and even up to a month or two if you can stand it, and you will have a surprisingly large population of micro and macro fauna upon which your fishes can forage between feedings.
Having a “pre-stocked” system helps reduce a considerable amount of stress for new inhabitants, particularly for wild fishes, or fishes that have reputations as “delicate” feeders.
And think about it for a second.
This is really a natural analog of sorts. Fishes that live in inundated forest floors (yeah, the igapo again!) return to these areas to "follow the food" once they flood. In fact, other than the physical flooding itself, this pursuit of food sources is the key factor in the migration of fishes into these habitats.
So, what would some candidate organisms be for "pre-stocking" a botanical-style aquarium?
How about starting with (okay, sounding a bit commercial, I know, but...) the versatile Purple Non Sulphur Bacteria (PNSB), Rhodopseudomonas palustris- the species which forms our product, "Culture." PNSB are useful for their ability to carry out a particularly unusual mode of metabolism: "anaerobic photoheterotrophy."

In this process, they consume organic wastes while inhabiting moderately illuminated and poorly oxygenated microhabitats (patches of detritus, leaf litter beds, shallow depths of substrate, deeper pores of expanded clay media, etc.). In addition to helping to maintain an ecologically stable microhabitat, "Culture" provides a nutritious live food source for zooplankton as well as soil mesofauna.
Yeah, these guys form the "foundation" of your food chain! (And yeah, we'll have "Culture" back in stock soon...we're re-thinking the packaging to make the product more affordable!)
Next, perhaps some "starter cultures" of organisms like Paramecium, Euglena, etc. You know, "infusoria" from the old school aquarium literature. And then, small crustaceans like Daphnia, and copepods of various types.

Pure cultures of all of these organisms are available online from various biological supply houses. They're a fantastic source of biodiversity for your aquarium!
Of course, the more daring among you may want to introduce various worms, like "Black Worms" or Tubifex worms, if you can find clean cultures of them. For that matter, even "blood worms", which are actually the larval phase of the midge.
Some organisms, such as nematodes and chironomids ("Bloodworms!") will dig into the leaf structures and feed on the tissues themselves, as well as the fungi and bacteria found in and among them. These organisms, in turn, become part of the diet for many fishes.

These organisms, in turn, become part of the diet for many fishes.
Food Web.
And the resulting detritus (here we go again!) produced by the "processed" and decomposing plant matter is considered by many aquatic ecologists to be an extremely significant food source for many fishes, especially in areas such as Amazonia and Southeast Asia, where the detritus is considered an essential factor in the food webs of these habitats.
It performs the same function in an aquarium- if we allow it to.

And of course, if you observe the behavior of many of your fishes in the aquarium, such as characins, cyprinids, Loricariids, and others, you'll see that, in between feedings, they'll spend an awful lot of time picking at "stuff" on the bottom of the tank. In a botanical method aquarium, this is a pretty common occurrence, and I believe an important benefit of this type of system.
When you start seeing your fishes "graze" casually on the materials that pop up on your driftwood and botanicals, you start realizing that, although it might not look like the aesthetics we have had in mind in years past, it is a beautiful thing to our fishes!
You can do this.
Remember, it's all part of the game with a botanical-influenced aquarium. Understanding, accepting, and celebrating "The Bloom" is all part of that "mental shift" towards accepting and appreciating a more truly natural-looking, natural-functioning aquarium.

The "price of admission", if you will- along with the tinted water, decomposing leaves, etc., the metaphorical "dues" you pay, which ultimately go hand-in-hand with the envious "ohhs and ahhs" of other hobbyists who admire your completed aquarium when they see it for the first time.
Stay studious. Stay diligent. Stay observant. Stay patient...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
Perpetual darkness...
Okay, that was an admittedly "dark"-sounding title, but it's perfectly appropriate for today's topic...How to get- and keep- your water as tinted as possible. Or, at least, what materials would do the best job in terms of "color production."
We as a group are kind of obsessed with this.

And yeah, it's a good question!
Now, first off- let's all remember that the color of the water has absolutely NO relationship to its pH or carbonate hardness. It just doesn't. You can have water that looks super dark brown, yet has a pH of 8.5 or whatever. And conversely, it's just as possible to have crystal clear blue-white water that's soft, and has a pH of 4.5. We have to get beyond the social media-style "blackwater" definition, which seems to be, "If the water is tinted, it's a blackwater aquarium!"
Now, look, if you just want the nice color but could care less about the pH and hardness, that's fine. For the benefit of the hobby as a whole, please don't perpetuate the confusing narrative about blackwater aquariums by telling others that you have "blackwater." You have a "tinted" aquairum.
And that's just fine.

So, yeah-I'm not going to launch into a long drawn out description today about how ecologists define "blackwater" and what specific chemical characteristics make it up- we've covered it enough over the years...you can deep dive here or elsewhere to get that.

Okay, micro-rant over. Let's get back to the topic.
Remember, this piece is not about how to make blackwater...It's a little more superficial than that...it's about creating an aquarium with color and maintaining it.
First off, one of the "keys" to getting your color that lovely brown is to select the right types and quantities of botanical materials to assist. Now, I'll be the very first to raise my hand and call BS on anyone who claims to have a perfect "recipe" for how many Catappa leaves per liter or whatever you must use to achieve a specific color. Sure, you could come up with some generic recommendations, but they're not always applicable to every tank or situation.
Yes...there are simply so many variables in the equation- many which we probably haven't even considered yet-that it would be simply guessing. Just like Nature, to some extent...
What I can do is recommend some materials which we have found over the years to generally impart the most reliable and significant color to water. In no particular order, I'll give you my thought on a few of my personal faves. There are a lot more, but these are some that consistently show up on my "fave" list.
Wood
Yep, you heard me. One of the very best sources of tint-producing tannins in our aquariums is wood. I've told you many times, wood imparts tannins, lignin, and all sorts of other "stuff" from the exterior surfaces and all of those nooks and crannies that we love so much into the water.
Ahh...the tannins.
Now, I don't know about you, but I'm always amused (it's not that hard, actually) by the frantic posts on aquarium forums from hobbyists that their water is turning brown after adding a piece of wood. I mean- what's the big deal?
Oh, yeah, not everyone likes it...I forgot that. 😂
The reality, though, as you probably have surmised, is that wood will continue to leach tannins to a certain extent pretty much for as long as it's submerged. As a "tinter", I see this as a great advantage in helping establish and maintain the blackwater look, and to impart humic substances that are known to have health benefits for fishes.
Some wood types, like Mangrove ( a wood we don't have at the moment), tend to release more tannins than others over long periods of time. Other types, like "Spider Wood", will release their tannins relatively quickly, in a big burst. Some, such as Manzanita wood, seem to be really "dirty", and release a lot of materials over long periods of time. All will recruit fungal growths and bacterial biofilms.
And the biocover on the wood is a unique functional aesthetic, too, as we rant on and on about here!

Bark
I'm a huge fan of tree bark to impart not only color, but beneficial tannins into the water. Because of its composition and structure, bark tends to last a very long time when submerged, and tends to impart a lot of color to the water over the long term.
And to be quite honest, almost all of the bark products we've played with over the years seem to work equally as well. The real difference in bark is the "form factor" (appearance) and the color that they impart to the water over time. Some, such as Red Mangrove bark or Cutch bark, will impart a much deeper, reddish-brown tint to the water than say, an equal quantity of catappa bark. And our soon-to-be-released Ichnocarpus bark really packs in this reddish brown color! You're gonna love this stuff!

Ounce for ounce, gram for gram, I've always felt that various types of bark always impart the most color to the water over almost any other materials.
"Skyfruit Pods"
These are very interesting, woody pods, derived from the outer "valve" of the fruit of the Swietenia macrophylla tree, which hails from a wide range of tropical locales (although native to Brazil), and are just the sort of thing you'd find floating or submerged in a tropical jungle stream. Often called "Skyfruit" by locals in the regions in which they're found because they hang from the trees- a name we fell in love with!
These botanicals can leach a terrific amount of tannins, akin to a similar-sized piece of Mopani wood or other driftwood. They are known to be full of flavonoids, saponins, and other humic substances, which have known positive health effects on fishes. Like bark, it lasts a good long time and recruits some biofilms and fungal growths for good measure.

Live Oak Leaves/Magnolia Leaves
Despite their humble North American origins, these leaf types impart more color, ounce per ounce, than just about any of our fave tropical leaves. And they both last very long time...Like, I've had specimens of live oak leaves stay intact for several months!
It's really important to think of leaves as not just a "coloring agent" for your water, but as a sort of biological support mechanism for your burgeoning ecosystem. They actively recruit fungi, bacterial biofilms, and other microorganisms which enrich the overall aquatic environment in your tank.

