- Continue Shopping
- Your Cart is Empty
The practicality of our developing ecology
As I ease back into the world of Tannin and botanical method aquariums, I think it's important to hit on some of the foundational philosophies, ideas, and "truths" that form the basis of our approach once again.
As I've reiterated time and again lately, upon my return from my self-imposed "sabbatical", I noticed a creeping, slowly-evolving "dumbing down" of what we do, placing higher emphasis on aesthetics than function in the popular social media.

Too many hobbyists have worked too hard for too long to research, understand, and develop this approach to allow it to become a "style of aquascaping", or to simply lose sight of what really drives these types of tanks...Nature.
Not goofy-sounding botanicals, "influencers", or entertaining YouTube videos. Not even our brand or the brands of my industry "besties" ( BWUK and Betta Botanicals).
We get that.
You need to, as well.
Although I'm the first person to tell you to enjoy the hobby how you want to, I'm also going to be the first guy to (metaphorically) "whack the hobby upside its head" when the situation dicates. As long as I'm cognitively functional and breathing, I'll continue to push out "the boring stuff" as required to keep this a methodology, not a Tok Tok trend, meme, or otherwise bubbly social media splash.
Yeah, I sort of pledged to myself a while back that, for every one of these dumbed down exercises in vapidity which I encounter on social media, I'm going to counter with something deeper, more informative, and more instructive... So, based on the current state of things, I'll be really f--king busy for the foreseeable future!
Honestly, the hobby doesn't have to be childish, vapid, and trendy to be fascinating and fun. It never did, and it doesn't have to be now. Nor does it need to be boring, snobby, or exclusive to be fun and cool. There IS a middle ground between some of the garbage that prevails in the hobby, and the boring stereotype of a bunch of old timers sitting around chugging beers, lamenting about how the hobby used to be cool when everyone had to build their own tanks and collect their own Daphnia and Tubifex worms
I think the recent audience numbers of "The Tint" podcast bare this out...They're really growing! There seems to be a "hunger" for more fundamental, deeper information on botanical-method aquariums.
That's super encouraging!
At it's core, what we do is about ecology. Or, rather, the development of an ecological system within our aquariums.

The development of an ecology based on botanical materials is foundational to the successful function of our aquariums- even if it looks a bit "unusual" to many! If we embark on a botanical-method aquarium journey with the mindset that we're helping to encourage the development of an ecological system in our tank, not just a "cool aquascape", the whole thing is that much better.
And guess what?
When you work with Nature to foster such an ecosystem, the cool aesthetics almost always follow...
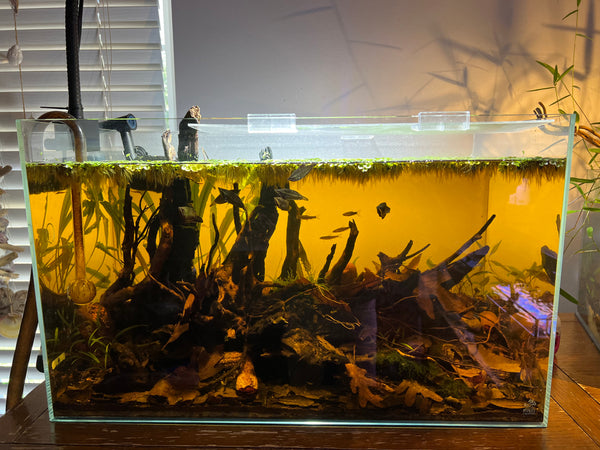

There is something truly remarkable about natural processes playing out in our own aquariums, as they have done for eons in the wild.
Remember, it's all part of the game with a botanical-influenced aquarium. Understanding, accepting, and celebrating the process of an ecological system "sorting itself out" in our tanks is all part of that "mental shift" towards accepting and appreciating a more truly natural-functioning - and natural-looking- aquarium.
The "price of admission", if you will- along with the tinted water, decomposing leaves, etc., the metaphorical "dues" you pay, which ultimately go hand-in-hand with the envious "ohhs and ahhs" of other hobbyists who admire your established aquarium when they see it for the first time.
.

We ask everyone who plays in the botanical-method aquairum world to be open-minded about accepting all sorts of unusual things. Things which, in our previous hobby experience freaked us out to no end!
It's a lot to ask, I'm sure. I mean, the idea of embracing an aquarium which looks and functions in a manner which is essentially contrary to virtually everything you've been brought up to believe in the hobby requires a certain leap of faith, doesn't it?

Yes, it's about aesthetics...but it's more about the beautiful function of botanical materials and soils which influence the chemical environment of the aquarium- just like they do in Nature.
There are aesthetic factors that you need to embrace to really appreciate what we do. They require fundamental shifts in our thinking about what is "cool" and "acceptable" in the aquarium hobby.

Of all the mental shifts asked of those who play in this arena, accepting the formation of biofilms is likely the biggest "ask" of all! Their very appearance- although indicative of a properly functioning ecosystem, simply looks like something that we as hobbyists should loathe.
This is a completely natural occurrence; bacteria and other microorganisms taking advantage of a perfect substrate upon which to grow and reproduce, just like in the wild. Freshly added botanicals offer a "mother load"of organic material for these biofilms to propagate, and that's occasionally what happens - just like in Nature.
Biofilms on decomposing leaves are pretty much the foundation for the food webs in rivers and streams throughout the world. They are of fundamental importance to aquatic life.
Fungi tend to colonize wood and botanical materials, because they offer them a lot of surface area to thrive and live out their life cycle. And cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin- the major components of wood and botanical materials- are degraded by fungi which posses enzymes that can digest these materials!
Fungi are regarded by biologists to be the dominant organisms associated with decaying leaves in streams, so this gives you some idea as to why we see them in our aquariums, right?
Yup.
In aquarium work, we see fungal colonization on wood and leaves all the time. Most hobbyists will look on in sheer horror if they saw this extensive amount of fungal growth on their carefully selected, artistically arranged wood pieces! Yet, it's one of the most common, elegant, and beneficial processes that occurs in Nature!

When we start one of these aquariums, I think that it's important that we go in with the understanding that Nature gets to do a lot of the "work"- if we let Her.
Let me finish by clarifying a few things.
I suppose my "attack on vapidity" sounds judgmental, hard, egotistical, and perhaps envious to some. Lest you think that it is, I beg to differ. Rather, I think it's just really important to have a greater understanding than our current state of culture deems necessary. You're NOT to damn "busy" to learn more about the hobby you love. You're NOT intellectually incapable. You're NOT supposed to be a pHd, or held to dogmatic thinking- even mine.
However, you, me- everyone- we ALL have a responsibility- to the hobby, the fishes we love, and to Nature Herself. A responsibility to take care of each other, the hobby, and the natural world.

And that starts with understanding what we do on a deeper level than a few dozen characters, a meme, or a cute, flashy video short can ever hope to convey.
From a "hobby culture" standpoint, we need to have a good understanding of what we talk about. And we need to ditch the pretentiousness. No one owns the damn title of "botanical method aquarium characteristics" or whatever.
Sure, some people might understand more about specific topics than others do, but their obligation at that point is to share, encourage, and mentor others- not to be a pretentious loudmouth bully. And not to keep dumbing stuff down in the belief that doing so will "reach a wider audience."
Reach people by teaching people everything...not just by sugar coating a few select topics that make a good video short.
Full stop.
So, if I'm a bit wound up at times about this stuff, it's really because I care about it so much..and I do care about you and your enjoyment of this amazing hobby.
Stay curious. Stay educated. Stay inspired. Stay gracious. Stay creative. Stay smart...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
As the seasons pass...
Every Corydoras breeder knows something that we all should know:
Environmental manipulations create unique opportunities to facilitate behavioral changes in our fishes.

It's hardly an earth-shattering idea in the aquarium hobby, but I think that the concept of "seasonal" environmental manipulation deserves some additional consideration.
It's been known for decades that environmental changes to the aquatic environment caused by weather (particularly "wet" or "dry" seasons/events) can stimulate fishes into spawning.

As a fish geek keen on not only replicating the look of our fishes' wild habitats, but as much of the "function" as possible, I can't help myself but to ponder the possibilities for greater success by manipulating the aquarium environment to simulate what happens in the wild.
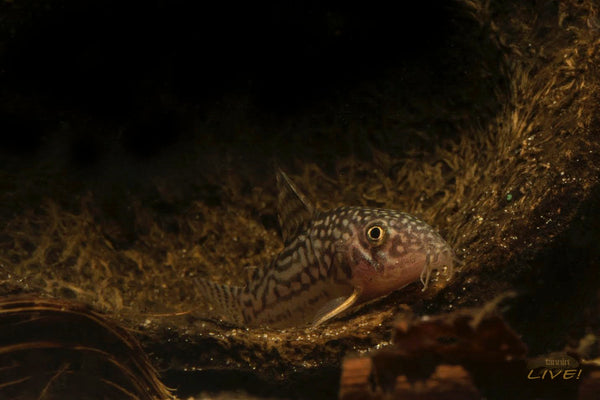
Probably the group of aquarists who has had the most experience and success at incorporating such environmental manipulations into their breeding procedures is Corydoras catfish enthusiasts!

Many hobbyists who have bred Corydoras utilize the old trick of a 20%-30% water exchange with water that is up to 10° F cooler (6.5° C) than the aquarium water is normally maintained at. It seems almost like one of those, "Are you &^%$#@ crazy- a sudden lowering of temperature?"
However, it works, and you almost never hear of any fishes being lost as a result of such manipulations.

I often wondered what the rationale behind such a change was. My understanding is that it essentially is meant to mimic a rainstorm, in which an influx of cooler water is a feature. Makes sense. Weather conditions are such an important part of the life cycle of our fishes.
Still others attempt to simulate a "dry spell" by allowing the water quality to "degrade" somewhat (what exactly that means is open to interpretation!), while simultaneously increasing the aquarium temperature a degree or two. This is followed by a water exchange with softer water (ie; pure RO/DI), and resetting the tank temp to the tank's normal range of parameters.
The "variation" I have heard is to do the above procedure, accompanied by an increase in current via a filter return or powerhead, which simulates the increased water volume/flow brought on by the influx of "rain."
Clever.

Many breeders will fast their fishes a few days, followed by a big binge of food after the temperature drop, apparently simulating the increased amount of food in the native waters when rains come.
Still other hobbyists will reduce the pH of their aquarium water to stimulate breeding. And I suppose the rationale behind this is once again to simulate an influx of water from rain or other external sources...
Weather, once again.

And another trick I hear from my Cory breeder friends from time to time is the idea of tossing in a few alder cones into the tank/vessel where their breeders' eggs are incubating.

This decades-old practice is justified by the assertion that the alder cones possess some type of anti-fungal properties...not entirely off base with some of the scientific research we've found about the allegedly anti-microbial/antifungal properties of catappa leaves and such...
And of course, I hear/read of recommendations to use the aforementioned catappa leaves, oak leaves, and Magnolia leaves for just this purpose...
Interesting.

Okay, cool.
Not really earth-shattering; however, it got me thinking about the whole idea of environmental manipulations as part of the routine "operation" of our botanical-mehtod aquariums.....Should we create true seasonal variations for our aquariums as part of our regular practice- not just when trying to spawn fishes? I mean, changing up lighting duration, intensity, angles, colors, increasing/decreasing water levels or flow?
With all of the high tech LED lighting systems, electronically controlled pumps; even advanced heaters- we can vary environmental conditions to mimic what occurs in our fishes' natural habitats during seasonal changes as never before. I think it would be very interesting to see what kinds of results we could get with our fishes if we went further into seasonal environmental manipulations than we have been able to before.
And of course, if we look at the natural habitats where many of our fishes originate, we see these seasonal changes having huge impact on the aquatic ecosystems. In The Amazon, for example, the high water season runs December through April.
And during the flooding season, the average temperature is 86 degrees F, around 12 degrees cooler than the dry season. And during the wet season, the streams and rivers can be between 6-7 meters higher on the average than they are during the dry season!

And of course, there are more fruits, flowers, and insects during this time of year- important food items for many species of fishes.
And the dry season? Well, that obviously means lower water levels, higher temperatures, and abundance of fishes, most engaging in spawning activity.
Mud and algal growth on plants, rocks, submerged trees, etc. is quite abundant in these waters at various times of the year. Mud and detritus are transported via the overflowing rivers into flooded areas, and contribute to the forest leaf litter and other botanical materials, coming nutrient sources which contribute to the growth of this epiphytic algae.

During the lower water periods, this "organic layer" helps compensate for the shortage of other food sources. When the water is at a high period and the forests are inundated, many terrestrial insects fall into the water and are consumed by fishes. In general, insects- both terrestrial and aquatic, support a large community of fishes.

So, it goes without saying that the importance of insects and fruits- which are essentially derived from the flooded forests, are reduced during the dry season when fishes are confined to open water and feed on different materials.

