- Continue Shopping
- Your Cart is Empty
Natural processes and the mental shifts we need to make...
We so often discuss natural processes and features in our aquarium work.
There are a lot of interesting pieces of information that we can interpret from Nature when planning, creating, and operating our aquariums. The idea of replicating natural processes and occurrences in the confines of our aquariums, by simply setting up the conditions necessary for them to occur is fundamental to our botanical-oriented approach.
It goes without saying that there are implications for both the biology and chemistry of the aquatic habitats when leaves and other botanical materials enter them. Many of these are things that we as hobbyists observe every day in our aquariums!

Example?
Well, let's talk about our old friend and sometimes nemesis, biofilm.
A lab study I came upon found out that, when leaves are saturated in water, biofilm is at its peak when other nutrients (i.e.; nitrate, phosphate, etc.) tested at their lowest limits. Hmm...This is interesting to me, because it seems that, in our botanical-style aquariums, biofilms tend to occur early on, when one would assume that these compounds are at their highest concentrations, right? And biofilms are essentially the byproduct of bacterial colonization, meaning that there must be a lot of "food" for the bacteria at some point if there is a lot of biofilm, right?

More questions...
Does this imply that the biofilms arrive on the scene and peak out really quickly; an indication that there is actually less nutrient in the water? Is the nutrient bound up in the biofilms? And when our fishes and other animals consume them, does this provide a significant source of sustenance for them? Can you have water with exceedingly low nutrient levels, while still having an abundant growth of biofilms?
Hmm...?

Oh, and here is another interesting observation:
When leaves fall into streams, field studies have shown that their nitrogen content typically will increase. Why is this important? Scientists see this as evidence of microbial colonization, which is correlated by a measured increase in oxygen consumption. This is interesting to me, because the rare "disasters" that we see in our tanks (when we do see them, of course, which fortunately isn't very often at all)- are usually caused by the hobbyist adding a really large quantity of leaves at once, resulting in the fishes gasping at the surface- a sign of...oxygen depletion?
Makes sense, right?

These are interesting clues about the process of decomposition of leaves when they enter into our aquatic ecosystems. They have implications for our use of botanicals and the way we manage our aquariums. I think that the simple fact that pH and oxygen tend to go down quickly when leaves are initially submerged in pure water during lab tests gives us an idea as to what to expect.
A lot of the initial environmental changes will happen rather rapidly, and then stabilize over time. Which of course, leads me to conclude that the development of sufficient populations of organisms to process the incoming botanical load is a critical part of the establishment of our botanical-style aquariums.
Fungal populations are equally important in the process of breaking down leaves and botanical materials in water as are higher organisms, like insects and crustaceans, which function as "shredders." So the “shredders” – the animals which feed upon the materials that fall into the streams, process this stuff into what scientists call “fine particulate organic matter.”

And that's where fungi and other microorganisms make use of the leaves and materials, processing them into fine sediments. Allochthonous material can also include dissolved organic matter (DOM) carried into streams and re-distributed by water movement.

And the process happens surprisingly quickly, too.
In experiments carried out in tropical rainforests in Venezuela, decomposition rates were really fast, with 50% of leaf mass lost in less than 10 days! Interesting, but is it tremendously surprising to us as botanical-style aquarium enthusiasts? I mean, we see leaves begin to soften and break down in a matter of a couple of weeks- with complete breakdown happening typically in a month or so for many leaves. And biofilms, fungi, and algae are still found in our aquariums in significant quantities throughout the process.
So, what's this all mean? What are the implications for aquariums?
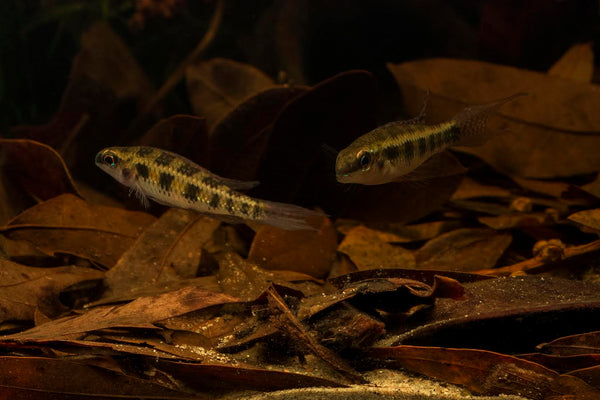

I think it means that we need to continue to foster the biological diversity of animals in our aquariums- embracing life at all levels- from bacteria to fungi to crustaceans to worms, and ultimately, our fishes...All of which form the basis of a closed ecosystem, and perhaps a "food web" of sorts for our little aquatic microcosms.