Cones
Alder cones (Aalnus glutinosa and Alnus incana) and Birch cones (Betula occidentalis), have been widely utilized by aquarium hobbyists in Europe for some time. Betta and ornamental shrimp breeders are fond of the tannins released into the water by these cones, and their alleged anti fungal and antibacterial properties. There has also been much study by hobbyists about the pH reduction attributes of these cones, too.
A study done a few years back by a Swedish hobbyist using from one to six cones in a glass containing about 10 ounces of tap water, with a starting ph of around 8.12, was able to affect a drop to 6.74 with one cone after about two weeks, 4.79 with 2 cones after two weeks, and an amazing 3.84 with 6 cones after the same time period! The biggest part of the drop in pH occurred in the first 12 hours after immersion of the cones!

Now, I'm the last guy to tell you that a bunch of cones is the perfect way to lower pH, but this and other hobby-level studies seem to have effectively have demonstrated their ability to drive pH down in "malleable" (soft) water...
Coconut-based products (Coco Curls, "Fundo Tropical", "Substrato Fino")
There's something about coconuts...The materials which are derived from the husks of coconuts seem to produce a significant amount of tannins and impart color to the water. Of course, "Substrate Fino" and "Fundo Tropical" are smaller, or finer-textured materials which work primarily as "substrate enhancers", and not strictly as "color-producing agents", because there is an initial "burst", which subsides over time.
Now, one of the novel applications for these finer botanical materials to take advantage of their color producing ability is to place them in a fine mesh filter bag and allow water to flow around or through them, like filter media. Essentially, a more sustainable alternative to the old peat moss trick...

Oak Twigs
For an interesting look and some nice color, I'm a big fan of oak twigs. Oak has a nice bark which imparts a deep brownish/yellow color to the water and it's quite distinctive. There is a reason why our "Twenty Twigs" packs are pretty popular, and it's not just because you get a bunch of cool sticks!

When mixed with leaves and/or other botanical materials, not only do you get an incredible "framework" for a cool ecosystem, you get an incredible aesthetic as well!

Now, this is an absolutely cursory list.. I could have easily listed 10 or more items. No doubt, some of you hardcore enthusiasts are screaming at your screens now: "WTF Fellman, you didn't include_______!"
And of course, that's the beauty of natural materials...There are numerous options!
Another note on the colors to expect from various botanical materials. As you might suspect, many of the lighter colored ones will impart a correspondingly lighter tint to the water. And, some leaves, such as Guava or Loquat, also impart a more yellowish or golden color to the water, as opposed to the brownish color which Jackfruit and Catappa are known for.

A lot of you ask about things that impact how long the water retains it's tint.
This kind stuff is a big deal for us- I get it! Many hobbyists who have perhaps added some catappa leaves, "blackwater extracts", or rooibos tea to their water contact me asking stuff like why the water doesn't stay tinted for more than a few days. Now, I'm flattered to be a sort of "clearing house" for this stuff, but I must confess, I don't have all the answers.
So, "Why doesn't my water stay tinted, Scott?"
Well, I admit I don't know. Well, not for certain, anyways!
I do, however, have some information, observations, and a bunch of ideas about this- any of which might be literally shot to pieces by someone with the proper scientific background. However, I can toss some of these seemingly uncoordinated facts out there to give our community some stuff to "chew on" as I offer my ideas up.
Now, perhaps it starts with the way we "administer" the color-producing tannins.
Like, I personally think that utilizing leaves, bark, and seed pods is perhaps the best way to do this. I'm sure that you're hardly surprised, right? Well, it's NOT just because I sell these material for a living...It's because they are releasing tannins, humic substances, and other compounds into the water "full time" during their presence in the aquarium as they break down. A sort of "on-board" producer of these materials, with their own "half life" (for want of a better term!).
And, they also perform an ecological role, providing locations for numerous life forms (like fungal growths) surface area upon which to colonize. They become part of the ecosystem itself. A few squirts of "blackwater extracts" won't do that, right?

The continuous release of tint-producing compounds from botanical materials keeps things more-or-less constant. And, if you're part of the "school" which leaves your botanicals in your aquarium to completely break down, you're certainly getting maximum value out of them! And if you are continuously adding/replacing them with new ones as they completely or partially break down, you're actively replenishing and adding additional "tint-producing" capabilities to your system, right?
There is another way to "keep the tint" going in your tanks, and it's pretty easy. Now, those of you who know me and read my rambling or listen to "The Tint" podcast regularly know that I absolutely hate shortcuts and "hacks" in the aquarium hobby. I preach a long, patient game and letting stuff happen in its own time...
Nonetheless, there ARE some that you can employ that don't make you a complete loser, IMHO.😆
When you prepare your water for water changes, it's typically done a few days to a week in advance, so why not use this time to your advantage and "pre-tint" the water by steeping some leaves in it? Not only will it keep the "aesthetics" of your water ( can you believe we're even talking about "the aesthetics of water?") consistent (i.e.; tinted), it will already have humic substances and tannins dissolved into it, helping you keep a more stable system.
Obviously, you'd still check your pH and other parameters, but the addition of leaves to your replacement water is a great little "hack" that you should take advantage of. (Shit, I just recommended a "hack" to you...)
It's also a really good way to get the "look" and some of the benefits of blackwater for your system from the outset, especially for those of you heathens that like the color of blackwater and despise all of the decomposing leaves and seed pods and stuff!
So, if you're just setting up a brand new aquarium, and have some water set aside for the tank, why not use the time while it's aging to "pre-tint" it a bit, so you can have a nice dark look from day one? It's also great if you're setting up a tank for an aquascaping contest or other same-day club event that would make it advantageous to have a tinted tank immediately.
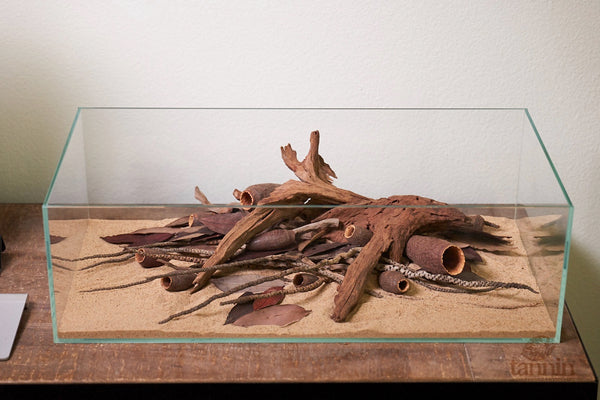

I must confess that yet another one of the more common questions we receive here from hobbyists is, "How can I get the tint in my tank more quickly?"- and this is definitely one way!
How many botanicals to use to accomplish this?
Well, that's the million dollar question.
Who knows?
It all gets back to the (IMHO) absurd "recommendations" that have been proffered by vendors over the years recommending using "x" number of leaves, for example, per gallon/liter of water. There are simply far, far too many variables- ranging from starting water chem to pH to alkalinity, and dozens of others- which can affect the "equation" and make specific numbers unreliable at best.

We did, too, in the early days of Tannin. And it was kind of stupid really. There just is no hard-and-fast answer to this. Every situation is different. You need to kind of go with your instinct. Go slowly. Evaluate the appearance of your water, the behaviors of the fishes...the pH, hardness, TDS, nitrate, phosphate, or other parameters that you like to test for.
It's really a matter of experimentation.

I'm a much bigger fan of "tinting" the water based on the materials in the aquarium. Letting Nature have at it. The botanicals will release their "contents" at a pace dictated by their environment. And, when they're "in situ", you have a sort of "on board" continuous release of tannins and humic substances based upon the decomposition rate of the materials you're using, the water chemistry, etc.
Replacement of botanicals, or addition of new ones, as we've pointed out many times, is largely a subjective thing, and the timing, frequency, and extent to which materials are removed or replaced is dependent upon multiple factors, ranging from base water chemistry to temperature, to the types of aquatic life you keep in the tank (ie; xylophores like certain Plecos, or strongly grazing fishes, like Headstanders, will degrade botanicals more quickly than in a tank full of characins and such).
(The part where Scott bashes the shit out of the idea of using "blackwater extracts" and Rooibos tea. This could get nasty!)
If you haven't heard of it before, there is this stuff called Rooibos tea, which, in addition to bing kind of tasty, has been a favored "tint hack" of many hobbyists for years. Without getting into all of the boring details, Rooibos tea is derived from the Aspalathus linearis plant, also known as "Red Bush" in South Africa and other parts of the world.

(Rooibos, Aspalathus linearis. Image by R.Dahlgr- used under CC-BY S.A. 2.5)
It's been used by fish people for a long time as a sort of instant "blackwater extract", and has a lot going for it for this purpose, I suppose. Rooibos tea does not contain caffeine, and and has low levels of tannin compared to black or green tea. And, like catappa leaves and other botnaicals, it contains polyphenols, like flavones, flavanols, aspalathin, etc.
Hobbyists will simply steep it in their aquariums and get the color that they want, and impart some of these substances into their tank water. I mean, it's an easy process. Of course, like any other thing you add to your aquarium, including leaves and botanicals, it's never a bad idea to know the impact of what you're adding.
Like using botanicals, utilizing Rooibos tea bags in your aquarium requires some thinking, that's all.
The things that I personally dislike about using tea or so-called "blackwater extracts" are that you are simply going for an effect, without getting to embrace the functional aesthetics imparted by adding leaves, seed pods, etc. to your aquarium as part of its physical structure and ecology, and that there is no real way to determine how much you need to add to achieve______.
Obviously, the same could be said of botanicals, but we're not utilizing botanicals simply to create brown water or to target specific pH parameters, etc. We're trying to create an ecology that is similar to what you'd see in such habitats in Nature.