So I wonder...is part of the key to successfully conditioning and breeding some of the fishes found in these habitats altering their diets to mimic the seasonal importance/scarcity of various food items? In other words, feeding more insects at one time of the year, and perhaps allowing fishes to graze on detritus and biocover at other times?
And then, there are those fishes whose life cycle is intimately tied into the seasonal changes.
The killifishes.
Any annual or semi-annual killifish species enthusiast will tell you a dozen ways to dry-incubate eggs; again, a beautiful simulation of what happens in Nature...So much of the idea can be applicable to other areas of aquarium practice, right?

Yeah... I think so.
It's pretty clear that factors such as the air, water and even soil temperatures, atmospheric humidity, the water level, the local winds as well as climatic variables have profound influence on the life cycle and reproductive behavior on the fishes that reside in these dynamic tropical environments!
In my "Urban Igapo" experiments, we get to see a little microcosm of this whole seasonal process and the influences of "weather."

And of course, all of this ties into the intimate relationship between land and water, doesn't it?
There's been a fair amount of research and speculation by both scientists and hobbyists about the processes which occur when terrestrial materials like leaves and botanical items enter aquatic environments, and most of it is based upon field observations.
As hobbyists, we have a unique opportunity to observe firsthand the impact and affects of this material in our own aquariums! I love this aspect of our "practice", as it creates really interesting possibilities to embrace and create more naturally-functioning systems, while possibly even "validating" the field work done by scientists!

And of course, there are a lot of interesting bits of information that we can interpret from Nature when planning, creating, and operating our aquariums.
It goes without saying that there are implications for both the biology and chemistry of the aquatic habitats when leaves and other botanical materials enter them. Many of these are things that we as hobbyists observe every day in our aquariums!

Example?
A lab study I came upon found out that, when leaves are saturated in water, biofilm is at it's peak when other nutrients (i.e.; nitrate, phosphate, etc.) tested at their lowest limits. This is interesting to me, because it seems that, in our botanical method aquariums, biofilms tend to occur early on, when one would assume that these compounds are at their highest concentrations, right? And biofilms are essentially the byproduct of bacterial colonization, meaning that there must be a lot of "food" for the bacteria at some point if there is a lot of biofilm, right?
More questions...
Does this imply that the biofilms arrive on the scene and peak out really quickly; an indication that there is actually less nutrient in the water? Is the nutrient bound up in the biofilms? And when our fishes and other animals consume them, does this provide a significant source of sustenance for them?
Hmm...?

Oh, and here is another interesting observation:
When leaves fall into streams, field studies have shown that their nitrogen content typically will increase. Why is this important? Scientists see this as evidence of microbial colonization, which is correlated by a measured increase in oxygen consumption. This is interesting to me, because the rare "disasters" that we see in our tanks (when we do see them, of course, which fortunately isn't very often at all)- are usually caused by the hobbyist adding a really large quantity of leaves at once, resulting in the fishes gasping at the surface- a sign of...oxygen depletion?
Makes sense, right?
These are interesting clues about the process of decomposition of leaves when they enter into our aquatic ecosystems. They have implications for our use of botanicals and the way we manage our aquariums. I think that the simple fact that pH and oxygen tend to go down quickly when leaves are initially submerged in pure water during lab tests gives us an idea as to what to expect.
A lot of the initial environmental changes will happen rather rapidly, and then stabilize over time. Which of course, leads me to conclude that the development of sufficient populations of organisms to process the incoming botanical load is a critical part of the establishment of our botanical-method aquariums.
Fungal populations are as important in the process of breaking down leaves and botanical materials in water as are higher organisms, like insects and crustaceans, which function as "shredders." The “shredders” – the animals which feed upon the materials that fall into the streams, process this stuff into what scientists call “fine particulate organic matter.”

And that's where fungi and other microorganisms make use of the leaves and materials, processing them into fine sediments. Allochthonous material can also include dissolved organic matter (DOM) carried into streams and re-distributed by water movement.

And the process happens surprisingly quickly.
In studies carried out in tropical rainforests in Venezuela, decomposition rates were really fast, with 50% of leaf mass lost in less than 10 days! Interesting, but is it tremendously surprising to us as botanical-method aquarium enthusiasts? I mean, we see leaves begin to soften and break down in a matter of a couple of weeks- with complete breakdown happening typically in a month or so for many leaves.
And biofilms, fungi, and algae are still found in our aquariums in significant quantities throughout the process.
So, what's this all mean? What are the implications for aquariums?
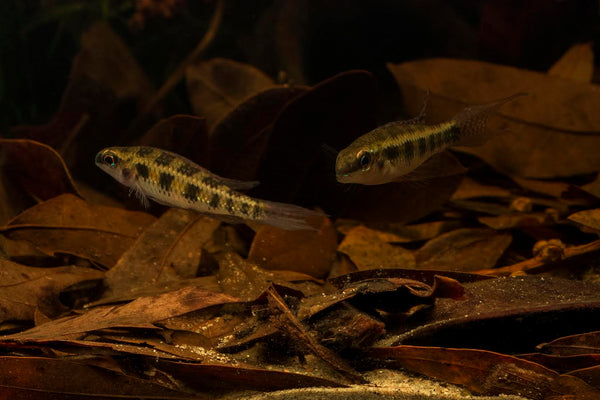

I think it means that we need to continue to foster the biological diversity of animals in our aquariums- embracing life at all levels- from bacteria to fungi to crustaceans to worms, and ultimately, our fishes...All forming the basis of a closed ecosystem, and perhaps a "food web" of sorts for our little aquatic microcosms. It's a very interesting concept- a fascinating field for research for aquarists, and we all have the opportunity to participate in this on a most intimate level by simply observing what's happening in our aquariums every day!
We've talked about this very topic many times right here over the years, haven't we? I can't let it go.
Bioversity is interesting enough, but when you factor in seasonal changes and cycles, it becomes an almost "foundational" component for a new way of running our botanical-style aquariums.
Consider this:
The wet season in The Amazon runs from November to June. And it rains almost every day.
And what's really interesting is that the surrounding Amazon rain forest is estimated by some scientists to create as much as 50% of its own precipitation! It does this via the humidity present in the forest itself, from the water vapor present on plant leaves- which contributes to the formation of rain clouds.

Yeah, trees in the Amazon release enough moisture through photosynthesis to create low-level clouds and literally generate rain, according to a recent study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (U.S.)!
That's crazy.
But it makes a lot of sense, right?
Okay, that's a cool "cocktail party sound bite" and all, but what happens to the (aquatic) environment in which our fishes live in when it rains?
Well, for one thing, rain performs the dual function of diluting organics, while transporting more nutrient and materials across the ecosystem. What happens in many of the regions of Amazonia - and likewise, in many tropical locales worldwide-is the evolution of some of our most compelling environmental niches...

We've literally scratched the surface, and the opportunity to apply what we know about the climates and seasonal changes which occur where our fishes originate, and to incorporate, on a broader scale, the practices which our Corydoras-enthusiast friends employ on all sorts of fishes!
So much to learn, experiment with, and execute on.
Stay fascinated. Stay intrigued. Stay observant. Stay creative. Stay astute...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
Inception.
We've had a lot of requests lately to discuss how we start up our botanical method aquariums. Now sure, we've covered this topic before over the years; yet, as our practices have evolved, so has our understanding about why we do things the way that we do- and why it works.
Establishing a new botanical method aquarium is an exciting, fun, and interesting time. And the process of creating your aquarium is shockingly easy, decidedly un-stressful, and extremely engaging.
The main ingredients that you need are vision, a bit of knowledge, and... patience.
Bringing your tank from a clean, dry,"static display" to a living, breathing microcosm, filled with life is an amazing process. This, to me is really the most exciting part of keeping botanical method aquariums.

And how do we usually do it? I mean, for many hobbyists, we've been more or less indoctrinated to clean the sand, age water, add wood, arrange plants, and add fishes. And that works, of course. It's the basic "formula" we've used for over a century.
Yet, I'm surprised how we as a hobby have managed to turn what to me is one of the most inspiring, fascinating, and important parts of our aquarium hobby journey into what is more-or-less a "checklist" to be run through- an "obstacle", really- to our ultimate enjoyment of our aquarium.

When you think about it, setting the stage for life in our aquariums is the SINGLE most important thing that we do. If we utilize a different mind set, and deploy a lot more patience for the process, we start to look at it a bit differently.
I mean, sure, you want to rinse sand as clean as possible. You want make sure that you have a piece of wood that's been soaked for a while, and..
Wait, DO you?
I mean, sure, if you don't rinse your sand carefully, you'll get some cloudy water for weeks...no argument there.

And if you don't clean your driftwood carefully, you're liable to have some soil or other "dirt" get into your system, and more tannins being released, which leads to...well, what does it lead to?
I mean, an aquarium is not a "sterile" habitat. Let's not fool ourselves.
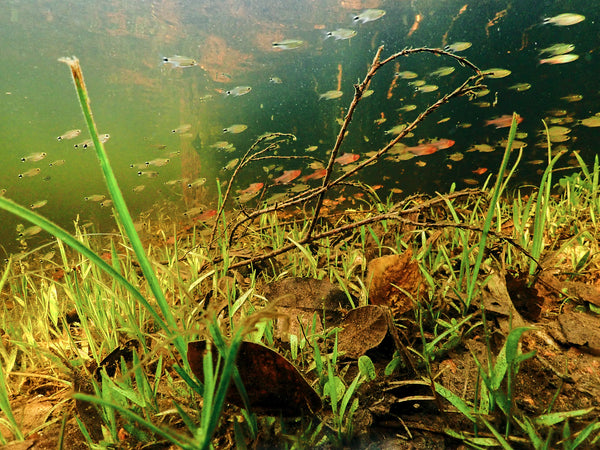
The natural aquatic habits which we attempt to emulate, although comprised of many millions of times the volumes of water volume and throughput that we have in our tanks- are typically not "pristine"- right? I mean, soils from the surrounding terrestrial environment carry with them decomposing matter, leaves, etc, all of which impact the chemistry, oxygen-carrying capacity, biological activity, and of course, the visual appearance of the water.

And that's kind of what our whole botanical-method aquarium adventure is all about- utilizing the "imperfect" nature of the materials at our disposal, and fostering and appreciating the natural interactions between the terrestrial and aquatic realms which occur.
Of course, much like Nature, our botanical-method aquariums make use of the "ingredients" found in the abundant materials which comprise the environment. And the "infusion" of these materials into the water, and the resulting biological processes which occur, are what literally make our tanks come alive.
And yeah, it all starts with the nitrogen cycle...
We can embrace the mindset that every leaf, every piece of wood, every bit of substrate in our aquariums is actually a sort of "catalyst" for sparking biodiversity, function, and yes- a new view of aesthetics in our aquariums.

I'm not saying that we should NOT rinse sand, or soak wood before adding it to our tanks. What I AM suggesting is that we don't "lose our shit" if our water gets a little bit turbid or there is a bit of botanical detritus accumulating on the substrate. And guess what? We don't have to start a tank with brand new, right-from-the-bag substrate.
Of course not.

We can utilize some old substrate from another tank (we have done this as a hobby for decades for the purpose of "jump starting" bacterial growth) which also has the side benefit of providing a different aesthetic as well!
And, you can/should take it further: Use that slightly algal-covered piece of driftwood or rock in our brand new tank...This gives a more "broken-in look", and helps foster a habitat more favorable to the growth of the microorganisms, fungi, and other creatures which comprise an important part of our closed aquarium ecosystems.
In fact, in a botanical-method aquarium, facilitating the rapid growth of such biotia is foundational.

It's perfectly okay for your tank to look a bit "worn" right from the start. Functional aesthetics once again! the look results from the function.
In fact, I think most of us actually would prefer that! It's okay to embrace this. From a functional AND aesthetic standpoint. Employ good husbandry, careful observation, and common sense when starting and managing your new aquarium.

So don't obsess over "pristine." Especially in those first hours.
The aquarium still has to clear a few metaphorical "hurdles" in order to be a stable environment for life to thrive.
I am operating on the assumption (gulp) that most of us have a basic understanding of the nitrogen cycle and how it impacts our aquariums. However, maybe we don’t all have that understanding. My ramblings have been labeled as “moronic” by at least one “critic” before, however, so it’s no biggie for me as said “moron” to give a very over-simplified review of the “cycling” process in an aquarium, so let’s touch on that for just a moment!