It's a very interesting concept- a fascinating field for research for aquarists, and we all have the opportunity to participate in this on a most intimate level by simply observing what's happening in our aquariums every day!
And facilitating this process is remarkably easy:
*Approach building an aquarium as if you are creating a biome.
*Foster the growth and development of a community of organisms at all levels.
*Allow these organisms to grow and multiply.
*Don't "edit" the growth of biofilms, fungal growths, and detritus.

By accepting and embracing these changes and little "evolutions", we're helping to create really great functional representations of the compelling wild systems we love so much!

Leaf litter beds, in particular, tend to evolve the most, as leaves are among the most "ephemeral" or transient of botanical materials we use in our aquariums. This is true in Nature, as well, as materials break down or are moved by currents, the structural dynamics of the features change.

We have to adapt a new mindset when aquascaping with leaves- that being, the 'scape will "evolve" on its own and change constantly...Other than our most basic hardscape aspects- rocks and driftwood- the leaves and such will not remain exactly where we place them.

To the "artistic perfectionist"-type of aquarist, this will be maddening.
To the aquarist who makes the mental shift and accepts this "wabi-sabi" idea (yeah, I'm sort of channeling Amano here...) the experience will be fascinating and enjoyable, with an ever-changing aquascape that will be far, far more "natural" than anything we could ever hope to conceive completely by ourselves.

It's not something to freak out about.
Rather, it's something to celebrate! Life, in all of it's diversity and beauty, still needs a stage upon which to perform...and you're helping provide it, even with this "remodeling" of your aquascape taking place daily. Stuff gets moved. Stuff gets covered in biofilm.
Stuff breaks down. In our aquairums, and in Nature.
Some people cannot fully grasp that.
Recently, I had a rather one-sided "discussion" (actually, it was mostly him attacking) with a "fanboy" of a certain style of aquarium keeping, who seemed to take a tremendous amount of pleasure in telling me that "our interpretation of Nature" and our embrace of decomposing leaves, biofilms, detritus, and such is a (and I quote) "...setback for the hobby of aquascaping..." (which, those of you who know me and my desire to provoke reactions, understand that I absolutely loved hearing!) and that "it's not possible to capture Nature" with our approach... (an ignorant, almost beyond stupid POV. I mean, WTF does "capture Nature" mean? Word salad.)
I was like, "C'mon, dude. Really? This is NOT a style of aquascaping!"
We repeat this theme a million times a year here: Nature is really not always clean and tidy. In fact- most of the time, it isn't. And if you buy into the head-scratching hobby narrative that every pristine "high-concept" contest aquarium is somehow what Nature "looks like", you're simply fooling yourself.
Sure, there are some really clear, sparkling habitats out there in the world, but they represent the exception, really.

Additionally, I'll go out on a limb and suggest that none of them have tidy rows of symmetrically trimmed, color- balanced plants, or neatly arranged rocks of related size and proportion. 😆
This is directed at a small, but vocal, and apparently misinformed crowd, but I can't stress this enough:
If you really want to understand the natural aquatic habitats of our fishes, some of you have to get out of the idealized aquascaping mindset for a bit and stop dissing everything that doesn't fit your idea of the way the world should be, and just accept the realities which Nature presents...
I am actually surprised we still get the occasional DM like this.
So I occasionally push back a bit.
Unfiltered Nature.

Okay, I'm not bragging that our avant-garde love of dirty, often chaotic-looking aquariums makes us cooler than the "sterile glass pipe-loving aquascaping crowd. It's not really even a comparison, but its typically that crowd which hurls the insults at our approach, so...😆
However, I do want everyone to understand the degree to which we love the concept of Nature in it's most compelling form, and how strongly we feel that we, as a global community of hobbyists need to look beyond what's regularly presented to us as a "natural aquarium" and really give this stuff some thought. We CAN and SHOULD interpret natural aquatic features more literally in our aquairums.
Now, not all of Nature requires us to make extreme aesthetic preference shifts in order to love it.
Well, maybe not all. A lot of it, though.