Yet, with tea or commercial blackwater extracts, you sort of miss out on replicating a little "slice of Nature" in your aquarium. The building of an ecosystem. Which is why we call this the botanical method. It's not a "style" of aquascaping! And of course, it's fine if your goal is just to color the water, but it's more of an aesthetically-focused aquarium at that point.
I also understand that some people, like fish breeders who need bare bottom tanks or whatever- like to condition water without all of the leaves and twigs and nuts we love. They want the humic substances and tannins, but really don't need/want the actual leaves and other materials in their tanks.
And, when it comes to tea and these commercial extracts, I don't think the stuff lasts all that long. I personally believe that the tint-producing tannins in "tea" are potentially taken up quickly by substrate materials, filter media, etc. And unless you're keeping tea bags in your tank on a continuous basis, you'll always experience some "color loss" after some period of time.
Yes it works to impart some color and tannins. Creating infusions or extracts is useful, if you understand their purpose and limitations. They have a place in the hobby for sure.
It's why we got into the game with our botanical-based "Shade" products. We're currently sold out and are working with our supplier on a reformulated version. Seems as though we need to make a "darker" mix!

On the other hand, if you're trying to replicate the look and function (and maybe some of the parameters) of THIS:

You won't achieve it by using THIS:

It's simply another shortcut.
Not good or bad. Just a way to get the end "effect" faster, and without the other collateral benefits we discussed.
And look, I understand that we are all looking for the occasional shortcuts and easier ways to do stuff. And I realize that none of what we proffer here at Tannin is an absolute science. It's likely more of an "art" at this point, with a little science behind it.
Think about it: There is no current way available to the hobby to test for "x" types or amounts of tannins (of which there are hundreds of types) in aquariums. I mean, there are tannin test kits, but they're used for wine making and such...Perhaps there is some tangential application for our purposes, but I'm not really sure what practical information. we could extract from the results.
And, I have not found a study thus far which analyzed wild habitats (say, Amazonia) for tannin concentrations and specific types, so we have no real model to go on.

The best we can do is create a reasonable facsimile of Nature.
And, in Naturę, a lot of the tint in blackwater environments comes from dissolved fulvic and humic acids from...soils. Yeah, geology is the key, IMHO, to truly "realistic" blackwater habitats. This is why I've been very picky on sourcing the materials and figuring out recipes for our NatureBase sediment substrates. They are intended to support these types of systems.

Understanding substrates and their role in both the physical environment and the ecology of our aquariums is still a wildly under-appreciated concept in the aquarium hobby, IMHO. We'll keep coming back to this in the future, I'm certain.
And keeping the water tinted is something that many botanical method aquarists are interested in. This wonderful "collateral benefit" of our approach is something that's easy to get addicted to!
Now, all of these ideas are okay to impart some color to your water. Some do more, as we've discussed ad nauseam. And none of them will work to full advantage if your aquarium is removing them as fast as you're imparting them into the water. So, go easy on chemical filtration media like carbon. I didn't say NOT to use them...Just don't use a ton of them! Use less than what the manufacturer recommends.
What about plants?

Well, I have a theory about plants and tannins...
First off, as you know by now, you absolutely can keep plants in blackwater aquariums. We've talked about this a million times over the years. And yet, interestingly, you can't always keep "blackwater conditions" (at least, color-wise) in planted aquariums! There has been much geeky discussion on this topic.
Tannin are interesting things. Think about this:
Tannins are known to bind up heavy metals and minerals. The roots of aquatic plants prefer to take up bound-up minerals and metals...So, another theory of mine is that heavily planted tanks do actually remove some of the visual "tint" (ie; the tannins) from the water via uptake from their roots.
Make sense? Maybe?
Okay, I could go on and on all day throwing out all sorts of theories and unsubstantiated (via lab tests and rigorous studies, anyways) ideas on this topic...But I think I gave you enough here to get the party started. I encourage you to do some homework. We need to ask these questions to people who really understand the chemistry here. I think that there might be some good answers out there.
And, back to the "color thing" to close on here...
I admit, visual "tint" is probably THE single most superficial aspect of what we experience with botanical-method aquariums- but the most obvious, and likely the most impactful to the casual hobbyist or observer.

It's just as important to understand the collateral benefits of utilizing botanical materials- a subject we've discussed dozens of times here. However, in the end, it's the look of your aquarium that is what you have to experience each and every day, and if having an understanding of which materials can bring you the aesthetic experience you're after in a more effective way- well, then this is a worthwhile discussion, right?
I think that it is.
Stay curious. Stay resourceful. Stay enthusiastic. Stay observant. Stay appreciative. Stay tinted...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
Anything goes? Well, sort of...
The garden suggests there might be a place where we can meet Nature halfway."-Michael Pollan
It's long been suggested that an aquarium is sort of like a garden, right? And, to a certain extent it is. Of course, we can also allow our tanks to evolve on a more-or-less "random" path than the word "garden" implies...

Perhaps one of the most liberating things about our botanical-method aquariums is that there is no set "style" that you have to follow to "arrange" botanical materials in your tank.
When you look at those amazing pictures of the natural habitats we love so much, you're literally bombarded with the "imperfection" and apparent randomness that is Nature. Yet, in all of the "clutter" of an igarape flooded forest, for example, there is a quiet elegance to it. There is a sense that everything is there for a reason- and not simply because it looks good. It IS perfect. Can't we bring this sense to our aquariums?
I think we can...simply by meeting Nature halfway.

To a certain extent, it's "anything goes" in terms of adding materials to represent the wild habitats. I mean, when you think about flooded forest floors and rainforest streams, you're talking about an aggregation of material from the forest that has accumulated via wind, rain, and current. The influences on the "design" are things like how something arrives into the water, and how it gets distributed by water movement.
Nature offers no "style guide."
Rather, she offers clues, based on her processes.
I mean, sure, you could and should certainly use some aesthetic thought in the concept, but when you're trying to recreate what in Nature is a more-or-less random thing, you probably don't want to dwell too much on the concept! You don't want to over-think "random" too much, right? Rather, put your effort into selecting suitable materials with which to do the job.

For a bit more context, just think for just a second, about the stems and branches that we love so much in our aquascaping. Those of us who obsessively study images of the wild tropical habitats we love so much can't help but note that many of the bodies of water which we model our aquariums after are filled with tree branches and stems.
Since many of these habitats are rather ephemeral in nature, they are only filled up with water part of the year. The remainder of the time, they're essentially dry forest floors.

And what accumulates on dry forest floors?
Branches, stems, leaves, and other materials from trees and shrubs. When the waters return, these formerly terrestrial materials become an integral part of the (now) aquatic environment. This is a really, really important thing to think of when we aquascape or contemplate how we will use botanical materials like the aforementioned stems and branches.
They impact both function and aesthetics of an aquarium...Yes, what we call "functional aesthetics" rears its head again!

There is no real rhyme or reason as to why stuff orients itself the way it does once submerged. There are numerous random factors involved.
I mean, branches fall off the trees, a process initiated by either rain or wind, and just land "wherever." Which means that we as hobbyists would be perfectly okay just literally tossing materials in and walking away! Now, I know this is actually aquascaping heresy- Not one serious 'scaper would ever do that...right?
On the other hand, I'm not so sure why they wouldn't!
I mean, what's wrong with sort of randomly scattering stems, twigs, and branches in your aquascape? It's a near-perfect replication of what happens in Nature. Now, I realize that a glass or acrylic box of water is NOT nature, and there are things like "scale" and "ratio" and all of that shit that hardcore 'scapers will hit you over the head with...
But Nature doesn't give a fuck about some competition's "rules"- and Nature is pretty damn inspiring, right? There is a beauty in the brutal reality of randomness. I mean, sure, the position of stones in an "Iwagumi" is beautiful...but it's hardly what I'd describe as "natural."
Natural looks...well, like what you'd see in Nature.

It's pretty hardcore stuff.
And it's all part of the reason that I spend so damn much time pleading with you- my fellow fish geeks- to study, admire, and ultimately replicate natural aquatic habitats as much as you do the big aquascaping contest winners' works. In fact, if every hobbyist spent just a little time studying some of these unique natural habitats and using them as the basis of their work, I think the hobby would be radically different.
When hobbyists interpret what they see in wild aquatic habitats stats more literally, the results are almost always stunning. And contest judges are starting to take notice...