During the "cycling" process, ammonia levels will build and then suddenly decline as the nitrite-forming bacteria multiply in the system. Because nitrate-forming bacteria don't appear until nitrite is available in sufficient quantities to sustain them, nitrite levels climb dramatically as the ammonia is converted, and keep rising as the constantly-available ammonia is converted to nitrite.
Once the nitrate-forming bacteria multiply in sufficient numbers, nitrite levels decrease dramatically, nitrate levels rise, and the tank is considered “fully cycled.”
And of course, the process of creating and establishing your aquariums ecology doesn't end there.
With a stabilized nitrogen cycle in place, the real "evolution" of the aquarium begins. This process is constant, and the actions of Nature in our aquariums facilitate changes.
And our botanical-method systems change constantly.
They change over time in very noticeable ways, as the leaves and botanicals break down and change shape and form. The water will darken. Often, there may be an almost "patina" or haziness to the water along with the tint- the result of dissolving botanical material and perhaps a "bloom" of microorganisms which consume them.
This is perfectly analogous to what you see in the natural habitats of the fishes that we love so much. As the materials present in the flooded forests, ponds, and streams break down, they alter it biologically, chemically, and even physically.

It's something that we as aquarists have to accept in our tanks, which is not always easy for us, right? Decomposition, detritus, biofilms- all that stuff looks, well- different than what we've been told over the years is "proper" for an aquarium. And, it's as much a perception issue as it is a husbandry one. I mean, we're talking about materials from decomposing botanicals and wood, as opposed to uneaten food, fish waste, and such.
What's really cool about this is that, in our community, we aren't seeing hobbyists freak out over some of the aesthetics previously associated with "dirty!"
It's seen as a fundamental part of the evolution of the tank.
And soon, you'll see the emergence of elegant, yet simple life forms, such as bacterial biofilms and fungal growths. We've long maintained that the appearance of biofilms and fungi on your botanicals and wood are to be celebrated- not feared. They represent a burgeoning emergence of life -albeit in one of its lowest and (to some) most unpleasant-looking forms- and that's a really big deal.
Biofilms, as we've discussed ad nauseam here, form when bacteria adhere to surfaces in some form of watery environment and begin to excrete a slimy, gluelike substance, consisting of sugars and other substances, that can stick to all kinds of materials, such as- well- in our case, botanicals. It starts with a few bacteria, taking advantage of the abundant and comfy surface area that leaves, seed pods, and even driftwood offer.
The "early adapters" put out the "welcome mat" for other bacteria by providing more diverse adhesion sites, such as a matrix of sugars that holds the biofilm together. Since some bacteria species are incapable of attaching to a surface on their own, they often anchor themselves to the matrix or directly to their friends who arrived at the party first.
Tannin's creative Director, Johnny Ciotti, calls this period of time when the biofilms emerge, and your tank starts coming alive "The Bloom"- a most appropriate term, and one that conjures up a beautiful image of Nature unfolding in our aquariums- your miniature aquatic ecosystem blossoming before your very eyes!
The real positive takeaway here:
Biofilms and fungal growths are really a sign that things are working right in your aquarium! A visual indicator that natural processes are at work, helping forge your tank's ecosystem.

About a year ago, had a discussion with our friend, Alex Franqui. His beautiful Igarape-themed aquarium pictured above, "bloomed" beautifully, with the biofilms, fungal growths, and sediments working together to create a stunning, very natural functioning- and appearing-ecosystem. He was not repulsed at all. Rather, he was awed and fascinated...He celebrated what was occurring in his tan. He has an innate understanding of the ecological process, and replaced "fear and loathing" with excitement.
Alex is a hardcore aquascaper, and to see him marveling and rejoicing in the "bloom" of biofilms in his tank is remarkable.
He gets it.
And it turns out that our love of biofilms is truly shared by some people who really appreciate them as food...Shrimp hobbyists! Yup, these people (you know who you are!) go out of their way to cultivate and embrace biofilms and fungi as a food source for their shrimp.

They get it.
And this makes perfect sense, because they are abundant in Nature, particularly in habitats where shrimp naturally occur, which are typically filled with botanical materials, fallen tree trunks, and decomposing leaves...a perfect haunt for biofilm and fungal growth!
Nature celebrates "The Bloom", too.

There is something truly remarkable about natural processes playing out in our own aquariums, as they have done for eons in the wild.
Time for a little thought experiment...
You're a fish.
Seriously. Make yourself a fish...for a second. (I think I'd be a Black Ghost Knife, FYI. What, you thought I'd be a Cardinal Tetra or something? Really? Sheesh!)

Your main goals in life are avoiding predators, finding food, and reproducing. The "finding food" part is what we're focusing on in this experiment.
Now, back to being you for a second.

Would you like to move into a house which didn’t have a refrigerator full of food? I wouldn’t, for sure. Unlike humans, fishes seem to have not lost their "genetic programming" for grazing and hunting for food. Let’s face it—most of the waking hours of aquatic animals are devoted to acquiring food and reproducing. They need to have some food sources available to "hunt and graze" for.
That’s reality.
So why not help accommodate our your animals’ needs by supplementing their prepared diet with some “pre-stocked” natural foods in their new home? You know, slow down, get things "going" a bit, and then add the fishes?
I’m not talking about tossing in a few frozen brine shrimp hours before the first fishes go in the tank—I’m talking about a deliberate, systematic attempt to cultivate some living food sources within the system before a fish ever hits the water! Imagine a “new” system offering numerous foraging opportunities for its new inhabitants!

in our world, that might mean allowing some breakdown of the botanicals, or time for wood or other botanicals to recruit some biofilms, fungi- even turf algae on their surfaces before adding the fishes to the aquarium.
“Scott. You’re being impractical here! It could take months to accomplish this. I’ve just spent tons of money and time setting up this tank and you want me to deliberately keep this tank devoid of fishes while the biofilms form and Daphnia reproduce?”
Yes. Seriously.
I am a bit crazy. I’ll give you that.
Yet, with my last few systems, this is exactly what I did.
Why?
Well, for one thing, it creates a habitat for sighs which is uniquely suited to their needs in a different way.
Think abut the way most fishes live. They spend a large part of their existence foraging for food. Even in the cozy, comfortable confines of the aquarium.
So, why not create conditions for them which help accommodate this instinctive behavior, and provide opportunities for supplemental (or primary!) nutrition to be available to them by foraging.
Now, I have no illusions about this idea of "pre-stocking" being a bit challenging to execute.
I’m no genius, trust me. I don’t have half the skills many of you do but I have succeeded with many delicate “hard-to-feed” fishes over my hobby “career.”
Any "secret" to this?
None at all. I'm simply really fucking patient.
Success in this arena is simply a result of deploying..."radical patience." The practice of just moving really slowly and carefully when adding fishes to new tanks.
A really simple concept.
I mean, to some extent, we already deploy this practice with our botanical-method tanks, right? The very process of creating a botanical-method aquarium lends itself to this "on board supplemental food production" concept. A concept that's pretty analogous to what occurs in Nature, right?

And one of the most important functions of many botanically-influenced wild habitats is the support of food webs. As we've discussed before in this blog, the leaf litter zones in tropical waters are home to a remarkable diversity of life, ranging from microbial to fungal, as well as crustaceans and insects...oh, and fishes, too! These life forms are the basis of complex and dynamic food webs, which are one key to the productivity of these habitats.
You can do this. You can foster such a "food web"- or the basis for one- in your aquarium!
Wait a minimum of three weeks—and even up to a month or two if you can stand it, and you will have a surprisingly large population of micro and macro fauna upon which your fishes can forage between feedings.
Having a “pre-stocked” system helps reduce a considerable amount of stress for new inhabitants, particularly for wild fishes, or fishes that have reputations as “delicate” feeders.
And think about it for a second.
This is really a natural analog of sorts. Fishes that live in inundated forest floors (yeah, the igapo again!) return to these areas to "follow the food" once they flood. In fact, other than the physical flooding itself, this pursuit of food sources is the key factor in the migration of fishes into these habitats.
So, what would some candidate organisms be for "pre-stocking" a botanical-style aquarium?
How about starting with (okay, sounding a bit commercial, I know, but...) the versatile Purple Non Sulphur Bacteria (PNSB), Rhodopseudomonas palustris- the species which forms our product, "Culture." PNSB are useful for their ability to carry out a particularly unusual mode of metabolism: "anaerobic photoheterotrophy."

In this process, they consume organic wastes while inhabiting moderately illuminated and poorly oxygenated microhabitats (patches of detritus, leaf litter beds, shallow depths of substrate, deeper pores of expanded clay media, etc.). In addition to helping to maintain an ecologically stable microhabitat, "Culture" provides a nutritious live food source for zooplankton as well as soil mesofauna.
Yeah, these guys form the "foundation" of your food chain! (And yeah, we'll have "Culture" back in stock soon...we're re-thinking the packaging to make the product more affordable!)
Next, perhaps some "starter cultures" of organisms like Paramecium, Euglena, etc. You know, "infusoria" from the old school aquarium literature. And then, small crustaceans like Daphnia, and copepods of various types.

Pure cultures of all of these organisms are available online from various biological supply houses. They're a fantastic source of biodiversity for your aquarium!
Of course, the more daring among you may want to introduce various worms, like "Black Worms" or Tubifex worms, if you can find clean cultures of them. For that matter, even "blood worms", which are actually the larval phase of the midge.
Some organisms, such as nematodes and chironomids ("Bloodworms!") will dig into the leaf structures and feed on the tissues themselves, as well as the fungi and bacteria found in and among them. These organisms, in turn, become part of the diet for many fishes.

These organisms, in turn, become part of the diet for many fishes.
Food Web.
And the resulting detritus (here we go again!) produced by the "processed" and decomposing plant matter is considered by many aquatic ecologists to be an extremely significant food source for many fishes, especially in areas such as Amazonia and Southeast Asia, where the detritus is considered an essential factor in the food webs of these habitats.
It performs the same function in an aquarium- if we allow it to.

And of course, if you observe the behavior of many of your fishes in the aquarium, such as characins, cyprinids, Loricariids, and others, you'll see that, in between feedings, they'll spend an awful lot of time picking at "stuff" on the bottom of the tank. In a botanical method aquarium, this is a pretty common occurrence, and I believe an important benefit of this type of system.
When you start seeing your fishes "graze" casually on the materials that pop up on your driftwood and botanicals, you start realizing that, although it might not look like the aesthetics we have had in mind in years past, it is a beautiful thing to our fishes!
You can do this.
Remember, it's all part of the game with a botanical-influenced aquarium. Understanding, accepting, and celebrating "The Bloom" is all part of that "mental shift" towards accepting and appreciating a more truly natural-looking, natural-functioning aquarium.

The "price of admission", if you will- along with the tinted water, decomposing leaves, etc., the metaphorical "dues" you pay, which ultimately go hand-in-hand with the envious "ohhs and ahhs" of other hobbyists who admire your completed aquarium when they see it for the first time.
Stay studious. Stay diligent. Stay observant. Stay patient...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
The "fungal filter?"
You saw the title.
What exactly am I talking about here?

Today, I want to double back and talk a bit about our gooey friends, the fungi- for just a few minutes. Despite their off-putting appearance to some, they may be among the most beautiful, elegant, and useful organisms we encounter in the aquatic world.
Why do I have such devotion to organisms which most of us find truly revolting in appearance?

Because they are among the most important and useful organisms which we can have in our botanical method aquariums. Think about how they arrive in aquatic ecosystems, what they consume, how they derive nutrition, and what they do for the overall ecosystem.
As everyone knows, when you put stuff in water, one of four things seems to happen:
1) Nothing.
2) It gets covered in a gooey slime of fungal growth, and "biofilm."
3) It starts to break down and decompose.
4) Both 2 and 3

Now, it's pretty much a "given" that any botanicals or leaves that you drop into your aquarium will, over time, break down. Wood, too. And typically, before they break down, they'll "recruit" (a fancy word for "acquire') a coating of some rather unsightly-looking growth. Well, "unsightly" to those who have not been initiated into our little world of decomposition, fungal growth, biofilms, tinted water, etc., and maintain that an aquarium by definition is a pristine-looking place without a speck of anything deemed "aesthetically unattractive" by the masses!
So, with that little explanatory passage out of the way, let's take a closer look at fungi-the stuff that you'll see covering the leaves, botanicals, and wood that you place into your aquarium, and why you actually WANT the stuff there in the first place.
The fungi known as aquatic hyphomycetes produce enzymes which break down botanical materials in water. Essentially, they are primary influencers of leaf maceration. They're remarkably efficient at what they do, too. In as little as 3 weeks, as much as 15% of the decomposing leaf biomass in many aquatic habitats is "processed" by fungi, according to one study I found!
Aquatic hyphomycetes play a key role in the decomposition of plant litter of terrestrial origin- an ecological process in rain forest streams that allows for the transfer of energy and nutrients to higher tropic levels.

This is what ecologists call "nutrient cycling", folks.
These fungi colonize leaf litter and twigs and such soon after they're immersed in water. The fungi mineralize organic carbon and nutrients and convert coarse particulate matter into fine particulate organic matter. They also increase leaf litter palatability to shredders, which helps facilitate physical fragmentation.