It's a very different type of "aesthetic beauty" than we are used to. It's an elegant, remarkably complex microhabitat which is host to an enormous variety of life forms. And it's a radical departure from our normal interpretation of how a tank should look. It challenges us, not only aesthetically- it challenges us to appreciate the function it can provide if we let it.
"Functional aesthetics." Again.

Our "movement" believes in representing Nature as it exists in both form and function, without "editing" the very attributes of randomness and resulting function that make it so amazing.
And it all starts with understanding and facilitating natural processes without "editing" them to meet some ingrained aesthetic preferences.
Can you do that? Can you make that mental shift?
I hope so. We'd love to have you here!
Stay bold. Stay curious. Stay patient. Stay observant. Stay creative. Stay enthralled...
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics
Epiphytes, macrophytes, allochthonous input, and other "natural" fish foods...
As a hardcore enthusiast of the blackwater/botanical-style aquarium, you're more than well-attuned to the nuances involved in managing a system filled with decomposing leaves, seed pods, wood, etc. And you're keenly aware of many of the physiological/ecological benefits that have been attributed to the use of these materials in the aquarium. However, I am willing to bet that most of us have not really considered the "nutritional" aspects of both botanicals and the life forms they foster as an important part of the "functional/aesthetic" dynamic we've touched on before.

Let's consider some of the types of food sources that our fishes might utilize in the wild habitats that we try so hard to replicate in our aquariums, and perhaps develop a greater appreciation for them when they appear in our tanks. Perhaps we will even attempt to foster and utilize them to our fishes' benefits in unique ways?

One of the important food resources in natural aquatic systems are what are known as macrophytes- aquatic plants which grow in and around the water, emerged, submerged, floating, etc. Not only do macrophytes contribute to the physical structure and spatial organization of the water bodies they inhabit, they are primary contributors to the overall biological stability of the habitat, conditioning the physical parameters of the water. Of course, anyone who keeps a planted aquarium could attest to that, right?
One of the interesting things about macrophytes is that, although there are a lot of fishes which feed directly upon them, the plants themselves are perhaps most valuable as a microhabitat for algae, zooplankton, and other organisms which fishes feed on. Small aquatic crustaceans seek out the shelter of plants for both the food resources they provide (i.e.; zooplankton, diatoms) and for protection from predators (yeah, the fishes!).
So, plants in the aquarium have been valued by aquarists "since the beginning" for all sorts of benefits- that's not really groundbreaking. I personally think that one of the more interesting functions of plants in the aquarium is to serve as this sort of "feeding ground" for fishes in all stages of their existence. Oh, yeah, they look cool, too!
Perhaps most interesting to us blackwater/botanical-style aquarium people are epiphytes. These are organisms which grow on the surface of plants or other substrates and derive their nutrients from the surrounding environment. They are important in the nutrient cycling and uptake in both nature and the aquarium, adding to the biodiversity, and serving as an important food source for many species of fishes.
In the case of our aquatic habitats, like streams, ponds, and inundated forests, epiphytes are abundant, and many fishes will spend large amounts of time foraging the biocover on tree trunks, branches, leaves, and other botanical materials. Although most animals use leaves and tree branches for shelter and not directly as a food item, grazing on this epiphytic growth is very important. Some organisms, such as nematodes and chironomids ("Bloodworms!") will dig into the leaf structures and feed on the tissues themselves, as well as the fungi and bacteria found in and among them. These organisms, in turn, become part of the diet for many fishes.