I think that there would also be hobby success on a different level with a variety of fishes that are perhaps considered elusive and challenging to keep. Success based on providing them with the conditions which they evolved to live in over the millennia, not a "forced fit" its what works for us humans.
More awareness of both the function and the aesthetics of fascinating ecological niches, such as the aforementioned flooded forests, would drive the acceptance and appreciation of Nature as it is- not as we like to "edit" and "sanitize" it.
Taking this approach is actually a "stimulus" for creativity, perhaps in ways that many aquarists have not thought of.
There are a lot of aquatic habitats in Nature which are filled with tangles of terrestrial plant roots, emergent vegetation, fallen branches, etc., which fill small bodies of water almost completely.

These types of habitats are unique; they attract a large populations of smaller fishes to the protection of their vast matrix of structures. Submerged fallen tree branches or roots of marginal terrestrial plants provide a large surface area upon which algae, biofilm, and fungal growth occurs. This, in turn, attracts higher life forms, like crustaceans and aquatic insects. Sort of the freshwater version of a reef, from a "functionality" standpoint, right?
Can't we replicate such aquatic features in the aquarium?
Of course we can!
This idea is a fantastic expression of "functional aesthetics." It's a "package" that is a bit different than the way we would normally present an aquarium. Because we as hobbyists hesitate to densely pack an aquarium like this, don't we?
Why do you think this is?
I think that we hesitate, because- quite frankly- having a large mass of tangled branches or roots and their associated leaves and detritus in the cozy confines of an aquarium tends to limit the number, size, and swimming area of fishes, right? Or, because its felt that, from an artistic design perspective, something doesn't "jibe" about it...

Sure, it does limit the amount of open space in an aquarium, which has some tradeoffs associated with it.
On the other hand, I think that there is something oddly compelling, intricate, and just beautiful about complex, spatially "full" aquatic features. Though seldom seen in aquarium work, there is a reason to replicate these systems. And when you take into account that these are actually very realistic, entirely functional representations of certain natural habitats and ecological niches, it becomes all the more interesting!

What can you expect when you execute something like this in the aquarium?
Well, for on thing, it WILL take up a fair amount of space within the tank. Of course. Depending upon the type of materials that you use (driftwood, roots. twigs, or branches), you will, of course, displace varying amounts of water.
Flow patterns within the aquarium will be affected, as will be the areas where leaves, detritus and other botanical materials settle out. You'll need to understand that the aquarium will not only appear different- it'll function differently as well. Yet, the results that you'll achieve- the more natural behaviors of your fishes, their less stressful existence- will provide benefits that you might not have even realized possible before.
This is something which we simply cannot bring up often enough. It's transformational in our aquarium thinking.
The "recruitment" of organisms (algae, biofilms, epiphytic plants, etc.) in, on, and among the matrix of wood/root structures we create, and the "integration" of the wood into other "soft components" of the aquascape- leaves and botanicals is something which occurs in Nature as well as in the aquairum.
This is an area that has been worked on by hobbyists rather infrequently over the years- mainly by biotope-lovers. However, embracing the "mental shifts" we've talked about so much here- allowing the growth of beneficial biocover, decomposition, tinted water, etc.- is, in our opinion, the "portal" to unlocking the many secrets of Nature in the aquarium.

The extraordinary amount of vibrance associated with the natural growth on wood underwater is an astounding revelation. However, our aesthetic sensibilities in the hobby have typically leaned towards a more "sterile", almost "antispetic" interpretation of Nature, eschewing algae, biofilm, etc.
However, a growing number of hobbyists worldwide have began to recognize the aesthetic and functional beauty of these natural occurances, and the realism and I think that the intricate beauty of Nature is starting to eat away at the old "sterile aquascape" mindset just a bit!

And before you naysayers scoff and assert that the emerging "botanical method" aquarium is simply an "excuse for laziness", as one detractor communicated to me not too long ago, I encourage you once again to look at Nature and see what the world underwater really looks like. There is a reason for the diversity, apparent "randomness", and success of the life forms in these bodies of water.
What is it?

It's that these materials are being utilized- by an enormous community of organisms- for shelter, food, and reproduction. Seeing the "work" of these organisms, transforming pristine" wood and crisp leaves into softening, gradually decomposing material, is evidence of the processes of life.

When you accept that seed pods, leaves, and other botanical materials are somewhat ephemeral in nature, and begin to soften, change shape, accrue biofilms and even a patina of algae- the idea of "meeting Nature halfway" makes perfect sense, doesn't it?
You're not stressing about the imperfections, the random patches of biofilm, the bits of leaves that might be present in the substrate. Sure, there may be a fine line between "sloppy" and "natural" (and for many, the idea of stuff breaking down in any fashion IS "sloppy")- but the idea of accepting this stuff as part of the overall closed ecosystem we've created is liberating.
Sure, we can't get every functional detail down- every component of a food web- every biochemical interaction...the specific materials found in a typical habitat- we interpret- but we can certainly go further, and continue to look at Nature as it is, and employ a sense of "acceptance"- and randomness-in our work.

I'm not telling you to turn your back on the modern popular aquascaping scene; to disregard or dismiss the brilliant work being done by aquascapers around the world, or to develop a sense of superiority or snobbery, and conclude that everyone who loves this stuff is a sheep...
Noooooo.
Not at all.
I'm simply the guy who's passing along the gentle reminder from Nature that we have this great source of inspiration that really works! Rejoice in the fact that Nature offers an endless variety of beauty, abundance, and challenge- and that it's all there, free for us to interpret it as we like. Without aesthetic rules, rigid standards, and ratios. The only "rules" are those which govern the way Nature works with materials in an aquatic environment.
A botanical-method aquarium features, life, death, and everything in between.
It pulses with the cycle of life, beholden only to the rules of Nature, and perhaps, to us- the human caretakers who created it.
But mainly, to Nature.
The processes of life which occur within the microcosm we create are indifferent to our desires, our plans, or our aspirations for it. Sure, as humans, we can influence the processes which occur within the aquarium- but the ultimate outcome- the result of everything that we did and did not do- is based solely upon Nature's response.

In the botanical-style aquarium, we embrace the randomness and unusual aesthetic which submerged terrestrial materials impart to the aquatic environment. We often do our best to establish a sense of order, proportion, and design, but the reality is that Nature, in Her infinite wisdom borne of eons of existence, takes control.
It's a beautiful process. Seemingly random, yet decidedly orderly.
Think about that for a bit.
Stay curious. Stay bold. Stay creative. Stay thoughtful...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
Specialized diets, "Leopard Frogs", and re-thinking assumptions...
I'm fascinated by the dietary preferences of fishes. How they've evolved over eons to consume various items found in their environments; how many fishes became "specialists" as an adaptation to the habitats in which they live.
And, as an aquarist who derives great pleasure from seeing his fishes "live off the land" and consume foods from the aquarium environment in which they reside, I really find some of the seunderlying feeding strategies fascinating. One of the more interesting examples is the consumption of wood by various species of fishes.

We read a lot about fishes which eat wood and wood-like materials.
Of course, the ones that come immediately to mind are the Loricariidae, specifically, Panaque species. Now, I admittedly am the last guy who should be authoritatively discussing the care of catfishes, having maintained maybe a couple dozen or so species during a lifetime of aquarium keeping. However, I do understand a little bit about their diets and the idea of utilizing wood- and botanical materials- in the aquarium for the purpose of supplementing our fishes' diets!

And of course, I'm equally fascinated by the world of biofilms, decomposition, microorganism growth and detritus...And this stuff plays right into that!
Now, the idea of xylophagy (the consumption and digestion of wood) is of course, a pretty cool and interesting adaptation to the environment from which these fishes come from. And as you'd suspect, the way that wood is consumed and digested by these fishes is equally cool and fascinating!

It's thought by ichthyologists that the scraping teeth and highly angled jaws of the Loricariidae are a perfect adaptation to this feeding habit of "scraping" wood. And of course, it's even argued among scientists that these fishes may or may not actually digest the wood they consume! While scientists have identified a symbiotic bacteria which is found in the gut of these fishes that helps break down wood components, it's been argued by some the the fishes don't actually digest and metabolize the wood; indeed deriving very little energy from the wood they consume!
Hmmm...
In fact, a lab study by Donovan P. German was described in the November, 2009 Journal of Comparative Physiology, in which several species were fed wood and found to actually digest it quite poorly:
"...in laboratory feeding trials, (Pterygoplichthys cf. nigrolineatus and Hypostomus pyrineusi) lost weight when consuming wood, and passed stained wood through their digestive tracts in less than 4 hours. Furthermore, no selective retention of small particles was observed in either species in any region of the gut. Collectively, these results corroborate digestive enzyme activity profiles and gastrointestinal fermentation levels in the fishes’ GI tracts, suggesting that the wood-eating catfishes are not true xylivores such as beavers and termites, but rather, are detritivores like so many other fishes from the family Loricariidae."
Did you see that? Detritioves. Like, they're taking in wood to get other stuff out of the deal... And detritus is comprised of stuff like macrophytes, algae, and particulate organic carbon.
Hmm...
And this little nugget from the same study: "...The fishes consumed 2–5% of their body mass (on a wet weight basis) in wood per day, but were not thriving on it, as Pt. nigrolineatus lost 1.8 ± 0.15% of their body mass over the course of the experiment, and Pt. disjunctivus lost 8.4 ± 0.81% of their body mass."
Oh, that's weird.
Yet, anatomical studies of these fishes showed that the so-called "wood-eating catfishes" had what physiologists refer to as "body size-corrected intestinal lengths" that were 35% shorter than the detritivore species. What does this mean? Could they have perhaps had at one time- and subsequently lost- their ability to digest wood?
Maybe?
Arrgh!