Fungi tend to colonize wood and botanical materials, because they offer them a lot of surface area to thrive and live out their life cycle. And cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin- the major components of wood and botanical materials- are degraded by fungi, which posses enzymes that can digest and assimilate these materials and their associated organics!
Fungi are regarded by biologists to be the dominant organisms associated with decaying leaves in streams, so this gives you some idea as to why we see them in our aquariums, right?
In aquarium work, we see fungal colonization on wood and leaves all the time. Most hobbyists will look on in sheer horror if they saw the same extensive amount of fungal growth on their carefully selected, artistically arranged wood pieces as they would in virtually any aquatic habitat in Nature!
Yet, it's one of the most common, elegant, and beneficial processes that occurs in natural aquatic habitats!
It's everywhere.

Of course, fungal colonization of wood and botanicals is but one stage of a long process, which occurs in Nature and our aquariums. And, as hobbyists, once we see those first signs of this stuff, the majority of us tend to reach for the algae scraper or brush and remove as much of it as possible- immediately! And sure, this might provide some "aesthetic relief" for some period of time- but it comes right back...because these materials will provide a continuous source of food and colonization sites for fungal growths for some time!
I know that the idea of "circumventing" this stuff is appealing to many, but the reality is that you're actually interrupting an essential, ecologically beneficial natural process. And, as we know, Nature abhors a vacuum, and new growths will return to fill the void, thus prolonging the process.

Again, think about the role of aquatic hyphomycetes in Nature.
Fungal colonization facilitates the access to the energy trapped in deciduous leaves and other botanical materials found in tropical streams for a variety of other organisms to utilize.
As we know by now, fungi play a huge role in the decomposition of leaves, both in the wild and in the aquarium. By utilizing special enzymes, aquatic fungi can degrade most of the molecular components in leaves, such as cellulose,, hemicelluloses, starch, pectin and even lignin.
Fungi, although not the most attractive-looking organisms, are incredibly useful...and they "play well" with a surprisingly large number of aquatic life forms to create substantial food webs, both in the wild and in our aquariums!
Natural habitats are absolutely filled with this stuff...It's like the whole game here- an explosion of life-giving materials, free for the taking...
Yet, we freak the fuck out about it when it shows up.

Another "mental shift", I suppose...one which many of you have already made, no doubt. I certainly look forward to seeing many examples of us utilizing "what we've got" to the advantage of our fishes! AGAIN: A truly "Natural" aquarium is not sterile. It encourages the accumulation of organic materials and other nutrients- not in excess, of course.
The love of pristine, sterile-looking tanks is one of the biggest obstacles we need to overcome to really advance in the aquarium hobby, IMHO.
Biofilms, fungi, algae...detritus...all have their place in the aquarium. Not as an excuse for lousy or lazy husbandry- but as supplemental food sources to "power" the ecology in our tanks.

And of course, as we've discussed many times here, fungi are actually an important food item for other life forms in the aquatic environments tha we love so much! In one study I stumbled across, gut content of over 100 different aquatic insects collected from submerged wood and leaves showed that fungi comprised part of the diet of more than 60% of them, and, in turn, aquatic fungi were found in gut content analysis of many species of fishes!

One consideration: Bacteria and fungi that decompose decaying plant material in turn consume dissolved oxygen for respiration during the process.
This is one reason why we have told you for years that adding a huge amount of botanical material at one time to an established, stable aquarium is a recipe for disaster. There is simply not enough fungal growth or bacteria to handle it. They reproduce extremely rapidly, consuming significant oxygen in the process.
Bad news for the impatient.
Support. Co-dependency. Symbiosis. Whatever you want to call it- the presence of fungi in aquatic ecosystems is extremely important to other organisms.
You can call it free biological filtration for your aquarium!
GREAT news for the patient, the studious, and the accepting.
Think about this: These life forms arrive on the scene in Nature, and in our tanks, to colonize appropriate materials, to process organics both in situ on the things that they're residing upon (leaves, twigs, branches, seed pods, wood, etc.).
Yeah, if you intervene by removing stuf-f bad things can happen. Like, worse things than just a bunch of gooey-looking fungal and biofilm threads on your wood. Your aquarium suddenly loses its capability of processing the leaves and associated organics, and- who's there to take over?
Okay, I'm repeating myself here- but there is so much unfounded fear and loathing over aquatic fungi that someone has to defend their merits, right? Might as well be me!
My advice; my plea to you regarding fungal growth in your aquarium? Just leave it alone. It will eventually peak, and ultimately diminish over time as the materials/nutrients which it uses for growth become used up. It's not an endless "outbreak" of unsightly (to some) fungal growth all over your botanicals and leaves. It goes away significantly over time.

"Over time."
That's "Fellman Speak" for "Please be more fucking patient!"
Seriously, though, hobbyists tend to overly freak out about this kind of stuff. Of course, as new materials are added, they will be colonized by fungi, as Nature deems appropriate, to "work" them.
It's one of those things in the botanical-method aquarium that we need to wrap our heads around. We need to understand, lose our fears, and think about the many positives these organisms provide for our tanks. These small, seemingly "annoying" life forms are actually the most beautiful, elegant, beneficial friends that we can have in the aquarium. When they arrive on the scene in our tanks, we should celebrate their appearance.
Why?
Because their appearance is yet another example of the wonders of Nature playing out in our aquariums, without us having to do anything of consequence to facilitate their presence, other than setting up a tank embracing the botanical method in the first place. We get to watch the processes of colonization and decomposition occur in the comfort of our own home. The SAME stuff you'll see in any wild aquatic habitat worldwide.
Amazing.

For those of you who MUST find some familiar comfort in established philosophy- look no further than the beloved master, Takashi Amano. He laid down this track decades ago...
Yup. I'm channeling Mr. Amano here.
In the botanical method aquairum, Amano's concept of embracing the Japanese philosophy of wabi-sabi takes over. Accepting the transient nature of things and enjoying the beauty of the changes that occur over time.

Part of the game, as we've discussed ad naseum here, is to understand, appreciate, and ultimately embrace the way the aquatic environment is influenced by the fungal growths, biofilms, and decomposition which occurs when botanicals are added into our aquariums.

Remember, your aquairum is not a pice of kinetic art. It's a miniature, closed aquatic ecosystem. Processes which occur in Nature play out daily in your tank.
Yeah, I admit, decades ago, I freaked out about seeing fungal growths in my tanks, too. I'd get a bit scared, wondering if something was wrong, and why no one else's aquariums ever seemed to look like mine. I used to think something was really wrong!
To reassure myself, I would stare for hours at underwater photos taken in the Amazon region, showing decaying leaves, biofilms,and fungi all over the leaf litter. I'd read the studies by researchers like Henderson and Walker, detailing the dynamics of wild leaf litter zones and how productive and unique they were.

I remember telling myself that what I was seeing in my tanks was remarkably similar to what I saw in images and videos of wild aquatic habitats that I wanted to replicate. They seem to look- and even function- so similarly.
I'd pour over my water quality tests, confirming for myself that everything was okay. It always was. And of course I would watch my fishes for any signs of distress...
I never saw them.
Truth be known, I knew that there wouldn't be any issues, because I created my aquariums with a solid embrace of basic aquatic biology; an understanding that an aquarium is not some sort of underwater art installation, but rather, a living, breathing microcosm of organisms which work together to create a biome..and that the appearance of the aquarium only tells a small part of the story.

And another big concept for you to wrap your head around:
Your aquarium- or more specificlally- the colonized botanical materials which comprise the botanical-method aquarium "infrastructure" acts as a biological "filter system."
In other words, the botanical materials present in our systems provide enormous surface area upon which beneficial bacterial biofilms and fungal growths can colonize. These life forms, like fungi, utilize the organic compounds present in the water as a nutritional source, thus creating a "nutrient assimilation process."

Understanding and embracing this has changed everything about how I look at aquarium management and the creation of functional closed aquatic ecosystems.
It's really put the word "natural" back into the aquarium keeping parlance for me. The idea of creating a multi-tiered ecosystem, which provides a lot of the requirements needed to operate successfully with just a few basic maintenance practices, the passage of time, a lot of patience, and careful observation.
It means adopting a different outlook, accepting a different, yet very beautiful aesthetic. It's about listening to Nature instead of the "influencer" on YouTube with the flashy, gadget-driven tank and nothing substantive to back up his vapid narrative. It means educating yourself a bit. It's not always fun at first for some, and it initially seems like you're somehow doing things wrong.

But you're not. And Mother Nature won't let you down if you don't lose faith in Her.
And yeah- it's about faith. Faith in Mother Nature, who's been doing this stuff for eons. She's got this. She'll hook you up...If you allow Her. If you have faith in Her processes.
Have faith.
Stay bold. Stay thoughtful. Stay curious. Stay patient...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
The slow(er) road to success with fish stocking...
One of the questions which we are asked less and less these days is, 'What kinds of fishes are suitable for a botanical-style aquarium?" I think that after 6 years of pounding all of these ideas into your heads about all of the strange nuances of botanical-style aquariums, it's almost universally understood that pretty much any fishes can live in them.
On the other hand, when it comes to how we stock our tanks, nothing has really changed...however, it could. And it should, IMHO.
We spend a pretty good amount of time studying, scheming, and pondering how to create a compatible, interesting, and attractive community of fishes within our aquariums.
It's probably among the most enjoyable things that we do in the hobby, right?

As a somewhat eccentric philosopher of all things fish, one of my favorite things to ponder is stuff that we do while creating our aquariums which is- intentionally or otherwise- analogous to the factors in Nature that result in the environments and fish populations that we find so compelling.

If you're like me, you likely spend a little too much time pondering all sorts of arcane aspects of the hobby...Okay, so maybe you're NOT like me, but you probably have a rather keen interest in the way Nature operates in the wild aquatic systems of the world, and stock your aquariums accordingly.

As one who studies a lot of details about some of the habitats from which our fishes come, I can't help but occasionally wonder exactly what it is that brings fishes to a given location or niche within a environment?

Now, the first answer we're likely to proffer is the most apparent...right? I mean, they follow the food!
Fishes tend to move into new areas in search suitable food sources as part of their life cycle. And food sources often become available in habitats such as flooded forest areas after the rains come, when decomposing leaves and botanical materials begin to create (or re-activate, as the case may be) "food webs", attracting ever more complex life forms into the area.

When we create our aquariums, we take into consideration a lot of factors, ranging from the temperament and size of our fish selections, to their appearance, right? These are all important factors. However, have you ever considered what the factors are in nature which affect the composition of a fish community in a given habitat?
Like, why "x" fish is living in a particular habitat?

What adaptations has the fish made that make it uniquely suitable for this environmental niche? Further, have you thought about how we as hobbyists replicate, to some extent, the actual selection processes which occur in Nature in our quest to create the perfect community aquarium?
Now, if you're an African Cichlid lover or reef hobbyist, I'm sure you have!
Social hierarchies, spatial orientations, and allopathic processes are vital to success in those types of aquariums; you typically can't get away with just throwing in a random fish or coral and hoping it will just mix perfectly.

However, for many hobbyists who aim to construct simple "community tanks", it isn't that vital to fill specific niches and such...we probably move other factors to the forefront when thinking about possible additions to our community of fishes: Like, how cool the fish looks, how large it grows, if it has a peaceful temperament, etc. More basic stuff.
However, in the end, we almost always make selections based upon factors which we deem important...again, a sort of near-mimicry of natural processes- and how the fishes work in the habitat we've created for them.

"Unnatural selection?" Or...Is it essentially what nature's does for eons?
Oh, and what exactly is an "aquatic habitat", by the way? In short, you could say that an aquatic habitat is the physical, chemical, and biological characteristics which determine the suitability for habitation and reproduction of fishes.

Of course, these characteristics can determine which fishes are found in a given area in the wild- pretty much without exception. It's been happening for eons.

Approaching the stocking of an aquarium by determining which fishes would be appropriate for the physical characteristics of the tank is not exactly groundbreaking stuff.
However, when we evaluate this in the context of "theme", and what fish would be found within, say, an Amazonian Igarape stream or a Southeast Asian peat swamp, the idea of adding fishes to "exploit" the features of the habitat we've created is remarkably similar to the processes which occur in Nature that determine what fish are found there, and it's the ultimate expression of good tank planning, IMHO.
It's just kind of interesting to think about in that context, right?
Competition is another one of the important factors in determining how fish populations in the wild. Specifically, competition for space, resources (e.g.; food) and mates are prevalent. In our aquariums, we do see this to some extent, right? The "alpha male" cichlid, the Pleco that gets the best cave, and the Tetra which dominates his shoal.
How we create the physical space for our fishes can have significant impact on this behavior. When good hiding spaces are at a premium, as are available spawning partners, their will be some form of social hierarchy, right?

Other environmental factors, such as water movement, dissolved oxygen, etc. are perhaps less impactful on our community once the tank is established. However, these factors figure prominently in our decisions about the composition of, or numbers or fishes in the community, don't they?