And the resulting detritus produced by the "processed" and decomposing pant matter is considered by many aquatic ecologists to be an extremely significant food source for many fishes, especially in areas such as Amazonia and Southeast Asia, where the detritus is considered an essential factor in the food webs of these habitats. And of course, if you observe the behavior of many of your fishes in the aquarium, such as characins, cyprinids, Loricarids, and others, you'll see that in between feedings, they'll spend an awful lot of time picking at "stuff" on the bottom of the tank. In a botanical style aquarium, this is a pretty common occurrence, and I believe an important benefit of this type of system.
I am of the opinion that a botanical-style aquarium, complete with its decomposing leaves and seed pods, can serve as a sort of "buffet" for many fishes- even those who's primary food sources are known to be things like insects and worms and such. Detritus and the organisms within it can provide an excellent supplemental food source for our fishes! It's well known that in many habitats, like inundated forests, etc., fishes will adjust their feeding strategies to utilize the available food sources at different times of the year, such as the "dry season", etc. And it's also known that many fish fry feed actively on bacteria and fungi in these habitats...so I suggest one again that a blackwater/botanical-style aquarium could be an excellent sort of "nursery" for many fish species!

You'll often hear the term "periphyton" mentioned in a similar context, and I think that, for our purposes, we can essentially consider it in the same manner as we do "epiphytic matter." Periphyton is essentially a "catch all" term for a mixture of cyanobacteria, algae, various microbes, and of course- detritus, which is found attached or in extremely close proximity to various submerged surfaces. Again, fishes will graze on this stuff constantly.

And then, of course, there's the "allochthonous input" that we've talked about so much here: Foods from the surrounding environment, such as flowers, fruits, terrestrial insects, etc. These are extremely important foods for many fish species that live in these habitats. We mimic this process when we feed our fishes prepared foods, as stuff literally "rains from the sky!" Now, I think that what we feed to our fishes directly in this fashion is equally as important as how it's fed.
I'd like to see much more experimentation with foods like ants, fruit flies, and other winged insects. Of course, I can hear the protests already: "Not in MY house, Fellman!" I get it. I mean, who wants a plague of winged insects getting loose in their suburban home because of some aquarium feeding experiment gone awry, right?

That being said, I would encourage some experimentation with ants and the already fairly common wingless fruit flies. Can you imagine one day recommending an "Ant Farm" as a piece of essential aquarium food culturing equipment? Why not right?
As many of you may recall, I've often been amused by the concerns many hobbyists express when a new piece of driftwood is submerged in the aquarium, often resulting in an accumulation of fungi, algal growth and biofilm. I realize this stuff looks pretty shitty to most of us, particularly when we are trying to set up a super-cool aquascaped tank. That being said, I think we need to let ourselves embrace this. I think that those of us who maintain blackwater. botanical-style aquariums have made the "mental shift" to understand, accept, and even appreciate the appearance of this stuff.
When you start seeing your fishes "graze" casually on the materials that pop up on your driftwood and botanicals, you start realizing that, although it might not look like the aesthetics we had in mind, it is a beautiful thing to our fishes. And this made me think that an "evolved" preparation technique for driftwood might be to "age" it in a large aquarium that also serves as an acclimation system for certain fishes. For example, fishes like Headstanders (Chilodus punctatus) and various loaches, catfishes, and others, would be excellent additions to this "driftwood prep tank." You could get the benefit of having the gunky stuff accumulate on the wood outside of your main display (if it bothers you, of course), while helping acclimate some cool fishes to captivity!
Just throwing the idea out there.

And of course, we've talked before about the "botanical nursery" concept- creating an aquarium for fish fry that has a large quantity of decomposing botanicals and leaves to foster the production of these materials, which serve as supplemental food for your fish fry. I have done this before myself and can attest to its viability. You fishes will have a constant supply of "natural" foods to supplement what you are feeding them in the early phases of their life. Learn to make peace with your detritus!

This little discussion has probably not created any earth-shattering "new" developments, but I believe that it has at least looked at a few of the terms you see bandied about now and again in hobby literature, perhaps clarifying their significance to us. And I think it's really about us understanding what happens in nature and how we can work with it instead of against it, taking advantage of the food sources that she provides to our fishes when we don't rush off for the algae scraper and siphon hose before considering the upside!
Another "mental shift", I suppose...one which many of you have already made, no doubt. I certainly look forward to seeing many examples of us utilizing "what we've got" to the advantage of our fishes!
Stay bold. Stay open-mined. Stay interested. Stay creative. Stay engaged.
And Stay Wet.
Scott Fellman
Tannin Aquatics