And to make it even weirder, check out this passage from a study by Lujan, Winemiller, and Armbruster:
"Loricariids have a dense endoskeleton and are covered with dermal plates composed primarily of calcium phosphate, giving them a high physiological demand for dietary phosphorus. Paradoxically, the rivers and streams inhabited by loricariids as well as the detritus and biofilm that most loricariids consume tend to be highly Phosporus deficient."
The same study noted that, "Loricariids as a whole are largely unable to digest lignocellulose, and instead derive most nutrients and energy from easily digestible breakdown products (e.g., disaccharides and dipeptides) that are produced during microbial degradation of submerged, decomposing wood."
Oh, interesting!
I think it's yet another case of us as hobbyists drawing innocent conclusions based on anecdotal or superficial observations. I mean,"... they're munching on my wood, therefore, they must be 'eating' it!"

Now, to the point of the argument that most loricariids are primarily detritivores, consuming a matrix of biofilm, algal growth, microorganisms, and (for want of a better word) "dirt"- what does this mean to us as hobbyists? Well, for one thing, this has made them remarkably adaptable fishes in the aquarium. They will definitely rasp at wood", but according to the studies I just cited, they are not "eating" it, per se.
Now, my personal experience with Loricariidae is nothing like many of yours, and an observation I've made over the years is at best anecdotal- but interesting:
If you follow "The Tint", you know I've had a years-long love affair with Peckolotia compta aka "L134 Leopard Frog"- a beautiful little fish that is filled with charms. Well, I recall, are years back, that my first specimen seemed to have vanished into the ether following a re-configuration/rescape of my home blackwater/botanical-method aquarium. I thought somehow I either lost the fish during the re-scape, or it died and subsequently decayed without my detecting it... Pretty upsetting either way, but I couldn't find any trace of it!

For almost three months, the fish was M.I.A., just....gone.
And then one, day- there she was, poking out from the "Spider Wood" thicket that formed the basis of my newer hardscape! To say I was overjoyed was a bit of an understatement, of course! And after her re-appearance, she was out every day. She looked just as fat and happy as when I last saw her in the other 'scape...which begs the question (besides my curiosity about how she evaded detection)- What the fuck was she feeding on during this time?
Well, I suppose it's possible that some bits of frozen food (I fed frozen almost exclusively at that time) got away from my population of hungry characins and fell to the bottom...However, I'm pretty fastidious- and the other fishes (characins) were voracious mid-water-column feeders! To think that any appreciable amount got away from the hungry hoard was a bit hopeful. I believed at the time (and now am fully convinced) that it was more likely the biofilms, fungal growth, and perhaps some of the compounds from surface tissues of the "Spider Wood" I used in the hardscape that she was feeding on.
"Spiderwood" (aka Azalea root) stuff does recruit significant biological growth on it's surfaces when submerged , and curiously, in this tank, I noticed that, during the first few months, the wood seemed to never accumulate as much of this stuff as I had seen it do in past tanks which incorporated it!
I attributed this to perhaps some feeding by a population of Nanostomus eques, which have shown repeatedly in the past to feed on the biofilm or "aufwuchs" accumulating on the wood.
I'm sure that was a valid observation, but they were actively taking prepared foods as the bulk of their diet, so I have a hard time that they solely were responsible.
There was also a layer of Live Oak leaves distributed throughout the booth of the wood matrix, which, although they break down very slowly compared to other leaves we use, DO ultimately soften over time and break down over time. Since they are rather "durable", they do accumulate a lot of fungal growth and biofilms on their surfaces.

Interestingly, in this tank, I was finding little tiny amounts of very broken-down leaves, which I attributed to decomposition, but thinking back on it, looks more like the end product of "digestion" by someone!
I don't think I ever saw my L134 consuming prepared food. When I did observe her activities, she was seemingly "grazing" away at the wood surfaces and on botanicals...That's all the proof that I needed to confirm my theory that she's pretty much 100% detritivorous, and that the botanical-method aquariums she's resided in provide a sufficient amount of this material for her to consume.
To this day, I've never seen her eat prepared foods!
I have since acquired three captive-bred specimens from my friend, master breeder Sumer Tiwari, and this group has been seen to take prepared food on occasion. At the very least, adding some pellets or frozen foods seems to initial some kind of response in the fish, wether they appear to eat it or not.
So, back the the whole "xylophore thing"... After reading the studies I mentioned, I think that in the aquarium, as well as in the wild, much of what we think is actually "consumption" of the wood by the fishes is simply incidental- as in, the fishes are trying to eat the biocover and detritus on the surface tissues of the wood, and perhaps obtain some nutrition from the compounds contained in the softer portions of the wood. They apparently do a pretty good job (with their specialized mouthparts) of rasping away the surface tissues of the wood!
So, yeah- apparently, some of the wood may pass through the digestive tract of the catfishes, but it's passed without metabolizing much from it...perhaps like the way chickens consume gravel, or whatever (don't they? City boy here! WTF do I know about chickens!)...or the way some marine Centropyge angelfishes "nibble" on corals in their pursuit of algae, detritus, and biofilms.

Again, my perusal of German's scientific paper seems to support this theory:
"Catfishes supplement their wood diet with protein-rich detritus, or even some animal material to meet their nitrogen requirements. Although I did not observe animal material in the wood-eating catfish guts, Pt. disjunctivus did consume some animal material (including insects parts, molluscs, and worms), and all three species consumed detritus."
And finally, the "clincher", IMHO: "The low wood fiber assimilation efficiencies in the catfishes are highly indicative that they cannot subsist on a wood only diet."
Boom.

I mean, it's just one paper, but when he's talking about isotopic tracing of materials not consistent with digestion of wood in the guts of Loricariids, I think that pretty much puts the "eats wood" thing to bed, right? His further mention that, although some cellulose and lignin (a component of wood and our beloved botanicals!) was detected in the fish's fecal material, it was likely an artifact of the analysis method as opposed to proof that the fishes derived significant nutrition from it.
So what does all of this stuff mean to us?
Well, for one thing, once again- detritus/biofilm/fungal growths = good. Don't loathe them. Love them.
Your fishes apparently do.
I think it means that, as hobbyists probably knew, theorized, and discussed for a long time- that the Loricariids consume detritus, biofilms, and prepared foods when available. This is not exactly earth-shattering or new.
However, I think understanding that our botanical-method aquariums can- and do- provide a large amount of materials from which which these and other fishes can derive significant nutrition furthers my assertion that this type of system is perfect for rearing and maintain a lot of specialized feeders.

Materials like the harder-"shelled" botanicals (ie; "Skyfruit" pods, Cariniana pods, Mokha pods, bark, etc.) tend to recruit significant fungal growths and biofilms, and accumulate detritus in and on their surfaces. And of course, as they soften, some fishes apparently rasp and "consume" some of them directly, likely passing most of it though their digestive systems as outlined in the cited study, extracting whatever nutrition is available to them as a result. This is likely the case with leaves and softer botanicals as well.
Incidental consumption.

The softer materials might also be directly consumed by many fishes, although the nutrition may or may not be significant. However, the detritus, fungal, and microorganism growth as a result of their decomposition is a significant source of nutrition for many fishes and shrimps.
Detritivores (of which the amount of species in the trade is legion), have always done very well in botanical-method aquariums, and the accumulation of biofilms and microbial growth is something that we've discussed for a long time. By their very nature, the structure and decomposition of botanical materials make the "functional aesthetics" of our aquariums an important way to accommodate the natural feeding behaviors of our fishes.
So, the answer to the question (literally!), "Who has the (literal) guts for this stuff?" is quite possibly, "everyone!"
Now, while while we're on the subject of loricariids, a further scan of scientific literature revealed some interesting things about what these fishes are actually taking in when they "graze" in the wild. It's kind of eye opening, to me. One study revealed that loricariids consumed five principal items: sponges, organic detritus, bryophytes, bryozoans and sediment.
Wood is definitely part of the equation somewhere, but for the species examined in one of the studies I found (Rhinelepis aspera, Hypostomus regani, H. ternetzi, H. maragaritifer, H. microstomus, and Megalancistrus aculeatus) the gut content analysis was quite revealing:
The food spectrum of R. aspera is primarily "organic detritus and small quantities of sediment"; with few periphytic organisms. Although H. regani was found to consume large quantities of organic detritus as well, it also consumed "plant detritus, various sediment, and periphytic organisms" (i.e.; bryozoans, sponges and aquatic insect larvae). Bryozoans and sponges, huh?
Wow! Freshwater sponges...
The study indicated that bryozoans and organic detritus were the main food food of H. ternetzi, which, according to the gut contents of a number of individuals, tended to consume more sediment, rotifers, chironomids (i.e.; "Bloodworms'), gastropods and harpacticoids than the other species.
Harpactoids...you mean, like "copepods?" Stuff we as reefers feed all the time? H. margaritifer was found to ingest plant material. Other periphytic organisms such as insect larvae, and those bryozoans and sponges contributed to the diet of H. margaritifer.