For example, you're unlikely to keep Hillstream loaches in a near stagnant, blackwater swamp biotope aquarium, just like you'd be unlikely to keep Altum Angelfish in a fast-moving stream biotope representation. And fishes which shoal or school will, obviously, best be kept in numbers.
"Aquarium Keeping 101", again.

One factor that we typically don't have in our aquaria is predation. I know very few aquarists who would be sadistic enough to even contemplate trying to keep predators and prey in the same tank, to let them "have at it" and see what happens, and who comes out on top!
I mean, there is a lot to this stuff, isn't there?
Again, the idea of creating a tank to serve the needs of certain fishes isn't earth-shattering. Yet, the idea of stocking the tank based on the available niches and physical characteristics is kind of a cool, educational, and ultimately very gratifying process. I just think it's truly amazing that we're able to actually do this these days.
And the sequence that you stock your tank in is extremely pertinent.
I think that you could literally create a sort of "sequence" to stocking various types of fishes based on the stage of "evolution" that your aquarium is in, although the sequence might be a bit different than Nature in some cases. For example, in a more-or-less brand new aquarium, analogous in this case to a newly-inundated forest floor, their might be a lot less in the way of lower life forms, such as fungi and bacteria, until the materials begin breaking down. You'd simply have an aggregation of fresh leaves, twigs, seed pods, soils, etc. in the habitat.
So, if anything, you're likely to see fishes which are much more dependent upon allochthonous input...food from the terrestrial environment. This is a compelling way to stock an aquarium, I think. Especially aquarium systems like ours which make use of these materials en masse.

Right from the start (after cycling, of course!), it would not be unrealistic to add fishes which feed on terrestrial fruits and botanical materials, such as Colossoma, Arowanna, Metynis, etc. Fishes which, for most aquarists of course, are utterly impractical to keep because of their large adult size and/or need for physical space!

(Pacu! Image by Rufus46, used under CC BY-SA 3.0)
Now, a lot of smaller, more "aquarium suited" fishes will also pick at these fruits and seeds, so you're not totally stuck with the big brutes if you want to go this route! Interestingly, the consumption and elimination of fruits by fishes is thought to be a major factor in the distribution of many plants in the region.
Do a little research here and you might be quite surprised about who consumes what in these habitats!
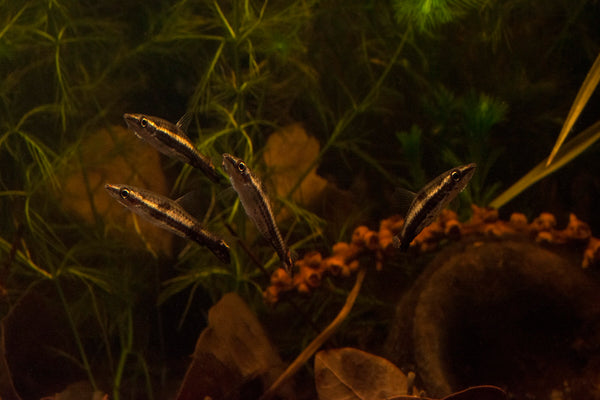

More realistically for most aquarists, I'd think that you could easily stock first with fishes like surface-dwelling (or near surface-dwelling) species, like hatchetfishes and some Pencilfishes, which are largely dependent upon terrestrial insects such as flies and ants, in Nature. In other words, they tend to "forage" or "graze" little, and are more opportunistic, taking advantage of careless insects which end up in the water of these newly-inundated environs.
I've read studies where almost 100 species were documented which feed near-exclusively on insects and arthropods from terrestrial sources in these habitats! As I mention often, if you dive a bit deeper than the typical hobbyist writings, and venture into scholarly materials and species descriptions, you'll be fascinated to read about the gut-content analysis of fishes, because they give you a tremendous insight about what to feed in the aquarium!

Continuing on, it's easy to see that, as the environments evolve, so does the fish population. And the possibilities for simulating this in the aquarium are many and are quite interesting!

Later, as materials start to decompose and are acted on by fungi and bacteria, you could conceivably add more of the "grazing" type fishes, such as Plecos, small Corydoras, Headstanders, etc.

As the tank ages and breaks in more, this would be analogous to the period of time when micro-crustaceans and aquatic insects are present in greater numbers, and you'd be inclined to see more of the "micropredators" like characins, and ultimately, small cichlids.

Interestingly, scientists have postulated that evolution favored small fishes like characins in these environments, because they are more efficient at capturing small terrestrial insects and spiders in these flooded forests than the larger fishes are!
And it makes a lot of sense, if you look at it strictly from a "density/variety" standpoint- lots of characins call these habitats home!

Then there are detritivores.
The detrivorus fishes remove large quantities of this material from submerged trees, branches, etc. Now, you might be surprised to learn that, in the wild, the gut-content analysis of almost every fish indicates that they consume organic detritus to some extent! And it makes sense...They work with the food sources that are available to them!
At different times of the year, different food sources are easier to obtain.

And, of course, all of the fishes which live in these habitats contribute to the surrounding forests by "recycling" nutrients locked up in the detritus. This is thought by ecologists to be especially important in blackwater inundated forests and meadows in areas like The Pantanal, because of the long periods of inundation and the nutrient-poor soils as a result of the slow decomposition rates.

All of this is actually very easy to replicate, to a certain extent, when stocking our aquaria. Why would you stock in this sort of sequence, when you're likely not relying on decomposing botanicals and leaves and the fungal and microbial life associated with them as your primary food source?

Well, you likely wouldn't be...However, what about the way that the fishes, when introduced at the appropriate "phase" in the tank's life cycle- adapt to the tank? Wouldn't the fishes take advantage of these materials as a supplement to the prepared foods that you're feeding them? Doesn't this impact the fishes' genetic "programming" in some fashion? Can it activate some health benefits, behaviors, etc?
I believe that it can. And I believe that this type of more natural feeding ca profoundly and positively impact our fishes' health.

I’m no genius, trust me. I don’t have half the skills many of you do but I have succeeded with many delicate “hard-to-feed” fishes over my hobby “career.”
Why?
Because I'm really patient.
Success with this approach is simply a result of deploying "radical patience." The practice of just moving really slowly and carefully when adding fishes to new tanks.
It's a really simple concept.
The hard part is waiting longer to add fishes.

Wait a minimum of three weeks—and even up to a month or two if you can stand it, and you will have a surprisingly large population of micro and macro fauna upon which your fishes can forage between feedings.
Having a “pre-stocked” system helps reduce a considerable amount of stress for new inhabitants, particularly for wild fishes, or fishes that have reputations as “delicate” feeders.
And think about it. This is really a natural analog of sorts. Fishes that live in inundated forest floors (yeah, the igapo again!) return to these areas to "follow the food" once they flood.

It just takes a few weeks, really. You’ll see fungal growth. You'll see some breakdown of the botanicals brought on by bacterial action or the feeding habits of small crustaceans and fungi. If you "pre-stock", you might even see the emergence of a significant population of copepods, amphipods, and other creatures crawling about, free from fishy predators, foraging on algae and detritus, and happily reproducing in your tank.
We kind of know this already, though- right?
This is really analogous to the tried-and-true practice of cultivating some turf algae on rocks either in or from outside your tank before adding herbivorous, grazing fishes, to give them some "grazing material."

Radical patience yields impressive results.
It’s not always easy to try something a little out of the ordinary, or a bit against the grain of popular practice, but I commend you for even thinking about the idea. At the very least, it may give you pause to how you stock your tank in the future, like "Herbivores first, micro predators last", or whatever thought you subscribe to.
Allow your system to mature and develop at least some populations of fauna for these fishes to supplement their diets with. You’ll develop a whole new appreciation for how an aquarium evolves when you take this long, but very cool road.
Stay patient. Stay observant. Stay creative. Stay studious. Stay resourceful...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
The Botanical-Style Aquarium: A "filter" of its own, and other biological musings...
A big thought about our botanical-style aquariums:
The aquarium-or, more specifically- the botanical materials which comprise the botanical-style aquarium "infrastructure" acts as a biological "filter system."
In other words, the botanical materials present in our systems provide enormous surface area upon which beneficial bacterial biofilms and fungal growths can colonize. These life forms utilize the organic compounds present in the water as a nutritional source.

Oh, the part about the biofilms and fungal growths sounds familiar, doesn't it?
Let's talk about our buddies, the biofilms, just a bit more. One more time. Because nothing seems as contrary to many hobbyists than to sing the praises of these gooey-looking strands of bacterial goodness!
Structurally, biofilms are surprisingly strong structures, which offer their colonial members "on-board" nutritional sources, exchange of metabolites, protection, and cellular communication. They form extremely rapidly on just about any hard surface that is submerged in water.
When I see aquarium work in which biofilms are considered a "nuisance", and suggestions that it can be eliminated by "reducing nutrients" in the aquarium, I usually cringe. Mainly, because no matter what you do, biofilms are ubiquitous, and always present in our aquariums. We may not see the famous long, stringy "snot" of our nightmares, but the reality is that they're present in our tanks regardless.
The other reality is that biofilms are something that we as aquarists typically fear because of the way they look. In and of themselves, biofilms are not harmful to our fishes. They function not only as a means to sequester and process nutrients ( a "filter" of sorts?), they also represent a beneficial food source for fishes.
Now, look, I can see rare scenarios where massive amounts of biofilms (relative to the water volume of the aquarium) can consume significant quantities of oxygen and be problematic for the fishes which reside in your tank. These explosions in biofilm growth are usually the result of adding too much botanical material too quickly to the aquarium. They're excaserbated by insufficient oxygenation/circulation within the aquarium.
These are very unusual circumstances, resulting from a combination of missteps by the aquarist.
Typically, however, biofilms are far more beneficial that they are reven emotely detrimental to our aquariums.
Nutrients in the water column, even when in low concentrations, are delivered to the biofilm through the complex system of water channels, where they are adsorbed into the biofilm matrix, where they become available to the individual cells. Some biologists feel that this efficient method of gathering energy might be a major evolutionary advantage for biofilms which live in particularly in turbulent ecosystems, like streams, (or aquariums, right?) with significant flow, where nutrient concentrations are typically lower and quite widely dispersed.

Biofilms have been used successfully in water/wastewater treatment for well over 100 years! In such filtration systems the filter medium (typically, sand) offers a tremendous amount of surface area for the microbes to attach to, and to feed upon the organic material in the water being treated. The formation of biofilms upon the "media" consume the undesirable organics in the water, effectively "filtering" it!
Biofilm acts as an adsorbent layer, in which organic materials and other nutrients are concentrated from the water column. As you might suspect, higher nutrient concentrations tend to produce biofilms that are thicker and denser than those grown in low nutrient concentrations.
Those biofilms which grow in higher flow environments, like streams, rivers, or areas exposed to wave action, tend to be denser in their morphology. These biofilms tend to form long, stringy filaments or "streamers",which point in the direction of the flow. These biofilms are characterized by characteristic known as "viscoelasticity." This means that they are flexible, and stretch out significantly in higher flow rate environments, and contract once again when the velocity of the flow is reduced.
Okay, that's probably way more than you want to know about the physiology of biofilms! Regardless, it's important for us as botanical-style aquarists to have at least a rudimentary understanding of these often misunderstood, incredibly useful, and entirely under-appreciated life forms.

And the whole idea of facilitating a microbiome in our aquariums is predicated upon supplying a quantity of botanical materials- specifically, leaf litter, for the beneficial organisms to colonize and begin the decomposition process. An interesting study I found by Mehering, et. al (2014) on the nutrient sequestration caused by leaf litter yielded this interesting little passage:
"During leaf litter decomposition, microbial biomass and accumulated inorganic materials immobilize and retain nutrients, and therefore, both biotic and abiotic drivers may influence detrital nutrient content."
The study determined that leaves such as oak "immobilized" nitrogen. Generally thinking, it is thought that leaf litter acts as a "sink" for nutrients over time in aquatic ecosystems.

Oh, and one more thing about leaves and their resulting detritus in tropical streams: Ecologists strongly believe that microbial colonized detritus is a more palatable and nutritious food source for detritivores than uncolonized dead leaves. The microbial growth which occurs on the leaves and their resulting detritus increases the nutritional quality of leaf detritus, because the microbial biomass on the leaves is more digestible than the leaves themselves (because of lignin, etc.).
Okay, great. I've just talked about decomposing leaves and stuff for like the 11,000th time in "The Tint"; so...where does this leave us, in terms of how we want to run our aquariums?
Let's summarize:
1) Add a significant amount of leaf litter, twigs, and botanicals to your aquarium as part of the substrate.
2) Allow biofilms and fungal growths to proliferate.
3) Feed your fishes well. It's actually "feeding the aquarium!"
4) Don't go crazy siphoning out every bit of detritus.
Let's look at each of these points in a bit more detail.
First, make liberal use of leaf litter in your aquarium. I'd build up a layer anywhere from 1"-4" of leaves. Yeah, I know- that's a lot of leaves. Initially, you'll have a big old layer of leaves, recruiting biofilms and fungal growths on their surfaces. Ultimately, it will decompose, creating a sort of "mulch" on the bottom of your aquarium, rich in detritus, providing an excellent place for your fishes to forage among.

Allow a fair amount of indirect circulation over the top of your leaf litter bed. This will ensure oxygenation, and allow the organisms within the litter bed to receive an influx of water (and thus, the dissolved organics they utilize). Sure, some of the leaves might blow around from time to time- just like what happens in Nature. It's no big deal- really!
The idea of allowing biofilms and fungal growths to colonize your leaves and botanicals, and to proliferate upon them simply needs to be accepted as fundamental to botanical-style aquarium keeping. These organisms, which comprise the biome of our aquariums, are the most important "components" of the ecosystems which our aquariums are.
I'd be remiss if I didn't at least touch on the idea of feeding your aquarium. Think about it: When you feed your fishes, you are effectively feeding all of the other life forms which comprise this microbiome. You're "feeding the aquarium." When fishes consume and eliminate the food, they're releasing not only dissolved organic wastes, but fecal materials, which are likely not fully digested. The nutritional value of partially digested food cannot be understated. Many of the organisms which live within the botanical bed and the resulting detritus will assimilate them.

Now, we could go on and on about this topic; there is SO much to discuss. However, let's just agree that feeding our fishes is another critical activity which provides not only for our fishes' well-being, but for the other life forms which create the ecology of the aquarium.
And, let's be clear about another thing: Detritus, the nemesis of many aquarists- is NOT our enemy. We've talked about this for several years now, and I cannot stress it enough: To remove every bit of detritus in our tanks is to deprive someone, somewhere along the food chain in our tanks, their nutritional source. And when you do that, imbalances occur...You know, the kinds which cause "nuisance algae" and those "anomalous tank crashes."
The definition of this stuff, as accepted in the aquarium hobby, is kind of sketchy in this regard; not flattering at the very least:
"detritus is dead particulate organic matter. It typically includes the bodies or fragments of dead organisms, as well as fecal material. Detritus is typically colonized by communities of microorganisms which act to decompose or remineralize the material."
Shit, that's just bad branding.
The reality is that this not a "bad" thing. Detritus, like biofilms and fungi, is flat-out misunderstood in the hobby.
Could there be some "upside" to this stuff?
Of course there is.

I mean, even in the above the definition, there is the part about being "colonized by communities of microorganisms which act to decompose or remineralize..."
It's being processed. Utilized. What do these microorganisms do? They eat it...They render it inert. And in the process, they contribute to the biological diversity and arguably even the stability of the system. Some of them are utilized as food by other creatures. Important in a closed system, I should think.
This is really important. It's part of the biological operating system of our botanical-style aquariums. I cannot stress this enough.
Now, I realize that the idea of embracing this stuff- and allowing it to accumulate, or even be present in your system- goes against virtually everything we've been indoctrinated to believe in about aquarium husbandry. Pretty much every article you see on this stuff is about its "dangers", and how to get it out of your tank. I'll say it again- I think we've been looking at detritus the wrong way for a very long time in the aquarium hobby, perceiving it as an "enemy" to be feared, as opposed to the "biological catalyst" it really is!
In essence, it's organically rich particulate material that provides sustenance, and indeed, life to many organisms which, in turn, directly benefit our aquariums.

We've pushed this narrative many times here, and I still think we need to encourage hobbyists to embrace it more.
Yeah, detritus.
Okay, I'll admit that detritus, as we see it, may not be the most attractive thing to look at in our tanks. I'll give you that. It literally looks like a pile of shit! However, what we're talking about allowing to accumulate isn't just fish poop and uneaten food. It's broken-down materials- the end product of biological processing. And, yeah, a wide variety of organisms have become adapted to eat or utilize detritus.
There is, of course, a distinction.

One is the result of poor husbandry, and of course, is not something we'd want to accumulate in our aquariums. The other is a more nuanced definition.
As we talk about so much around here- just because something looks a certain way doesn't mean that it alwaysa bad thing, right?
What does it mean? Take into consideration why we add botanicals to our tanks in the first place. Now, you don't have to have huge piles of the stuff littering your sandy substrate. However, you could have some accumulating here and there among the botanicals and leaves, where it may not offend your aesthetic senses, and still contribute to the overall aquatic ecosystem you've created.

If you're one of those hobbyists who allows your leaves and other botanicals to break down completely into the tank, what really happens? Do you see a decline in water quality in a well-maintained system? A noticeable uptick in nitrate or other signs? Does anyone ever do water tests to confirm the "detritus is dangerous" theory, or do we simply rely on what "they" say in the books and hobby forums?
Is there ever a situation, a place, or a circumstance where leaving the detritus "in play" is actually a benefit, as opposed to a problem?
I think so. Like, almost always.

Yes, I know, we're talking about a closed ecosystem here, which doesn't have all of the millions of minute inputs and exports and nuances that Nature does, but structurally and functionally, we have some of them at the highest levels (ie; water going in and coming out, food sources being added, stuff being exported, etc.).
There is so much more to this stuff than to simply buy in unflinchingly to overly-generalized statements like, "detritus is bad."
The following statement may hurt a few sensitive people. Consider it some "tough love" today:
If you're not a complete incompetent at basic aquarium husbandry, you won't have any issues with detritus being present in your aquarium.
Just:
Don't overstock.
Don't overfeed.
Don't neglect regular water exchanges.
Don't fail to maintain your equipment.
Don't ignore what's happening in your tank.
This is truly not "rocket science." It's "Aquarium Keeping 101."
And it all comes full circle when we talk about "filtration" in our aquariums.
People often ask me, "What filter do you use use in a botanical-style aquarium?" My answer is usually that it just doesn't matter. You can use any type of filter. The reality is that, if allowed to evolve and grow unfettered, the aquarium itself- all of it- becomes the "filter."
You can embrace this philosophy regardless of the type of filter that you employ.
My sumps and integrated filter compartments in my A.I.O. tanks are essentially empty.

I may occasionally employ some activated carbon in small amounts, or throw some "Shade" sachets in there if I am feeling it- but that's it. The way I see it- these areas, in a botanical-style aquarium, simply provide more water volume, more gas exchange; a place for bacterial attachment (surface area), and perhaps an area for botanical debris to settle out. Maybe I'll remove them, if only to prevent them from slowing down the flow rate of my return pumps.
But that's it.
A lot of people are initially surprised by this. However, when you look at it in the broader context of botanical style aquariums as miniature ecosystems, it all really makes sense, doesn't it? The work of these microorganisms and other life forms takes place throughout the aquarium.

I admit, there was a time when I was really fanatical about making sure every single bit of detritus and fish poop and all that stuff was out of my tanks. About undetectable nitrate. I was especially like that in my earlier days of reef keeping, when it was thought that cleanliness was the shit!
It wasn't until years into my reef keeping work, and especially in my coral propagation work, that I begin to understand the value of food, and the role the it plays in aquatic ecosystems as a whole. And that "food" means different things to different aquatic organisms. The idea of scrubbing and removing every single trace of what we saw as "bad stuff" from our grow-out raceways essentially deprived the corals and supporting organisms of an important natural food source.

We'd fanatically skim and remove everything, only to find out that...our corals didn't look all that good. We'd compensate by feeding more heavily, only to continue to remove any traces of dissolved organics from the water...
It was a constant struggle- the metaphorical "hamster wheel"- between keeping things "clinically clean" and feeding our animals. We were super proud of our spotless water. We had a big screen when you came into our facility showing the parameters in each raceway. Which begged the question: Were we interested in creating sterile water, or growing corals?

Eventually, it got through my thick skull that aquariums- just like the wild habitats they represent-are not spotless environments, and that they depend on multiple inputs of food, to feed the biome at all levels. This meant that scrubbing the living shit (literally) out of our aquariums was denying the very biotia which comprised our aquariums their most basic needs.
That little "unlock" changed everything for me.
Suddenly, it all made sense.
This has carried over into the botanical-style aquarium concept: It's a system that literally relies on the biological material present in the system to facilitate food production, nutrient assimilation, and reproduction of life forms at various trophic levels.

It's changed everything about how I look at aquarium management and the creation of functional closed aquatic ecosystems.
It's really put the word "natural" back into the aquarium keeping parlance for me. The idea of creating a multi-tiered ecosystem, which provides a lot of the requirements needed to operate successfully with just a few basic maintenance practices, the passage of time, a lot of patience, and careful observation.
It means adopting a different outlook, accepting a different, yet very beautiful aesthetic. It's about listening to Nature instead of the asshole on Instagram with the flashy, gadget-driven tank. It's not always fun at first for some, and it initially seems like you're somehow doing things wrong.
It's about faith. Faith in Mother Nature, who's been doing this stuff for eons.

It's about nuance.
It's about looking at things a bit different that we've been "programmed" to do in the aquarium hobby for so long. It's about not being afraid to question the reasons why we do things a certain way in the hobby, and to seek ways to evolve and change practices for the benefits of our fishes.
It takes time to grasp this stuff. However, as with so many things that we talk about here, it's not revolutionary...it's simply an evolution in thinking about how we conceive, set up, and manage our aquariums.

Sure, the aquairum is a "filter" of sorts, if you want to label it as such. However, it's so much more: A small, evolving ecosystem, relying on natural processes to bring it to life.
Wrap you head around that.
It might just change everything in the hobby for you.
Stay open-minded. Stay thoughtful. Stay bold. Stay curious. Stay diligent. Stay observant...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
Evolving techniques
It's kind of fun to make little "tweaks" or adjustments to our aquarium methodology or approaches to how we do certain things. This is what pushes the state of the art in aquaristics further down the road. Now, not every one of these adjustments is a quantum leap forward, at least, not initially. Many are simply subtle iterations of things we've played with before.
An example?
One of our fave approaches, sort of derived out of our "Urban Igapo" work, has been to "dry set" the aquarium. A sort of technique I call the "transitional approach."

Basically, all you're doing is adding the prepared botanicals and leaves to your aquarium before it's filled, and spraying them down with water and our sprayable Purple Non-Sulphur bacterial inoculant, "Nurture" to kick-start the biological processes. Let it sit. Spray it down daily.
Then fill it.
Unlike in our "Urban Igapo" approach, you're not trying to grow terrestrial grasses or plants during the "dry phase." You're simply creating and managing what will ultimately be the submerged habitat in your aquarium for a while before filling it.
I've done this a number of times and had great results.

Stupidly simple. Yet, profoundly different.
Why?
Because, rather than our "traditional" approach of adding the botanicals and leaves to the aquarium after it's already filled, you're sort of replicating what happens in Nature in the wild when forest floors and other terrestrial environments are inundated by overflowing streams and rivers.
The thing I like about this approach (besides how it replicates what happens in the wild) is that it gives you the ability to really saturate and soften the botanicals and leaves, and to begin the process of decomposition and bacterial colonization before you add the water.

When do you fill the aquarium?
You can wait a few days, a week or two, or as long s you'd like, really. The idea is to get the materials physically placed, and to begin the process of colonization and "softening" by fungi and bacterial biofilms- known as "conditioning" by ecologists who study these habitats.
And of course, fishes and invertebrates which live amongst and feed directly upon the fungi and decomposing leaves and botanicals will contribute to the breakdown of these materials as well! Aquatic fungi can break down the leaf matrix and make the energy available to feeding animals in these habitats. And look at this little gem I found in my research:
"There is evidence that detritivores selectively feed on conditioned leaves, i.e. those previously colonized by fungi (Suberkropp, 1992; Graca, 1993). Fungi can alter the food quality and palatability of leaf detritus, aecting shredder growth rates. Animals that feed on a diet rich in fungi have higher growth rates and fecundity than those fed on poorly colonized leaves. Some shredders prefer to feed on leaves that are colonized by fungi, whereas others consume fungal mycelium selectively..."
"Conditioned" leaves, in this context, are those which have been previously colonized by fungi! They make the energy within the leaves and botanicals more available to higher organisms like fishes and invertebrates!

We've long maintained that the appearance of biofilms and fungi on your botanicals and wood are to be celebrated- not feared. They represent a burgeoning emergence of life -albeit in one of its lowest and most unpleasant-looking forms- and that's a really big deal.
"Oh shit, he's going to talk about biofilms AGAIN!"
Well, just for a second.
Biofilms, as we probably all know by now, form when bacteria adhere to surfaces in some form of watery environment and begin to excrete a slimy, gluelike substance, consisting of sugars and other substances, that can stick to all kinds of materials, such as- well- in our case, botanicals. It starts with a few bacteria, taking advantage of the abundant and comfy surface area that leaves, seed pods, and even driftwood offer.
The "early adapters" put out the "welcome mat" for other bacteria by providing more diverse adhesion sites, such as a matrix of sugars that holds the biofilm together. Since some bacteria species are incapable of attaching to a surface on their own, they often anchor themselves to the matrix or directly to their friends who arrived at the party first.
It's a literal explosion of life. It's a gift from Nature. And we can all receive it and benefit from it!
Another advantage of this approach? The traditional "cycling" time of a new tank seems to go much faster. Almost undetectable, in many of my experiments. I can only hypothesize and assume that it's likely a result of all of the bacterial growth in the "terrestrial" phase, and the concurrent "conditioning" of the botanical materials.