And it gets more interesting still...
Sponges- I can't let that go.
Sponges were the principal food resource of H. microstomus and M. aculeatus, along with a healthy does of chironomids, various gastropods, Trichoptera (insects), and some bryozoans also consumed. Diets of these two fishes were composed of larger-sized items, with the finer organic detritus and such being less important than it was to the other species in the study.
This kind of information is tantalizing. It's compelling.
And what really gets me going is learning that some of our favorite, most beloved fishes are consuming large quantities of materials that I doubt any freshwater aquarist adds to his/her arsenal of foodstuffs. We're really good at feeding our catfishes baby vegetables and stuff, while typically overlooking many species' surprisingly high dietary dependency on items like insects, bryozoans, harpactoid copepods, and interestingly...sponges!

While we kind of always knew that these fishes ingested wood and "stuff", it's interesting to see what they're actually eating in the wild...especially the "stuff"- and configuring our aquariums and the supplemental and primary feeding opportunities available to the fishes accordingly.
We have some interesting, yet perhaps overlooked possibilities to provide some of these items.
In fact, there are a number of marine aquarium-purposed foods (typically targeted at certain marine angelfishes, many of which consume significant quantities of sponge) which contain sponges in their formulation. One of my favorite is Ocean Nutrition's "Angel Formula." Granted, these foods contain stuff like mussels, and other marine foods, and the sponges included are marine sponges, but I can't help but wonder if these are that morphologically or nutritionally different/palatable to the fishes than a freshwater/tree sponge would be?

Could the next great frozen Loricarid food include sponges? And we DO have harpactoid copepods available live, and in a variety of other formats intended for marine fishes and corals...Interestingly, I remember that the big "knock" by us reefers, for a long time, about some of these copepods was that they were "freshwater" varieties, and therefore didn't have the "correct" nutritional profile for marine organisms.
Hmm. We're talking about freshwater fishes here, right? Yeah.
So, like, why the hell haven't we been feeding these foods to our freshwater fishes all of these years?

Try some of these foods with your loricariids..and other fishes as well. What's to lose?
Oh, I can hear the objections:
"Impractical!"
Is it?. Online ordering is really cool. It might just catch on.
"Too much work!"
Really? C'mon. Ever cultured Grindal Worms or wingless fruit flies? THAT is "too much work" by definition.
"This is ridiculous; No need to experiment with these wacky foods. We're doing just fine now with Zucchini and stuff! Stupid."
Urghhhhh. "If man was meant to fly, he'd have wings..."
To not experiment is stupid, IMHO.
Don't be stupid. And I mean that in the kindest way possible. Don't just accept "what works" as "the way."
Push forward. Experiment. Fail quickly, or move forward rapidly with success. Play a hunch or two. Try something different. This is how advances in the hobby are made. This is how breakthroughs happen.
You gotta try.
Stay studious. Stay curious. Stay observant. Stay engaged. Stay resourceful...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
The commendable power of restraint.
One of the things that we find ourselves doing in the aquarium hobby is using " a little of this and that" in our tanks, because-well- because we seem to be fixated on lots of variety of "stuff" in our tanks, right?
I mean, there is nothing wrong with using a diversity of materials in our aquariums to express our creativity, and I DO own a company which sells a significant variety of natural aquascaping materials...However, I think it's important to consider exactly what it is we're trying to accomplish in our tanks when we select and employ botanical materials in our aquariums.

Huh?
As we've discussed a lot around here, the idea of using natural materials, like wood, leaves, seed pods, and roots is a faithful representation of many of the wild habitats we obsess over. And more important, it's a functional methodology of fostering natural processes and a healthy ecology in our tanks.

Are you simply trying to add some aquascaping interest to your tank? Are you interested in manipulating the aquarium water chemistry? Perhaps you're attempting to replicate a very specific ecological niche? Setting up a system for breeding fishes or rearing their fry?
There are many, many applications for botanicals in aquariums. A wide range of things you can do with them, and an even wider range of botanicals to do the job. And the most important "job" for botanicals in our aquariums, IMHO, is to foster the ecology of the aquarium...The so-called "microbiome."
And the important thing to know in this context is that you don't have to use 25 different botanicals and leaves in your aquarium to achieve this ecology within your tank. The reality is that, organisms like fungal growth, bacteria, Paramecium, and other microfauna are typically not tied to a specific leaf or seed pod, so not having a huge variety doesn't mean that you won't be able to achieve a significant microbiome within your tank.

So from a "biodiversity" or ecological standpoint, there is no reason why you would need a huge variety of botanicals in a given aquarium. It really boils down to aesthetics. Or, if you're trying to be more "biotopically accurate"- it depends upon the variety of materials that you'd expect to find in the habitat you're interested in replicating.

For example, a flooded forest might have a lot more ( in both density and variety) leaves and seed pods than say, a fast-flowing river, stream, or a small oxbow lake might have. Other locales might simply have a lot of a few materials, like branches and leaves, but minimal amounts of seed pods and other materials.

Maybe you're not trying to replicate any specific habitat at all. Perhaps it's simply a creative expression with botanicals. That's fine. You can use as many or as little as you want...and you still get the "functional" aspects if you don't "edit" them!

How your botanical-style aquarium looks and (to a lesser extent, functions) is dependent upon these types of characteristics. Yet, it's really a matter of what works best for the aquarium that you are trying to create. The power of restraint is a very important factor when playing with botanicals!
Now again, with all of the cool botanical materials available to hobbyists here and elsewhere, it's certainly fun to use a large variety of different materials in your tank! I personally have always been of the opinion that too much variety in a given tank is sort of distracting and just somehow doesn't always look good. I mean, it certainly can..it just doesn't always! Somehow, using a little less variety in a given tank seems to just look a bit better, IMHO.

However, as we've mentioned already, if you're replicating a specific habitat that might have a wide variety of materials in a given small locale, it makes sense, right?
And there is the benefit of a field of botanicals not only cultivating microbial and fungal food sources for fishes, there is the direct consumption of the botanicals (or their constituent materials) by fishes.
Yes, direct consumption of botanicals by fishes is something that we haven't talked all that much about over the years here.
It's long been known that many species of fishes, particularly Panaque/Panaqolus and some Hypostomus/Cochliodon love botanical stuff. These species are equipped with teeth specifically "designed" to gouge wood. And there's probably another odd one or two that consume it as well. Now, you should be aware that wood "eaters" don't consume the wood per se, they consume it as a "by-product" of their overall feeding strategy.

(The "business end" of Panaque nigrolineatus by Neale Monks, used under CC BY-SA 3.0)
In fact, some recent scientific studies have corroborated digestive enzyme activity profiles and gastrointestinal fermentation levels in the fishes’ GI tracts, suggesting that the "wood-eating catfishes" are not true xylivores, such as beavers and termites, but rather, are detritivores like so many other fishes from the family Loricariidae.
In fact, the conclusion of one study indicated that "..the fishes’ whole digestive strategy ranging from intake, to passage rate, digestive enzyme activities, gastrointestinal fermentation, and decreasing surface area in the distal intestine suggests that these fishes are geared for the digestion and assimilation of soluble components of their detrital diet.
However, the wood-eating catfishes do take macroscopic detritus (i.e., woody debris) and reduce it to <1 mm in diameter, which likely has significant consequences for carbon cycling in their environment. Given that much of the Amazonian basin is unstudied, and much of it is under threat of deforestation (leading to more wood in waterways), the wood-eating catfishes may play a crucial role in the dynamics of the Amazonian ecosystem, and certainly in the reduction of coarse woody debris."
(German DP. Inside the guts of wood-eating catfishes: can they digest wood? Journal of Comparative Physiology B, Biochemical, Systemic, and Environmental Physiology. 2009;179(8):1011-1023. doi:10.1007/s00360-009-0381-1.)
Interesting, right?
And it has some implication for how we keep these fishes in our botanical-style aquariums, right? I mean, we have no shortage of pics of your Plecos tearing into various botanicals, ranging from leaves to seed pods, like the Calotropis pods, Cariniana pods, etc. So, based on the study above, it would suggest that at least part of the pods do form a part of the diet of these fishes, and in the process of consuming them, the fishes are helping enrich the aquarium habitat.
Now, the botanicals themselves may not be "the whole meal" for many fishes, but the biofilms, algal threads, and other biocover which grow on them do provide foraging for many fishes. A number of us have noticed a wide-ranging variety of fishes, from Barbs to characin to cichlids, feeding actively on the materials on the materials which are "recruited" by submerged botanicals.