Tannin's creative Director, Johnny Ciotti, calls this period of time when the biofilms emerge, and your tank starts coming alive "The Bloom"- a most appropriate term, and one that conjures up a beautiful image of Nature unfolding in our aquariums- your miniature aquatic ecosystem blossoming before your very eyes!
The real positive takeaway here: Biofilms are really a sign that things are working right in your aquarium! A visual indicator that natural processes are at work, helping forge your tank's ecosystem.

So, what about the botanicals?
The idea of utilizing botanicals in the aquarium can be whatever you want, sure. However, if you ask me (and you likely didn't)- the idea of utilizing these materials in our tanks has always been to create unique environmental conditions and foster a biome of organisms which work together to form a closed microcosm. That is incredible to me.
And the idea of "dry setting" your botanical materials and sort of "conditioning" them before adding the water, this "transitional approach", while not exactly some "revolutionary" thing, IS an evolutionary step in the development of botanical-style aquarium keeping.

The "transitional approach" is definitely a bit different than what we've done in the past, and may create a more stable, more biologically diverse aquarium, because you're already fostering a biome of organisms which will make the transition to the aquatic habitat and "do their thing" that much more quickly.
This IS unique.
We're talking about actually allowing some of the decomposition to start before water is ever added to our tanks. It's a functional approach, requiring understanding, research, and patience to execute. There's really nothing difficult about it.
And the aesthetics? They're going to be different than what you're used to, no doubt. They will follow as a result of the process, and will resemble, on a surprisingly realistic level, what you see in Nature.
But the primary reason is NOT for aesthetics...

The interactions and interdependencies between terrestrial and aquatic habitats are manifold, beneficial, and quite compelling to us as hobbyists. To be able to study this dynamic first hand, and to approach it somewhat methodically, is a significant change in our technique.
And yeah, it's almost absurdly easy to do.
The hard part is that it requires a bit more patience; not everyone will see the advantages, or value, and the trade-off between waiting to fill your tank and filling it immediately. It may not be one that some are willing to make.

If you do, however, you will get to see, firsthand, the fascinating dynamic between the aquatic and the terrestrial environment in a most intimate way.
It could change your thinking about how we set up aquariums.
It could.
At the most superficial level, it's an acknowledgement that, after many decades, we as hobbyists are acknowledging and embracing this terrestrial-aquatic dynamic. It's a really unique approach, because it definitely goes against the typical "aquatic only" approach that we are used to.

When you consider that many aquatic habitats start out as terrestrial ones, and accumulate botanical materials and provide colonization points for various life forms, and facilitate biological processes like nutrient export and production of natural food resources, the benefits are pretty obvious. Again, the "different aesthetics" simply come along as "part of the package"- both in Nature and in the aquarium.
Replicating this process and managing it in the aquarium also provides us as hobbyists highly unique insights into the function of these habitats.

From a hobby perspective, evolving and managing a closed ecosystem is really something that we should take to easily.
Setting up an aquarium in this fashion also provides us with the opportunity to literally "operate" our botanical-style aquariums; that is, to manage their evolution over time through deliberate steps and practices is not entirely unknown to us as aquarium hobbyists.
It's not at all unlike what we do with planted aquarium or reef aquarium. In fact, the closest analog to this approach is the so-called "dry start" approach to planted aquariums, except we're trying to grow bacteria and other organisms instead of plants.

Yes, it's an evolution.
Simply, a step forward out of the artificially-induced restraints of "this is how it's always been done"- even in our own "methodology"- yet another exploration into what the natural environment is REALLY like, how it evolves, and how it works- and understanding, embracing and appreciating its aesthetics, functionality, and richness.
Earth-shattering? Not likely.
Educational? For sure.
Thought provoking and fun? Absolutely.

A simple, yet I think profound "tweak" to our approach.
Stay curious. Stay open-minded. Stay thoughtful. Stay observant. Stay creative.
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
Stuff we've been told to fear...
A couple of days back, I was chatting with a fellow hobbyist who wanted to jump in to something a bit different within the aquarium hobby, but was afraid of the possible consequences-both socially and in his aquariums. He feared criticism from "them", and that just froze him. I felt bad that he was so afraid of criticism from others should he question the "status quo" within the hobby.
Perhaps my story might be helpful to you if you're afraid of such criticisms.
For generations, we've been told in the aquarium hobby that we need to be concerned about the appearance of all kinds of stuff in our tanks, like algae, detritus, and "biocover".
For some strange reason, we as a hobby group seems emphasize stuff like understanding some biological processes, like the nitrogen cycle, yet we've also been told to devote a lot of resources to siphoning, polishing, and scrubbing our tanks to near sterility.
It's a strange dichotomy.

I remember the first few botanical-style tanks I created, almost two decades ago now, would hit that phase early on when biofilms and fungal growths began to appear, and I'd hear my friends telling me, "Yeah, your tank is going to turn into a big pile of shit. Told you that you can't put that stuff in there."
Because that's what they've been told. The prevailing mindset in the hobby was that the appearance of these organisms was an indication of an unsuitable aquarium environment.
Anyone who's studied basic ecology and biology understands that the complete opposite is true. The appearance of these valuable life forms is an indicator that your aquatic environment is ideal to foster a healthy, diverse community of aquatic organisms, including fishes!
Exactly like in Nature.

I remember telling myself that this is what I knew was going to happen. I knew how biofilms and fungal growths appear on "undefended" surfaces, and that they are essentially harmless life forms, exploiting a favorable environment. I knew that fungi appear as they help break down leaves and botanicals. I knew that these are perfectly natural occurrences, and that they typically are transitory and self-limiting to some extent.
Normal for this type of aquarium approach. I knew that they would go away, but I also knew that there would be a period of time when the tank might look like a big pool of slimy shit. Or, rather, it'd look like a pile of slimy shit to those who weren't familiar with these life forms, how they grow, and how the natural aquatic habitats we love so much actually function and appear!

To reassure myself, I would stare for hours at underwater photos taken in the Amazon region, showing decaying leaves, biofilms,and fungi all over the leaf litter. I'd read the studies by researchers like Henderson and Walker, detailing the dynamics of leaf litter zones and how productive and unique they were.
I'd pour over my water quality tests, confirming for myself that everything was okay. It always was. And of course I would watch my fishes for any signs of distress...

I never saw them.
I knew that there wouldn't be any issues, because I created my aquariums with a solid embrace of basic aquatic biology; an understanding that an aquarium is not some sort of underwater art installation, but rather, a living, breathing microcosm of organisms which work together to create a biome..and that the appearance of the aquarium only tells a small part of the story.

I knew that this type of aquatic habitat could be replicated in the aquarium successfully. I realized that it would take understanding, trial and error, and acceptance that the aquariums I created would look fundamentally different than anything I had experienced before.

I knew I might face criticism, scrutiny, and even downright condemnation from some quarters for daring to do something different, and then for labeling what most found totally distasteful, or have been conditioned by "the hobby" for generations to fear, as simply "a routine part of the process."


It's what happens when you venture out into areas of the hobby which are a bit untested. Areas which embrace ideas, aesthetics, practices, and occurrences which have existed far out of the mainstream consciousness of the hobby for so long. Fears develop, naysayers emerge, and warnings are given.
Yet, all of this stuff- ALL of it- is completely normal, well understood and documented by science, and in reality, comprises the aquatic habitats which are so successful and beneficial for fishes in both Nature and the aquarium. We as a hobby have made scant little effort over the years to understand it. And once you commit yourself to studying, understanding, and embracing life on all levels, the world of natural, botanical-style aquariums and its untapped potential opens upon to you.
Mental shifts are required. Along with study, patience, time, and a willingness to look beyond hobby forums, aquarium literature, and aquascaping contests for information. A desire to roll up your sleeves, get in there, ignore the naysayers, and just DO.

Don't be afraid of things because they look different, or somehow contrary to what you've heard or been told by others is "not healthy" or somehow "dangerous." Now sure, you can't obey natural "laws" like the nitrogen cycle, understanding pH, etc.
You can, however, question things you've been told to avoid based on superficial explanations based upon aesthetics.
Mental shifts.
Stuff that makes you want to understand how life forms such as fungi, for example, arise, multiply, snd contribute to the biome of your aquarium.
Let's think about fungi for a minute...a "poster child" for the new way of embracing Nature as it is.
Fungi reproduce by releasing tiny spores that then germinate on new and hospitable surfaces (ie, pretty much anywhere they damn well please!). These aquatic fungi are involved in the decay of wood and leafy material. And of course, when you submerge terrestrial materials in water, growths of fungi tend to arise. Anyone who's ever "cured" a piece of wood for your aquarium can attest to this!

Fungi tend to colonize wood because it offers them a lot of surface area to thrive and live out their life cycle. And cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin, the major components of wood and botanical materials, are degraded by fungi which posses enzymes that can digest these materials! Fungi are regarded by biologists to be the dominant organisms associated with decaying leaves in streams, so this gives you some idea as to why we see them in our aquariums, right?

And of course, fishes and invertebrates which live amongst and feed directly upon the fungi and decomposing leaves and botanicals contribute to the breakdown of these materials as well! Aquatic fungi can break down the leaf matrix and make the energy available to feeding animals in these habitats. And look at this little gem I found in my research:
"There is evidence that detritivores selectively feed on conditioned leaves, i.e. those previously colonized by fungi (Suberkropp, 1992; Graca, 1993). Fungi can alter the food quality and palatability of leaf detritus, aecting shredder growth rates. Animals that feed on a diet rich in fungi have higher growth rates and fecundity than those fed on poorly colonized leaves. Some shredders prefer to feed on leaves that are colonized by fungi, whereas others consume fungal mycelium selectively..."
"Conditioned" leaves, in this context, are those which have been previously colonized by fungi! They make the energy within the leaves and botanicals more available to higher organisms like fishes and invertebrates!

The aquatic fungi which will typically decompose leaf litter and wood are the group known as “aquatic hyphomycetes”. Another group of specialists, "aero-aquatic hyphomycetes," colonize submerged plant detritus in stagnant and slow- flowing waters, like shallow ponds, puddles, and flooded forest areas. Fungal communities differ between various environments, such as streams, shallow lakes and wetlands, deep lakes, and other habitats such as salt lakes and estuaries.
And we see them in our own tanks all the time, don't we? Sure, it's easy to get scared by this stuff...and surprisingly, it's even easier to exploit it as a food source for your animals! We just have to make that mental shift... As the expression goes, "when life gives you lemons, make lemonade!"

I knew when I started Tannin that I had to "walk the walk." I had to explain by showing my tanks, my work, and giving fellow hobbyists the information, advice, and support they needed in order to confidently set out on their own foray into this interesting hobby path.

I'm no hero. Not trying to portray myself as a visionary.
The point of sharing my personal experience is to show you that trying new stuff in the hobby does carry risk, fear, and challenge, but that you can and will persevere if you believe. If you push through. IF you don't fear setbacks, issues, criticisms from naysayers.

You have to try. In my case, the the idea of throwing various botanical items into aquariums is not my invention. It's not a totally new thing. People have done what I've done before. Maybe not as obsessively or thoroughly presented (and maybe they haven't built a business around the idea!), but it's been done many, many times.
The fact is, we can and should all take these kinds of journeys.

Stay the course. Don't be afraid. Open your mind. Study what is happening. Draw parallels to the natural aquatic ecosystems of the world. Look at this "evolution" process with wonder, awe, and courage.
And know that the pile of decomposing leaves, fungal growth, and detritus that you're looking at now is just a steppingstone on the journey to an aquarium which embrace nature in every conceivable way.
Stay brave. Stay curious. Stay diligent. Stay observant...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
Great...Expectations?
By now, this whole idea of adding botanical materials to our aquariums for the purpose of helping create the physical, biological, and chemical environment of our aquariums is becoming way more familiar. Yet, no matter how many times you've created a botanical-influenced natural aquarium, the experience seems new and somehow different.
Expectations are funny things, aren't they?
There is something very pure and evocative-even a bit "uncomfortable" about utilizing botanical materials in the aquarium. Selecting, preparing, and utilizing them is more than just a practice- it's an experience. A journey. One which we can all take- and all benefit from.
Right along with our fishes, of course!

And yeah, it can even be seen as a bit of a spiritual journey, too- leading to some form of enlightenment and education about Nature, from a totally unique perspective.
The energy and creativity that you bring with you on the journey tends to become amplified during the experience. As you work with botanicals in your aquariums, your mind takes you to different places; new ideas for how your aquarium's microcosm can evolve start flooding your mind. Every tank- like every hobbyist- is different- and different inspirations arise. We don’t want everyone walking away feeling the same thing, quite the opposite actually.
That uniqueness is a large part of the experience.
The experience is largely about discovery. And today's piece is a bit about some of the interesting discoveries- expectations, and revelations that we as a community have learned along the way during our experiences working with botanicals in our aquariums.

Our aquariums evolve, as do the materials within them. We've discussed this concept many times, but it's one that we keep coming back to.
If we think of an aquarium as we do a natural aquatic ecosystem, it's certainly realistic to assume that some of the materials in the ecosystem will change, re-distribute, or completely decompose over time.
Botanicals are not "forever" aquascaping materials. We consider them ephemeral in nature. They will soften, break down, and otherwise decompose over time. Some materials, like leaves- particularly Catappa and Guava, will break down more rapidly than others, and if you're like our friend Jeff Senske of Aquaiuim Design Group, and like the look of intact leaves versus partially decomposed ones, you'll want to replace them more frequently; typically on the order of every three weeks or so, in order to have more-or-less "intact" leaves in your tank.
On the other hand, if you're like me, and enjoy the more natural look that occurs as the leaves break down, just keep 'em in. You may need to remove some materials if you find fungal growth, biofilm, or other growth unsightly or otherwise untenable, or if material gets caught up in filter inlets, etc. However, "operational concerns" aside, and if you've made that "mental shift" and can tolerate the stuff decomposing, just let them be and enjoy!

Botanicals like the really hard seed pods (Sterculia Pods", "Cariniana Pods", "Afzelia Pods"), etc., can last for many, many months, and generally will soften on their interiors long before any decomposition occurs on the exterior "shell" of he botanical. In fact, they'll typically recruit biofilms, which almost seem to serve as a sort of "protective cover" that preserves them.

Often times, fishes like Plecos, Otocinculus catfish, loaches, Headstanders, and bottom-dwelling fishes will rasp or pick at the decomposing botanicals, which further speeds up the process. Others, like Caridina shrimp, Apistos, characins, and others, will pick at biofilms covering the interior and exterior of various botanicals, as well as at the microfauna which live among them, just as they do in Nature.
Sometimes, the fishes will use botanical materials for a spawning site.

We receive a lot of questions about which botanicals will "tint the water the darkest" or whatever. Cool questions. Well, here's the deal: Virtually all botanical materials will impact the color of the water. You'll find, as we have, that different materials will impart different colors into the water. It will typically be clear, but with a golden, brownish, or perhaps a slight reddish tint.
The degree of tint imparted will be determined by various factors, such as how much of the materials you use in your tank, how long they were boiled and soaked during the preparation process, if you're using activated carbon or other chemical filter media, and how much water movement is in your system. However, rest assured, almost any botanical materials you submerge in your tank will impart some color to the water.
Unfortunately, since botanicals are natural materials, there is no "recipe'; no formula with a set "X number of leaves/pods per ___ gallons of aquarium capacity", and you'll have to use your judgement as to how much is too much! It's as much of an "art" as it is a "science!"

Now, If you really dislike the tinted water, but love the look of the botanicals you can mitigate some of this by employing a lmuch onger "post-boil" soaking period- like over a week. Keep changing the water in your soaking container daily, which will help eliminate some of the accumulating organics, as well as to help you to determine the length of time that you need to keep soaking the botanicals to minimize the tint.
Of course, it's far easier to simply employ chemical filtration media, such as activated carbon, and/or synthetic adsorbents such as Seachem Purigen, to help eliminate a good portion of the excess discoloration within the display aquarium where the botanicals will ultimately "reside."

Another interesting phenomenon about "living with your botanicals" is that they will "redistribute" throughout the aquarium. They're being moved around by both current and the activities of fishes, as well as during our maintenance activities, etc. This is, not surprisingly, very similar to what occurs in Nature, where various events carry materials like seed pods, branches, leaves, etc. to various locales within a given body of water.
In our opinion, this movement of materials, along with the natural and "assisted" decomposition that occurs, will contribute to a surprisingly dynamic environment!

Your aquarium water may appear turbid at various times. We are pretty comfortable with this idea; however, some of you may not be. As bacteria act to break down botanical materials, they may impart a bit of "cloudiness" into the the water. Also, materials such as lignin and good old terrestrial soils/silt find their way into our tanks at times.
Some of these inputs, such as soils- are intentional! Others are the unintended by-product of the materials we use, The look is definitely different than what we as aquarists have been indoctrinated to accept as "normal." One of my good friends, and a botanical-style aquarium freak, calls this phenomenon "flavor"- and we see it as an ultimate expression of a truly natural-looking aquarium.

Yeah, the water itself becomes part of the attraction. The color, the "texture", and the clarity of the water are as engrossing and fascinating as the materials which affect it. It's something that you either love or simply hate...everyone who ventures into this method of aquarium keeping needs to make their own determination of wether or not they like it.

Need a bit more convincing to embrace the charm of the water itself in botanical-style aquariums?
Simply look at a natural underwater habitat, such as an igapo or flooded varzea grassland, and see for yourself the allure of these dynamic habitats, and how they're ripe for replication in the aquarium. You'll understand how the terrestrial materials impact the now aquatic environment- the function AND the aesthetic-fundamental to the philosophy of the botanical-style aquarium.

Speaking of the impact of terrestrial materials on the aquatic habitat- remember, too, that just like in Nature, if new botanicals are added into the aquarium as others break down, you'll have more-or-less continuous influx of materials to help provide enrichment to the aquarium environment. This type of "renewal" creates a very dynamic, ever-changing physical environment, while helping keep water chemistry changes to a minimum.

This is the perfect analog to the concept of "allochthonous input" which occurs in wild aquatic habitats- materials from outside the aquatic environment- such as the surrounding forest- entering and influencing the aquatic environment.

The fishes in your system may ultimately display many interesting behaviors, such as foraging activities, territorial defense, and even spawning, as a result of this regular influx of "fresh" aquatic botanicals. You could even get pretty creative, and attempt to replicate seasonal "wet" and "dry" times by adding new materials at specified times throughout the year...The possibilities here are as diverse and interesting as the range of materials that we have to play with!
Go into this with the expectation that you might get to experience an entirely different way of looking at aquariums- and the natural environments we try to replicate- and you'll never be disappointed.
It's all a part of your "life with botanicals"- an ever-changing, always interesting dynamic that can impact your fishes in so many beneficial ways.
Stay dedicated. Stay excited. Stay engaged. Stay resourceful...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
It's about the microbiome...
As we've all started to figure out by now, our botanical-influenced aquariums are a lot more of a little slice of Nature that you're recreating in your home then they are just a "pet-holding container."

The botanical-style aquarium is a microcosm which depends upon botanical materials to impact the environment.

This microcosm consists of a myriad of life format all levels and all sizes, ranging from our fishes, to small crustaceans, worms, and countless microorganisms. These little guys, the bacteria and Paramecium and the like, comprise what is known as the "microbiome" of our aquariums.

A "microbiome", by definition, is defined as "...a community of microorganisms (such as bacteria, fungi, and viruses) that inhabit a particular environment." (according to Merriam-Webster)

Now, sure, every aquarium has a microbiome to a certain extent:
We have the beneficial bacteria which facilitate the nitrogen cycle, and play an indespensible role in the function of our little worlds. The botanical-style aquarium is no different; in fact, this is where I start wondering...It's the place where my basic high school and college elective-course biology falls away, and you get into more complex aspects of aquatic ecology in aquariums.
Yet, it's important to at least understand this concept as it can relate to aquariums. It's worth doing a bit of research and pondering. It'll educate you, challenge you, and make you a better overall aquarist. In this little blog, we can't possibly cover every aspect of this- but we can touch on a few broad points that are really fascinating and impactful.
So much of this proces-and our understanding starts with...botanicals.
With botanicals breaking down in the aquarium as a result of the growth of fungi and microorganisms, I can't help but wonder if they perform, to some extent, a role in the management-or enhancement-of the nitrogen cycle.
Yeah, you understand the nitrogen cycle, right?

How do botanicals impact this process? Or, more specifically, the microorganisms that they serve?
In other words, does having a bunch of leaves and other botanical materials in the aquarium foster a larger population of these valuable organisms, capable of processing organics- thus creating a more stable, robust biological filtration capacity in the aquarium?

I believe that they do.
With a matrix of materials present, do the bacteria (and their biofilms- as we've discussed a number of times here) have not only a "substrate" upon which to attach and colonize, but an "on board" food source which they can utilize as needed?
Facultative bacteria, adaptable organisms which can use either dissolved oxygen or oxygen obtained from food materials such as sulfate or nitrate ions, would also be capable of switching to fermentationor anaerobic respiration if oxygen is absent.
Hmm...fermentation.
Well, that's likely another topic for another time. Let's focus on some of the other more "practical" aspects of this "biome" thing.
Like...food production for our fishes.
In the case of our fave aquatic habitats, like streams, ponds, and inundated forests, epiphytes, like biofilms and fungal mats are abundant, and many fishes will spend large amounts of time foraging the "biocover" on tree trunks, branches, leaves, and other botanical materials.

The biocover consists of stuff like algae, biofilms, and fungi. It provides sustenance for a large number of fishes all types.
And of course, what happens in Nature also happens the aquarium- if we allow it to, right? And it can function in much the same way?

Yeah.
I am of the opinion that a botanical-style aquarium, complete with its decomposing leaves and seed pods, can serve as a sort of "buffet" for many fishes- even those who's primary food sources are known to be things like insects and worms and such. Detritus and the microorganisms within it can provide an excellent supplemental food source for our fishes!
Sustenence...from the microbiome.
It's well known that in many habitats, like inundated forests, etc., fishes will adjust their feeding strategies to utilize the available food sources at different times of the year, such as the "dry season", etc.

And it's also known that many fish fry feed actively on bacteria and fungi in these habitats...So I suggest once again that a botanical-style aquarium could be an excellent sort of "nursery" for many fish and shrimp species!

Again, it's that idea about the "functional aesthetics" of the, botanical-style aquariums. The idea which acknowledges the fact that the botanicals we use not only look cool, but they provide an important function (supplemental food production) as well. As we repeat constantly, the "look" is a collateral benefit of the function.
This is a profoundly important idea.
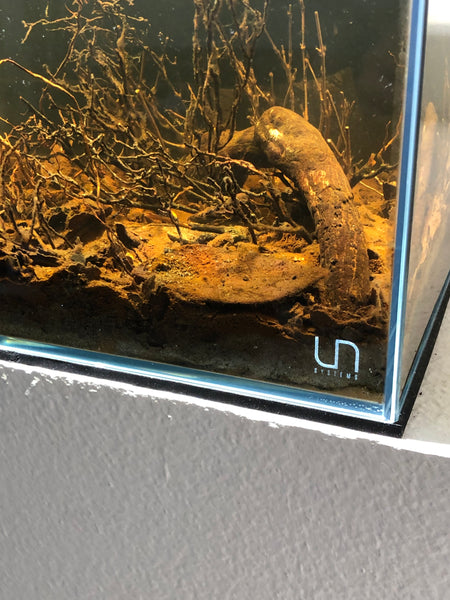

Perhaps arcane to some- but certainly not insignificant.
And of course, we've talked before about this "botanical nursery" concept- creating an aquarium for fish fry that has a large quantity of decomposing botanicals and leaves to foster the production of these materials, which serve as supplemental food for your fish fry. I have done this before myself and can attest to its viability. You fishes will have a constant supply of "natural" foods to supplement what you are feeding them in the early phases of their life.
Learn to make peace with your detritus! As always, look to the wild aquatic habitats of the world for an example of how this food source functions within the greater biome.

I'm fascinated by the "mental adjustments" that we need to make to accept the aesthetic and the processes of natural decay, fungal growth, the appearance of biofilms, and how these affect what's occurring in the aquarium. It's all a complex synergy of life and aesthetic.
And, in order to make the mental shifts which make this all work, we we have to accept Nature's input here.
Understand that, when we create a botanical-filled aquarium, not only do we have the opportunity to create an aquarium which differs significantly from those in years past- we have a unique window into the natural world and the role of these materials in the wild.

One thing that's very unique about the botanical-style approach is that we tend to accept the idea of decomposing materials accumulating in our systems. We understand that they act, to a certain extent, as "fuel" for the micro and macrofauna which reside in the aquarium, and that they perform this function as long as they are present in the system.

A profound mental shift...
And it's all about the microbiome. today's simple idea with enormous impact!
Stay curious. Stay thoughtful. Stay observant. Stay diligent...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics


