This type of activity has led me to postulate that the use of botanicals can perform a definite "feeding support function" for a wide variety of fishes. So, I suppose, one advantage of a variety of botanical materials in one tank is that it increases your chances of having something palatable to someone in the tank!
If you've followed us for any length of time, you're well aware that we are not just pushing you to play with natural, botanical-style aquariums only for the pretty aesthetics. I mean, yeah, they look awesome, but there is so much more to it than that. We are almost as obsessed with the function of these aquariums and the wild habitats which they attempt to represent!

Understanding why you're choosing to throw botanicals in your aquarium is as important as it is to understand how to employ them. Regardless of how you employ the botanicals, I cannot stress enough the need to go SLOWLY. There is no need to rush and dump everything in at one time, or in huge quantities. Particularly in an established aquarium, where your animals are used to a certain stable range of parameters...It goes without saying that if your introducing materials which can influence water chemistry and quality, you will need to go slow and exercise common sense.

And, since botanicals are actively "breaking down" in your aquarium over their "service lifetimes", it's important to employ good husbandry techniques (i.e.; monitoring of water quality, water changes, regular filter media changes, etc.). Just remind yourself that aquatic botanicals create a "dynamic" environment, and you'll enjoy using them that much more!
Apart from, "What pods should I use for a _____________ style setup?" the most common question we receive is ""Do I leave them in or let them break down in my tank?"
And of course, our simple, likely unsatisfying answer is..."It's your call!"
It's as much about your aesthetic preferences as it is long-term ecological stability of the aquarium. It's a decision that each of us makes based on our tastes, management "style", and how much of a "mental shift" we've made o except the transient nature of a botanical-style aquarium and its function. There really is no "right" or "wrong" answer here. It's all about how much you enjoy what happens naturally versus what you choose to control in your tank.
I tend to favor Nature. Every time. It's not even close.
But that's just me.

And of course, we can't ever lose sight of the fact that we're creating and adding to a closed aquatic ecosystem, and that our actions in how we manage our tanks must map to our ambitions, tastes, and the "regulations" that Nature imposes upon us.
Yes, anything that you add into your aquarium that begins to break down is bioload.
Everything that imparts proteins, lignins, tannins, organics, etc. into the water is something that you need to consider. However, it's always been my personal experience and opinion that, in an otherwise well-maintained aquarium, with regular attention to husbandry, stocking, and maintenance, the"burden" of botanicals on your water quality is surprisingly insignificant.
Even in test systems which I intentionally "neglected" by conducting very sporadic water exchanges, once I hit my preferred "population" of botanicals (by building them up gradually), I have never noticed significant phosphate or nitrate increases that could be attributed to their presence.

So, once and for all- is adding a bunch of botanicals to your aquarium "dangerous?"
I mean, it could be, in some instances. Like, adding large quantities of fresh botanicals to an established, stable tank all at once is a recipe for problems. But, this is "Aquarium Keeping 101", right? Like, what would you expect that would happen? Why would you even do that?
It's about common sense.
The reality is, adding botanicals to your tank and using them, replacing them regularly, etc, is no more "dangerous" than anything else we do as aquarists. You simply need to go slowly, apply common sense, follow our prep instructions, and observe your tank carefully.

Look, stuff can still occasionally go wrong, even when you follow instructions and employ common sense. Never lose sight of the fact that aquariums are closed natural ecosystems, and changing the delicate ecological balance within them always risks disrupting established biological processes- and that can have consequences for your fishes.
But, you already KNOW that
It's the reality of Nature, and a reminder that, although we can control some things, Mother Nature calls the shots...

So, the power of "chilling out"- the ability to exercise restraint; to not go crazy adding a ton of stuff all at once- is a huge and very, very important skill for all who play with botanicals to acquire.
I'll bet that you already have.
Stay creative. Stay curious. Stay excited. Stay restrained...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
Movement...
One of the things that drives most hobbyists crazy is when "stuff" gets blown around, covered or moved about in the aquarium. It can be because of strong current, the activity of fishes, or simply overgrown by plants. I understand the annoyance that many hobbyists feel; I recall this same aggravating feeling in many reef tanks where I had high flow and sand on the bottom- almost always a combination for annoyance!
I mean, I get it. We have what feel is a carefully thought-out aquascape, looking exactly how we expected it would after setup. Yet, despite our ideas and thoughts, stuff moves around in the aquarium. It's something we can either accept, or modify in our aquariums, depending upon our preferences.

Yet, movement and "covering" of various materials by sediments, biofilms, etc., which accumulate on the substrate in natural habitats are everyday occurrences, and they help forge a very dynamic ecosystem. And they are constantly creating new opportunities for the fishes which reside in them to exploit.

When you think about how materials "get around" in the wild aquatic habitats, there are a few factors which influence both the accumulation and distribution of them. In many topical streams, the water depth and intensity of the flow changes during periods of rain and runoff, creating significant re-distribution of the materials which accumulate on the bottom, such as leaves, branches, seed pods, and the like.
Larger, more "hefty" materials, such as branches, submerged logs, etc., will tend to move less frequently, and in many instances, they'll remain stationary, providing a physical diversion for water as substrate materials accumulate around them.

A "dam", of sorts, if you will.
And this creates known structures within streams in areas like Amazonia, which are known to have existed for many years. Semi-permanent aquatic features within the streams, which influence not only the physical and chemical environment, but the very habits and abundance of the fishes which reside there.

Most of the small stuff, like leaves, tend to move around quite a bit... One might say that the "material changes" created by this movement of materials can have significant implications for fishes. As we've talked about before, they follow the food, often existing in, and subsisting off of what they can find in these areas.
New accumulations of leaves, detritus, and other materials benefit the entire ecosystem.

In the case of our aquariums, this "redistribution" of material can create interesting opportunities to not only switch up the aesthetics of our tanks, but to provide new and unique little physical areas for many of the fishes we keep.
And yeah, the creation of new feeding opportunities for life forms at all levels is a positive which simply cannot be overstated! As hobbyists, we tend to lament changes to the aquascape of our tanks caused by things outside of our control, and consider them to be a huge inconvenience, when in reality, they're not only facsimile of very natural dynamic processes-they are fundamental to their evolution.
The benthic microfauna which our fishes tend to feed on also are affected by this phenomenon, and as mentioned above, the fishes tend to "follow the food", making this a case of the fishes adapting to a changing environment. And perhaps...maybe...the idea of fishes sort of having to constantly adjust to a changing physical environment could be some sort of "trigger", hidden deep in their genetic code, that perhaps stimulates overall health, immunity or spawning?

Something in their "programing" that says, "You're at home..." Perhaps something which triggers specific adaptive behaviors?
I find this possibility fascinating, because we can learn more about our fishes' behaviors, and create really interesting habitats for them simply by adding botanicals to our aquariums and allowing them to "do their own thing"- to break apart as they decompose, move about as we change water or conduct maintenance activities, or add new pieces from time to time.
Again, just like Nature.
We just need to "get over ourselves" on this aesthetic thing!
Another mental shift? Yeah, it is. An easy one, but one that we need make, really.

Like any environment, botanical/ leaf litter beds have their own "rhythm", fostering substantial communities of fishes. The dynamic behind this biotope can best be summarized in this interesting excerpt from an academic paper on blackwater leaf-litter communities by biologist Peter Alan Henderson, that is useful for those of us attempting to replicate these communities in our aquaria:
"..life within the litter is not a crowded, chaotic scramble for space and food. Each species occupies a sub-region defined by physical variables such as flow and oxygen content, water depth, litter depth and particle size…
...this subtle subdivision of space is the key to understanding the maintenance of diversity. While subdivision of time is also evident with, for example, gymnotids hunting by night and cichlids hunting by day, this is only possible when each species has its space within which to hide.”

In other words, different species inhabit different sections of the leaf litter beds. As aquarists, we should consider this when creating and stocking our botanical-style aquariums.
It just makes sense, right?

So, when you're attempting to replicate such an environment, consider how the fishes would utilize each of the materials you're working with. For example, leaf litter areas would be an idea shelter for many juvenile fishes, catfishes, and even young cichlids to shelter among.
Submerged branches, larger seed pods and other botanicals provide territory and areas where fishes can forage for macrophytes (algal growths which occur on the surfaces of these materials). Fish selection can be influenced as much by the materials you're using to 'scape the tank as anything else, when you think about it!
And it's not just fishes, of course. It's a multitude of life forms.

There are numerous life forms which are found on ad among these materials as well, such as fungal growths, bacterial biofilms, etc. which we likely never really consider, yet are found in abundance in nature and in the aquarium, and perform vital roles in the function of the aquatic habitat.
Perhaps most fascinating and rarely discussed in the hobby, are the unique freshwater sponges, from the genus Spongilla. Yes, you heard. Freshwater sponges! These interesting life forms attach themselves to rocks and logs and filter the water for various small aquatic organisms, like bacteria, protozoa, and other minute aquatic life forms. Some are truly incredible looking organisms!

(Spongilla lacustris Image by Kirt Onthank. Used under CC-BY SA 3.0)
Unlike the better-known marine sponges, freshwater sponges are subjected to the more variable environment of rivers and streams, and have adapted a strategy of survival. When conditions deteriorate, the organisms create "buds", known as "gemmules", which are an asexually reproduced mass of cells capable of developing into a new sponge! The Gemmules remain dormant until environmental conditions permit them to develop once again!
Oh, cool!
To my knowledge, these organisms have never been intentionally collected for aquariums, and I suspect they are a little tricky to transport (despite their adaptability), just ike their marine cousins are. One species, Metania reticulata, is extremely common in the Brazilian Amazon. They are found on rocks, submerged branches, and even tree trunks when these areas are submerged, and remain in a dormant phase in the aforementioned gemmules during periods of desiccation!

Now, I'm not suggesting that we go and collect freshwater sponges for aquarium use, but I am curious if they occur as "hitchhikers" on driftwood, rocks or other materials which end up in our aquariums. When you think about how important sponges are as natural "filters", one can only wonder how they might perform this beneficial role in the aquarium as well!
We've encountered them in reef tanks for many years...I wonder if they could ultimately find their way into our botanical-style aquariums as well? Perhaps they already have. Have any of you encountered one before in your tanks?
The big takeaway from all of this: A botanical bed in our aquariums and in Nature is a physical structure, ephemeral though it may be- which functions just like an aggregation of branches, or a reef, rock piles, or other features would in the wild benthic environment, although perhaps even "looser" and more dynamic.
Stuff gets redistributed, covered, and often breaks down over time. Exactly like what happens in Nature.

Think about the possibilities which are out there, under every leaf. Every sunken branch. Every root. Every rock.
It's all brought about by the dynamic process of movement.
Perhaps instead of looking at the movement of stuff in our tanks as an annoyance, we might enjoy it a lot more if we look at it as an opportunity! An opportunity to learn more about the behaviors and life styles of our fishes and their ever-changing environment.
Stay observant. Stay creative. Stay excited. Stay open-minded...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
Letting go...
So, you have this idea for an aquarium.
You kind of see it in your head...you've assembled the materials, got it sort of together.

You add water.
Then, you walk in the room one day, look at it and- you just HATE it.
Like, you're done with it. Like, no re-hab on the design. No "tweaking" of the wood or whatever...You're just over the fucking thing. Ever felt that?
What do you do?
Well, I had this idea for a nano tank a while back. It seemed good in my head...I had it up for a nanosecond.
Even memorialized it with some Instagram Stories posts. Doing that is almost always the sort of thing that forces me to move on something...I mean, if you lay down a public "marker", you've got to go, right?

I thought that the tank would be a sort of "blank canvas" for an idea I had...I liked the idea, in principle.
But I didn't see a way forward with this one. I even took the extraordinary step of removing one element of the tank (the wood) altogether, in the hope of perhaps pivoting and just doing my "leaf only scape V3.0"- but I wasn't feeling it.
Nope.
A stillborn idea. A tank not capable of evolving to anything that interested me at this time.
So...I let it go.
Yeah, made away with it. Shut it down. Terminated it...
Whatever you want to call it.
That's really a kind of extraordinary step for me. I mean, I'm sort of the eternal optimist. I try to make almost everything work if I can...

I mean, some of my favorite tanks evolved out of this mindset of sticking with something...We'll come back to that in bit.
Not this time, however.
I killed it.
Now, in the hours after the aborted aquarium move, I was actually able to gain some clarity about why I did it.
What made me do it?
I almost always do a sort of "post mortem" analysis when I abort on an idea, and this time was no different. It was pretty obvious to me...the "writing was on the wall" with this one!
I think it centered around two things that I simply can't handle in aquariums anymore.
Don't laugh:
1) I absolutely can't stand aquariums which don't have some sort of background- be it opaque window tint, photo paper, or paint. This tank had no background. You could see the window behind it, and the trees outside on the street, and...yeah.
2) I disdain seeing filters or other equipment in my aquariums. Like, I hate it more than you can ever even imagine. With really few exceptions, I simply hate seeing filters and stuff. It's only in recent years that I've been able to tolerate seeing filter returns in my all-in-one tanks...and just barely. Now, this nano had a little hang-on-the-back outside power filter...Which I not only saw from the top, but from behind...because-you got it- I didn't have a goddam background on the tank, yes.
I mean, am I that much of a primadonna that I can't handle that? I mean, maybe, but I like to think of it as a situation where I have simply developed an aesthetic sense that just can't tolerate some stuff anymore. I have good ideas, and then I get to equipment...and it sort of "stifles" them a bit.
This is weird.

Okay, yeah, maybe I am prima donna.
What could I have done to salvage this tank? Add a background?
Use a canister filter and glassware, you say?
Oh, sure. That's easy, right? I mean, all you see in the tank are these elegant curves of "lily pipes" and intakes...Maybe a surface skimmer...You just take 'em out and bleach 'em every once in a while and they stay nice and clean, and..
Okay, yeah. Great. On paper, anyways.
IMHO, glassware isn't the "organic art" that everyone seems to place on some lofty pedestal in the hobby. It reminds me of high school chemistry lab (which I think I got a C minus in, so some residual trauma there, no doubt). You think it's beautiful...I think it's simply dreadful.

It's another piece of equipment, which you see on the outside of the tank, too, with its "umbilical" of return lines shooting up along the sides. Now sure, I know these were developed to make an obvious, visible necessity (filter returns) more elegant and beautiful...However, to me, they're just that- obvious, visible, distracting...and ugly.
Hell, I've even made crazy efforts to hide the canister filters beneath my tanks before, when I couldn't hide them within the tank. It's like, I had to do something!

I know, I'm being waaaaay too stupid about this.
Because, really, with a lot of my reef aquarium work, and for that matter, some of my fave botanical-style tanks, you can see some of this stuff. When you see my next reef tank, you might see couple of submersible pumps in the tank , low and deep behind the rock work.
Yeah.
For some reason, it doesn't completely fry my brain in every single situation. I suppose it's a hypocritical thing, but man, sometimes it freaks me out and sometimes I can give it a pass.
Weird, huh?

Like, why do some tanks get a pass, and others just freak me out with this stuff.
I think, maybe, it's about the "concept"of the tank. Or the context. Like, some of my fave ever tanks, like my leaf-litter-only tanks, typically will have some equipment evident, because they are essentially a "zero-releaf" aquascape, with nothing that you can hide this stuff behind, like wood or rocks, or whatever. It's as "honest" as it gets. If you want to filter and heat the tank, you only have few options.
It never bothered me all that much in those types of tanks.
Yet, in other tanks? Just fugettaboutit!
Yeah, it MUST be about the concept of the tank. Not only will I forgive the visible equipment, sometimes I'll forgive myself the entire poor execution, too. Because, when I look back at some of the stuff I've done, that was definitely the mindset. Like, I was just happy to sort of pull it off, despite how crappy it looked, as this little gem from 2004 graphically illustrates:

Now that I look back on it, there were actually tons of times when I just let a tank evolve, unmolested and unhurried, because something spoke to me...no matter how weird or seemingly dumb the concept may have initially appeared. There was something about it that I believed in...

And occasionally, I'll try something, tear it down, and just regret it. Like, I'll realize, too late, that there was something I liked about the idea, and that I should have kept at it; let it do it's thing.
Like, what IF I kept it in play for little longer?

I mean, could it have evolved into something cool?
Maybe.
I recall a particular experiment I did with Spider Wood, which I let go very early in the game. The arrangement was almost a "reef like" concept...It didn't look right at the time, so I killed it way too early.

Like, a few tweaks to the wood stack, a buildup of substrate in the back of it, a buildup of some leaves and maybe some plants in the back, and it could have been a respectable recreation of the banks of some of the forest floor streams that I've seen in South America.
Yeah, I'd love to try that one again.
Then there were others which I had great faith in right from the start. Even though they looked a bit weird initially, I knew that they'd evolve into something special if I let them be.

Some just hit the right note, despite a possibly shaky start. Just knew that the idea was so special, that given the space and time, they'd eventually hit the right notes...And they did.

And, then, there were those ideas which, despite their unconventional appearance, were iconic to me, because they represented the culmination of although experiment; a transformation from research to idea to reality. Stuff which created a real transformation in the way I look at aquariums. The "Urban Igapo" style aquairums that many of us execute now, arose from just such an idea.

Sometimes, you just know it. You just feel that letting go of your preconceptions, doubts, and fears, rather than letting go of the tank-is just the right move.

Regardless of the idea, or the appearance of your tank, if there is any way to salvage what you feel is a great idea- even if it means just waiting it out for awhile- do it.

You just never know if that one "not so good"idea will turn out to be the one that changes everything for you, and inspires others in the process. Your "fail" might be the unlock- the key- for someone else who was about give up, and then suddenly saw something in your work, and created a tank based on your "failed" concept- executed on an idea-which truly touched others in ways you might not have even thought of.

So, yeah- let go...in the right way.
Stay bold. Stay patient. Stay creative. Stay optimistic. Stay enthusiastic. Stay persistent...
And Stay Wet.





























